Abstract
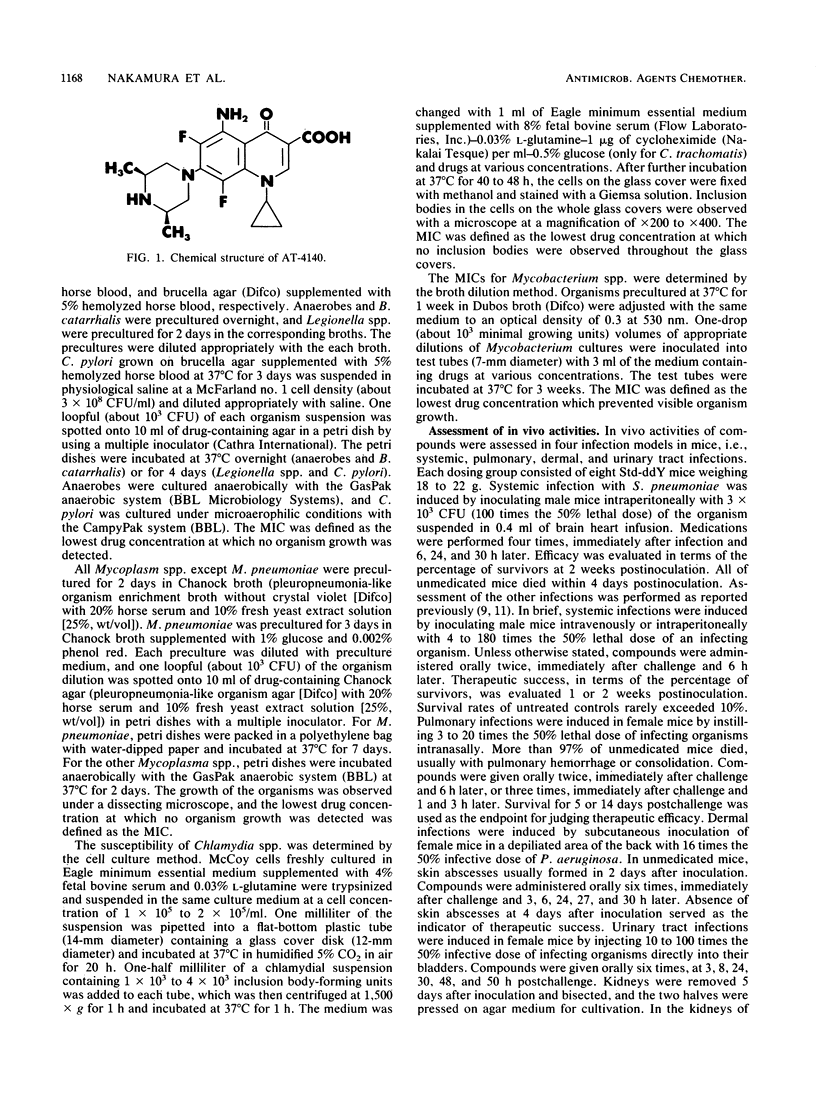
