Abstract
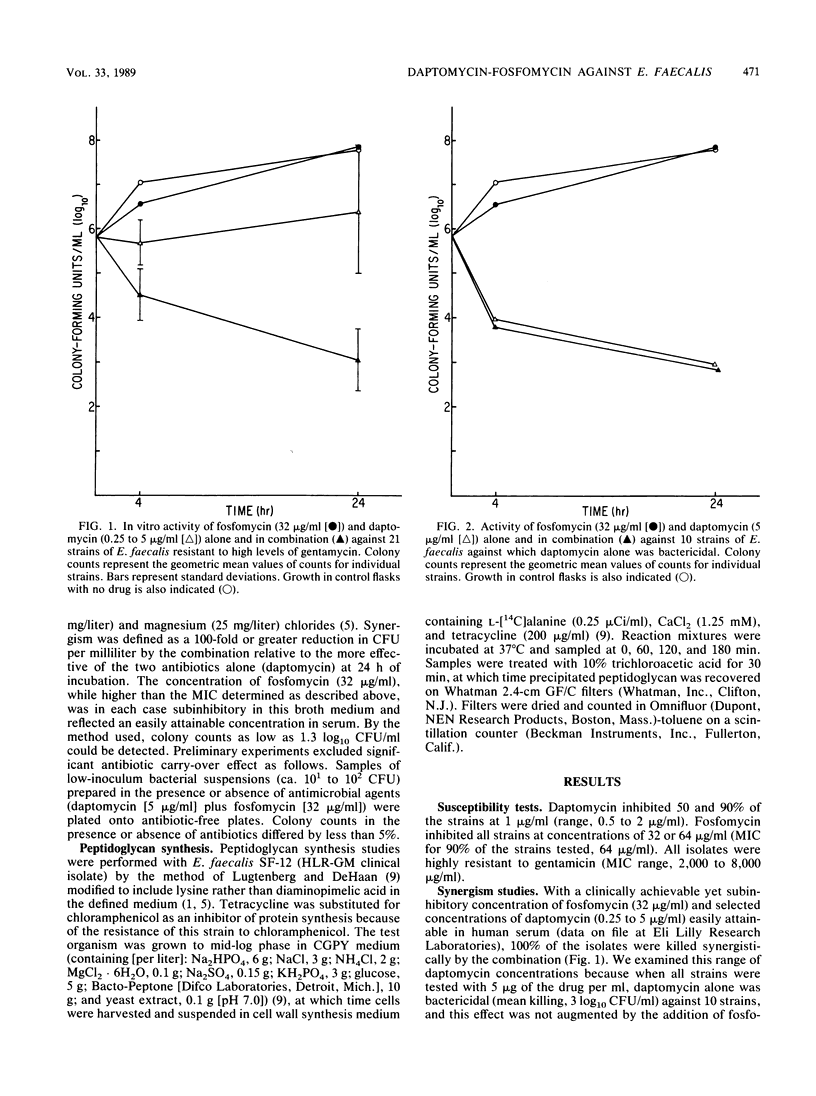
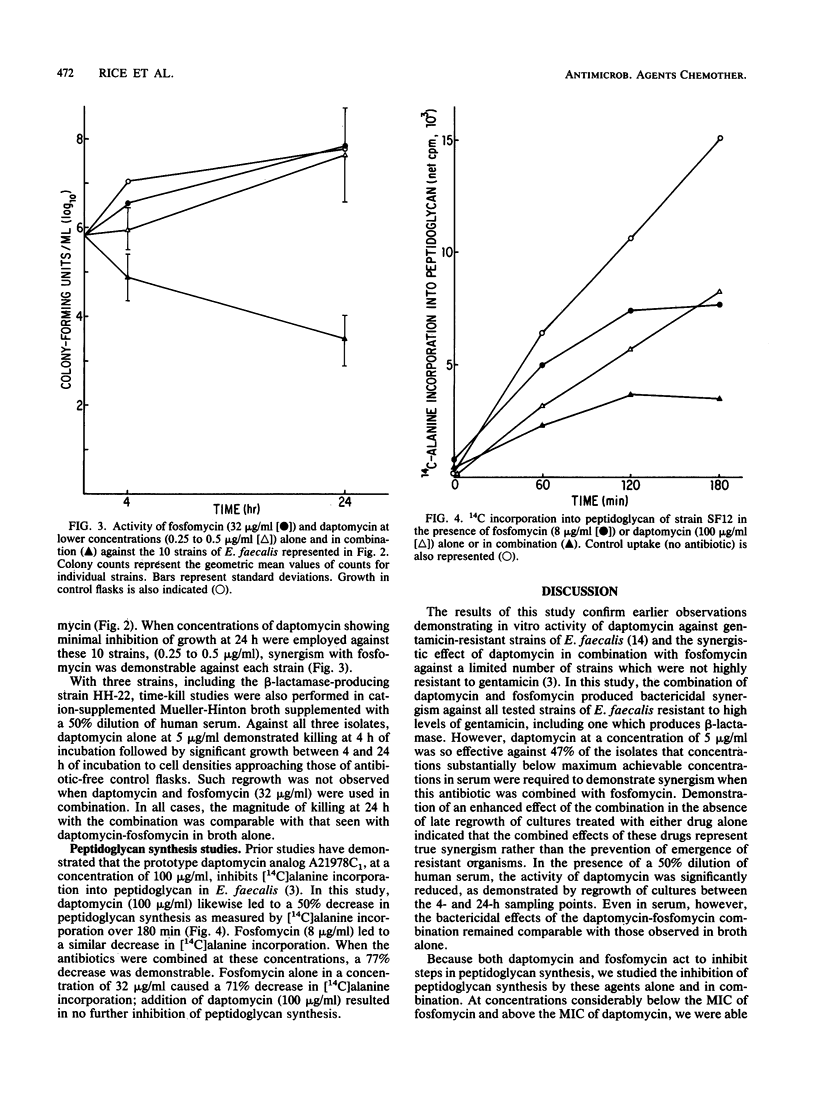
Daptomycin and fosfomycin are two agents which inhibit different steps in peptidoglycan synthesis. We studied the in vitro activities of these drugs, alone and in combination, by time-kill techniques against 21 clinical isolates of Enterococcus (Streptococcus) faecalis demonstrating high-level resistance to gentamicin. Combinations of fosfomycin and daptomycin exhibited synergistic bactericidal activity (100-fold decrease in CFU per milliliter at 24 h compared with daptomycin alone) against all strains (mean +/- standard deviation of increment in killing = 2.7 +/- 0.7 log10 CFU/ml). In a subgroup of strains against which daptomycin (5 micrograms/ml) alone was bactericidal (greater than 3 log10 killing), synergistic activity was demonstrable only when the concentration of daptomycin was lowered to 0.25 to 0.5 microgram/ml. A 50% dilution of human serum diminished the bactericidal activity of daptomycin alone at 24 h but did not affect killing observed with the daptomycin-fosfomycin combination. The inhibition of peptidoglycan synthesis by the combination was greater than the inhibition observed with either drug alone. The combination of daptomycin and fosfomycin exhibited consistent synergistic bactericidal activity against strains of E. faecalis possessing high-level resistance to gentamicin. This synergism may be the result of sequential inhibition of early steps in peptidoglycan synthesis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen N. E., Hobbs J. N., Alborn W. E., Jr Inhibition of peptidoglycan biosynthesis in gram-positive bacteria by LY146032. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1093–1099. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush L. M., Boscia J. A., Kaye D. Daptomycin (LY146032) treatment of experimental enterococcal endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jun;32(6):877–881. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.6.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debbia E., Pesce A., Schito G. C. In vitro activity of LY146032 alone and in combination with other antibiotics against gram-positive bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Feb;32(2):279–281. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Moellering R. C., Jr Susceptibility of enterococci and Listeria monocytogenes to N-Formimidoyl thienamycin alone and in combination with an aminoglycoside. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):789–793. