Abstract
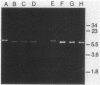
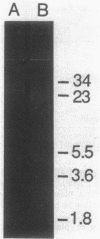
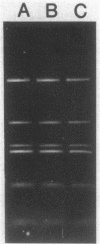
One hundred fifty-three isolates of Pasteurella multocida, representing the causative agent of 95% of all known outbreaks of fowl cholera occurring in California meat and breeder turkeys from August 1985 through February 1987, were examined for susceptibility to antimicrobial agents. Of the 153 isolates, 6 were shown to be resistant to one or more antimicrobial agents. Of the six resistant isolates, five contained R plasmids. All but one of the R plasmids were small (6 to 7 megadaltons) and nonconjugative, encoding resistance to tetracycline or kanamycin, streptomycin, and sulfonamides; the other was large (70 megadaltons) and conjugative, transferring resistance to kanamycin, streptomycin, sulfonamides, and tetracycline to P. multocida and Escherichia coli. The three plasmids encoding resistance to tetracycline alone appeared identical.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman S. M., Hirsh D. C. Partial characterization of R-plasmids from Pasteurella multocida isolated from turkeys. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):348–352. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond R. E., Donahue J. M., Olson L. D. Colony features of Pasteurella multocida and their use in diagnosing fowl cholera in turkeys. Avian Dis. 1970 Feb;14(1):24–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brogden K. A., Rhoades K. R., Heddleston K. L. A new serotype of Pasteurella multocida associated with fowl cholera. Avian Dis. 1978 Jan-Mar;22(1):185–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter G. R., Rundell S. W. Identification of type A strains of P multocida using staphylococcal hyaluronidase. Vet Rec. 1975 Apr 12;96(15):343–343. doi: 10.1136/vr.96.15.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W. Host ranges of R factors. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):453–460. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue J. M., Olson L. D. The in vitro sensitivity of Pasteurella multocida of turkey origin to various chemotherapeutic agents. Avian Dis. 1972 May-Jun;16(3):506–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubel J. R., Zink D. L., Kelley L. M., Naqi S. A., Renshaw H. W. Bacterial antibiotic resistance: frequency of gentamicin-resistant strains of Escherichia coli in the fecal microflora of commercial turkeys. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Oct;43(10):1786–1789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekperigin H. E., Jang S., McCapes R. H. Effective control of a gentamicin-resistant Salmonella arizonae infection in turkey poults. Avian Dis. 1983 Jul-Sep;27(3):822–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., van Embden J., Falkow S. Molecular nature of two nonconjugative plasmids carrying drug resistance genes. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):619–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.619-630.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsh D. C., Ikeda J. S., Martin L. D., Kelly B. J., Ghazikhanian G. Y. R plasmid-mediated gentamicin resistance in salmonellae isolated from turkeys and their environment. Avian Dis. 1983 Jul-Sep;27(3):766–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsh D. C., Martin L. D., Rhoades K. R. Conjugal transfer of an R-plasmid in Pasteurella multocida. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Sep;20(3):415–417. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsh D. C., Martin L. D., Rhoades K. R. Resistance plasmids of Pasteurella multocida isolated from turkeys. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Jul;46(7):1490–1493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reece R. L., Coloe P. J. The resistance to anti-microbial agents of bacteria isolated from pathological conditions of birds in Victoria, 1978 to 1983. Aust Vet J. 1985 Nov;62(11):379–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1985.tb14214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. P., Leming B., Garon C. F., Hjerpe C. A. R-Plasmids in Pasteurella multocida. Plasmid. 1979 Jul;2(3):493–497. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snipes K. P., Carpenter T. E., Hird D. W., McCapes R. H., Hirsh D. C. A descriptive study of fowl cholera in California meat turkeys: August 1985-July 1986. Avian Dis. 1987 Oct-Dec;31(4):792–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walser M. M., Davis R. B. In vitro characterization of field isolants of Pasteurella multocida from Georgia turkeys. Avian Dis. 1975 Jul-Sep;19(3):525–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]