Abstract
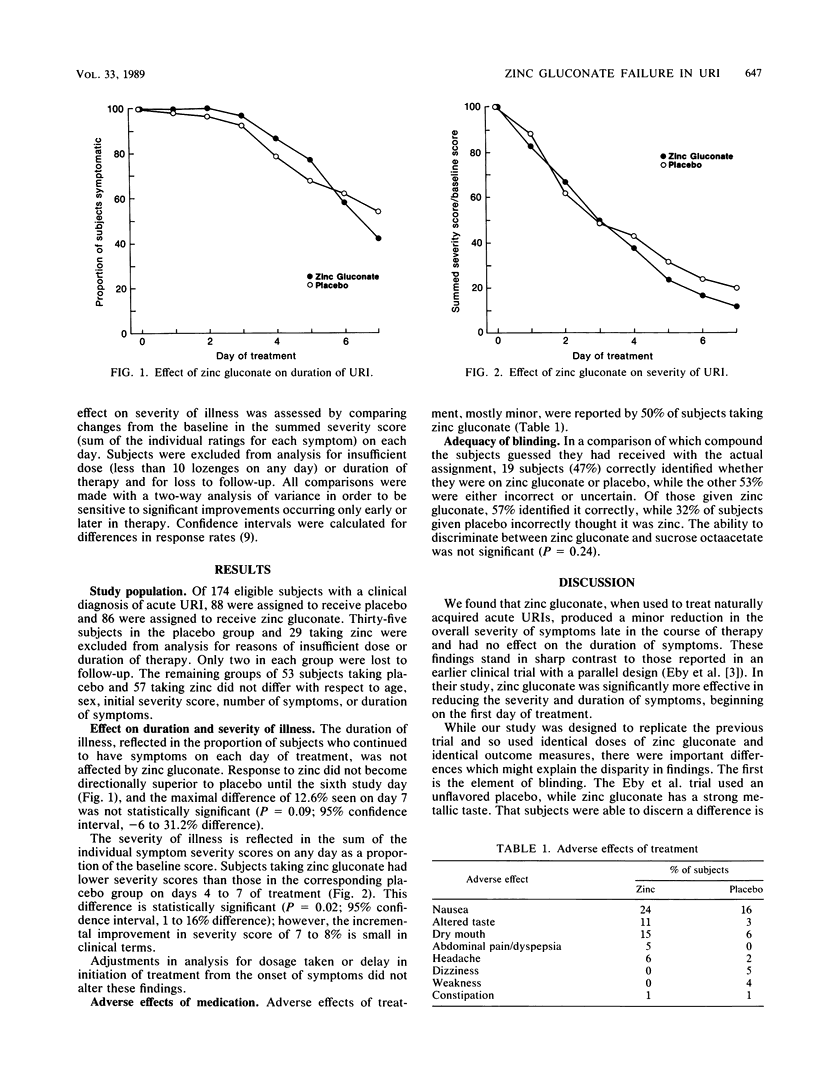
Zinc is a trace metal with in vitro activity against rhinovirus, the major etiologic agent in acute upper respiratory tract infections (URIs). A previous trial of zinc gluconate supported its efficacy in treating URIs, but the effectiveness of blinding was uncertain. We conducted a prospective randomized trial of zinc gluconate versus a taste-matched placebo of sucrose octaacetate. Lozenges containing either 23 mg of elemental zinc or placebo were taken every 2 h. Eleven URI symptoms were rated daily on a scale of 0 (not present) to 3 (severe). Duration of illness, reflected in the proportion of subjects remaining symptomatic on each day, was not significantly reduced (maximum difference of 12.6% on day 7, P = 0.09; 95% confidence interval, -6 to 31%) by either treatment. Severity of illness, assessed by using a summed severity score, was reduced incrementally by 7 to 8% on days 5 to 7 (P = 0.02) in subjects taking zinc. Adverse effects, mostly nausea and altered taste, were reported by 50% of subjects taking zinc. We conclude that while zinc gluconate may produce a small reduction in overall severity of symptoms, this is not clinically significant. Given the additional high incidence of adverse effects, zinc gluconate cannot be recommended for use in the treatment of acute URIs.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chalmers T. C. Effects of ascorbic acid on the common cold. An evaluation of the evidence. Am J Med. 1975 Apr;58(4):532–536. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas R. M., Miles H. B., Moore B. W., Ryan P., Pinnock C. B. Failure of effervescent zinc acetate lozenges to alter the course of upper respiratory tract infections in Australian adults. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Aug;31(8):1263–1265. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.8.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eby G. A., Davis D. R., Halcomb W. W. Reduction in duration of common colds by zinc gluconate lozenges in a double-blind study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jan;25(1):20–24. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr B. M., Conner E. M., Betts R. F., Oleske J., Minnefor A., Gwaltney J. M., Jr Two randomized controlled trials of zinc gluconate lozenge therapy of experimentally induced rhinovirus colds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Aug;31(8):1183–1187. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.8.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwaltney J. M., Jr, Hendley J. O., Simon G., Jordan W. S., Jr Rhinovirus infections in an industrial population. I. The occurrence of illness. N Engl J Med. 1966 Dec 8;275(23):1261–1268. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196612082752301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden F. G., Albrecht J. K., Kaiser D. L., Gwaltney J. M., Jr Prevention of natural colds by contact prophylaxis with intranasal alpha 2-interferon. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jan 9;314(2):71–75. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198601093140202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D., Butterworth B. E. Inhibition by zinc of rhinovirus protein cleavage: interaction of zinc with capsid polypeptides. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):298–306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.298-306.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. Confidence intervals for reporting results of clinical trials. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Sep;105(3):429–435. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-3-429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


