Abstract
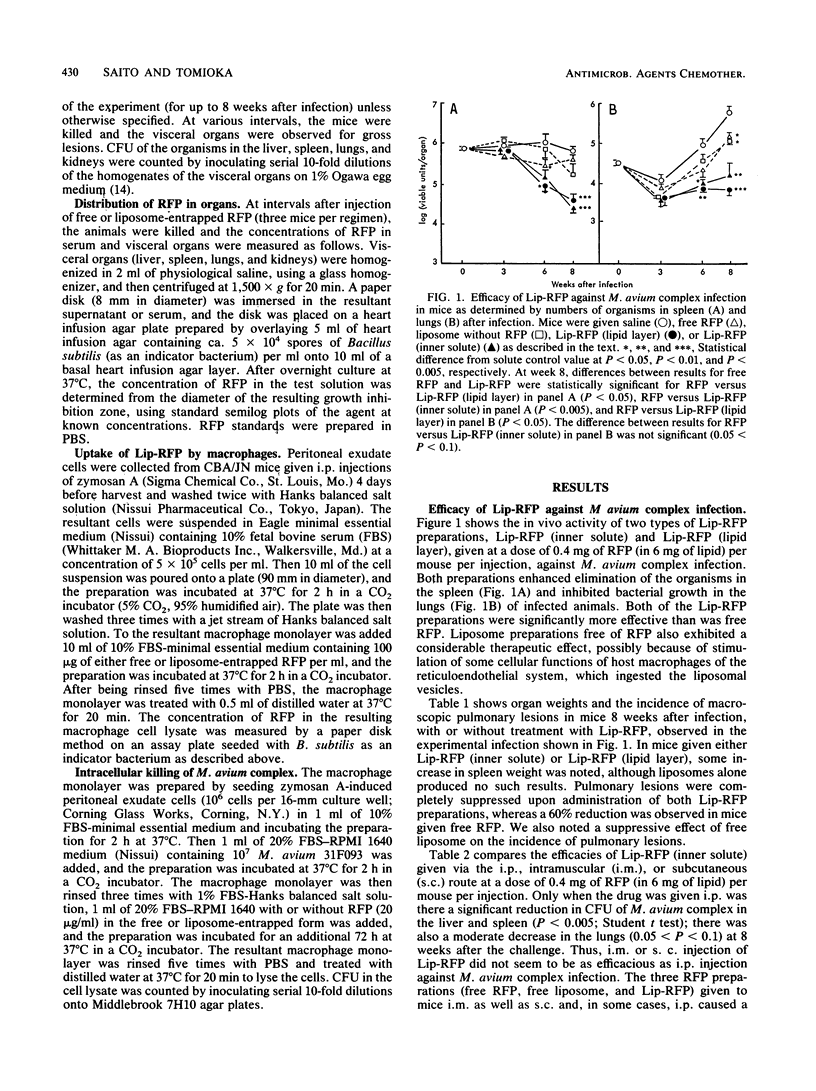
Liposome-entrapped rifampin (RFP) was examined for therapeutic efficacy against experimental infection induced in mice by the Mycobacterium avium complex. Intraperitoneal injections (once daily, six times weekly) of liposome-entrapped RFP led to a greater reduction in bacterial growth in the lungs and spleen of infected mice than did free RFP alone. Liposome-entrapped RFP given to mice via the intramuscular or subcutaneous route failed to show such an increased therapeutic efficacy. RFP entrapped in the lipid layer of liposomal vesicles exhibited a level of therapeutic activity similar to that seen with RFP encapsulated in the inner solute of the vesicles. Entrapment of RFP in liposomal vesicles increased incorporation of the drug into host peritoneal macrophages and increased the activity of the agent against M. avium complex phagocytosed into the macrophages.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alving C. R., Steck E. A., Hanson W. L., Loizeaux P. S., Chapman W. L., Jr, Waits V. B. Improved therapy of experimental leishmaniasis by use of a liposome-encapsulated antimonial drug. Life Sci. 1978 Mar;22(12):1021–1026. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90270-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., Lokerse A. F., Roerdink F. H., Regts D., Michel M. F. Free versus liposome-entrapped ampicillin in treatment of infection due to Listeria monocytogenes in normal and athymic (nude) mice. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):917–924. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., Lokerse A. F., Vink-van den Berg J. C., Roerdink F. H., Michel M. F. Effect of liposome-entrapped ampicillin on survival of Listeria monocytogenes in murine peritoneal macrophages. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):295–300. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates J. H. A study of pulmonary disease associated with mycobacteria other than Mycobacterium tuberculosis: clinical characteristics. XX. A report of the Veterans Administration-armed forces cooperative study on the chemotherapy of tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 Dec;96(6):1151–1157. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.96.6.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Gregoriandis G. Killing of intraphagocytic Staphylococcus aureus by dihydrostreptomycin entrapped within liposomes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jun;13(6):1049–1051. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.6.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cynamon M. H. Comparative in vitro activities of MDL 473, rifampin, and ansamycin against Mycobacterium intracellulare. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):440–441. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desiderio J. V., Campbell S. G. Intraphagocytic killing of Salmonella typhimurium by liposome-encapsulated cephalothin. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):563–570. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desiderio J. V., Campbell S. G. Liposome-encapsulated cephalothin in the treatment of experimental murine salmonellosis. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1983 Oct;34(4):279–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra J., van Galen M., Regts D., Scherphof G. Uptake and processing of liposomal phospholipids by Kupffer cells in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 15;148(2):391–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08851.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra J., van Galen W. J., Hulstaert C. E., Kalicharan D., Roerdink F. H., Scherphof G. L. Interaction of liposomes with Kupffer cells in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Jan;150(1):161–176. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90711-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Bodey G. P., Frankel L. S., Mehta K. Treatment of hepatosplenic candidiasis with liposomal-amphotericin B. J Clin Oncol. 1987 Feb;5(2):310–317. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1987.5.2.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G. Liposomes as carriers of antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 May;31(5):675–678. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.5.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Mehta R., Hopfer R. L., Mills K., Kasi L., Mehta K., Fainstein V., Luna M., Hersh E. M., Juliano R. Treatment and prophylaxis of disseminated infection due to Candida albicans in mice with liposome-encapsulated amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):939–945. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirson P., Steiger R. F., Trouet A., Gillet J., Herman F. Primaquine liposomes in the chemotherapy of experimental murine malaria. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1980 Aug;74(4):383–391. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1980.11687359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi N., David H. L. Mechanisms of pathogenicity in mycobacteria. Biochimie. 1988 Aug;70(8):1101–1120. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi N., Frehel C., Ryter A., Ohayon H., Lesourd M., David H. L. Multiple drug resistance in Mycobacterium avium: is the wall architecture responsible for exclusion of antimicrobial agents? Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Nov;20(5):666–677. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.5.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Sato K., Tomioka H. Comparative in vitro and in vivo activity of rifabutin and rifampicin against Mycobacterium avium complex. Tubercle. 1988 Sep;69(3):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(88)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadakuma T., Ikewaki N., Yasuda T., Tsutsumi M., Saito S., Saito K. Treatment of experimental salmonellosis in mice with streptomycin entrapped in liposomes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jul;28(1):28–32. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolinsky E. Nontuberculous mycobacteria and associated diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Jan;119(1):107–159. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodley C. L., David H. L. Effect of temperature on the rate of the transparent to opaque colony type transition in Mycobacterium avium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):113–119. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Inderlied C. B., Berlin O. G., Gottlieb M. S. Mycobacterial infections in AIDS patients, with an emphasis on the Mycobacterium avium complex. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;8(6):1024–1033. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.6.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