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Thauvin C., Gerson B., Moellering R. C., Jr In vitro activity and mechanism of action of A21978C1, a novel cyclic lipopeptide antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):357–362. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii R. Fosfomycin in the treatment of bacterial infections: summary of clinical trials in Japan. Chemotherapy. 1977;23 (Suppl 1):234–246. doi: 10.1159/000222054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan F. M., Kahan J. S., Cassidy P. J., Kropp H. The mechanism of action of fosfomycin (phosphonomycin). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):364–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg E. J., de Haan P. G. A simple method for following the fate of alanine-containing components in murein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1971;37(4):537–552. doi: 10.1007/BF02218524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L., Kaye D., Levison M. E., Hook E. W. Enterococcal endocarditis. An analysis of 38 patients observed at the New York Hospital-Cornell Medical Center. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Feb;125(2):258–264. doi: 10.1001/archinte.125.2.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mederski-Samoraj B. D., Murray B. E. High-level resistance to gentamicin in clinical isolates of enterococci. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):751–757. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Tsao J., Panida J. Enterococci from Bangkok, Thailand, with high-level resistance to currently available aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):799–802. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez A., Vicente M. V., Olay T. Experimental endocarditis and fosfomycin. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1985;11(1):55–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanger A. R., Murray B. E. Activity of LY146032 against Enterococci with and without high-level aminoglycoside resistance, including two penicillinase-producing strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1779–1781. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessler S. Enterococcal endocarditis. JAMA. 1968 Jun 3;204(10):916–921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zervos M. J., Kauffman C. A., Therasse P. M., Bergman A. G., Mikesell T. S., Schaberg D. R. Nosocomial infection by gentamicin-resistant Streptococcus faecalis. An epidemiologic study. Ann Intern Med. 1987 May;106(5):687–691. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-5-687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