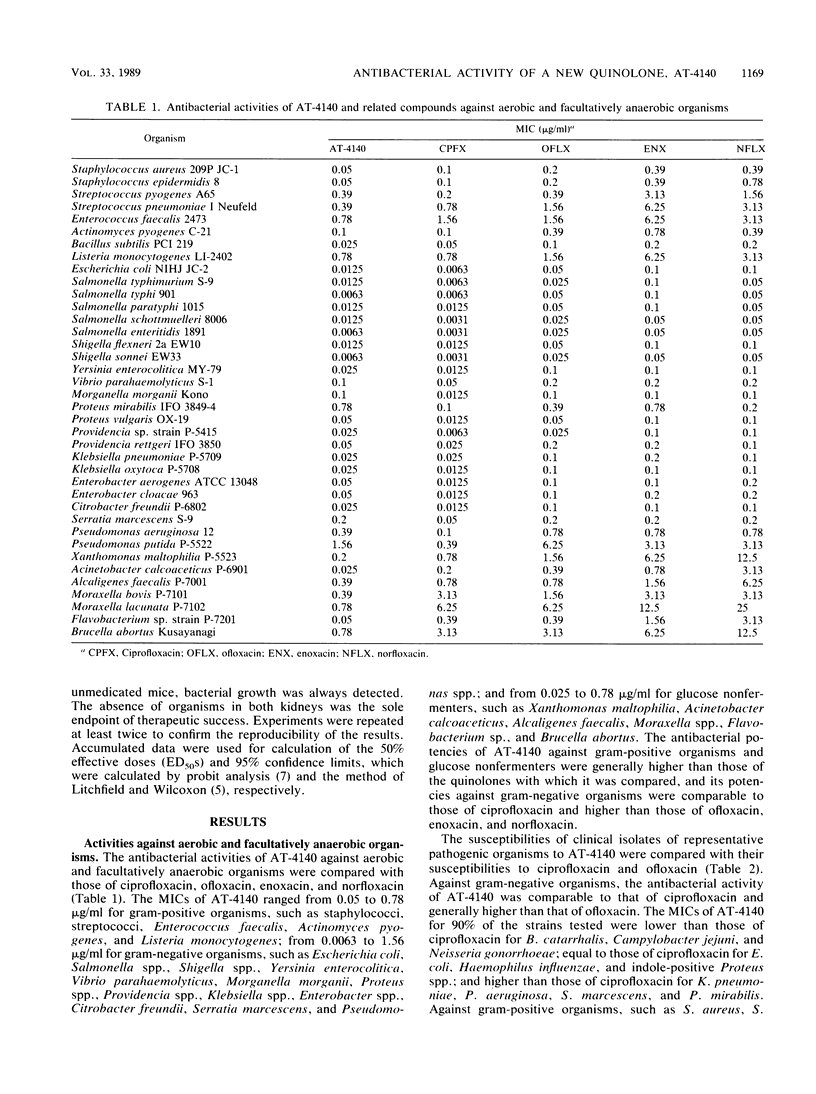
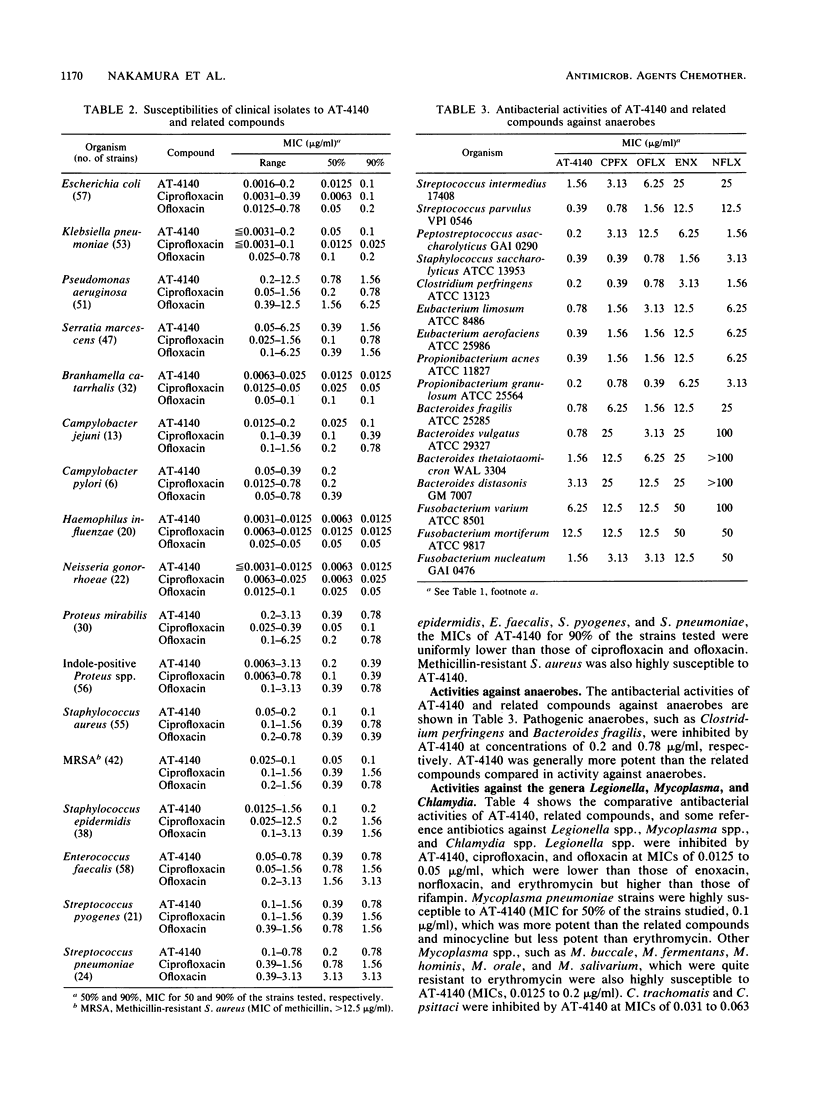
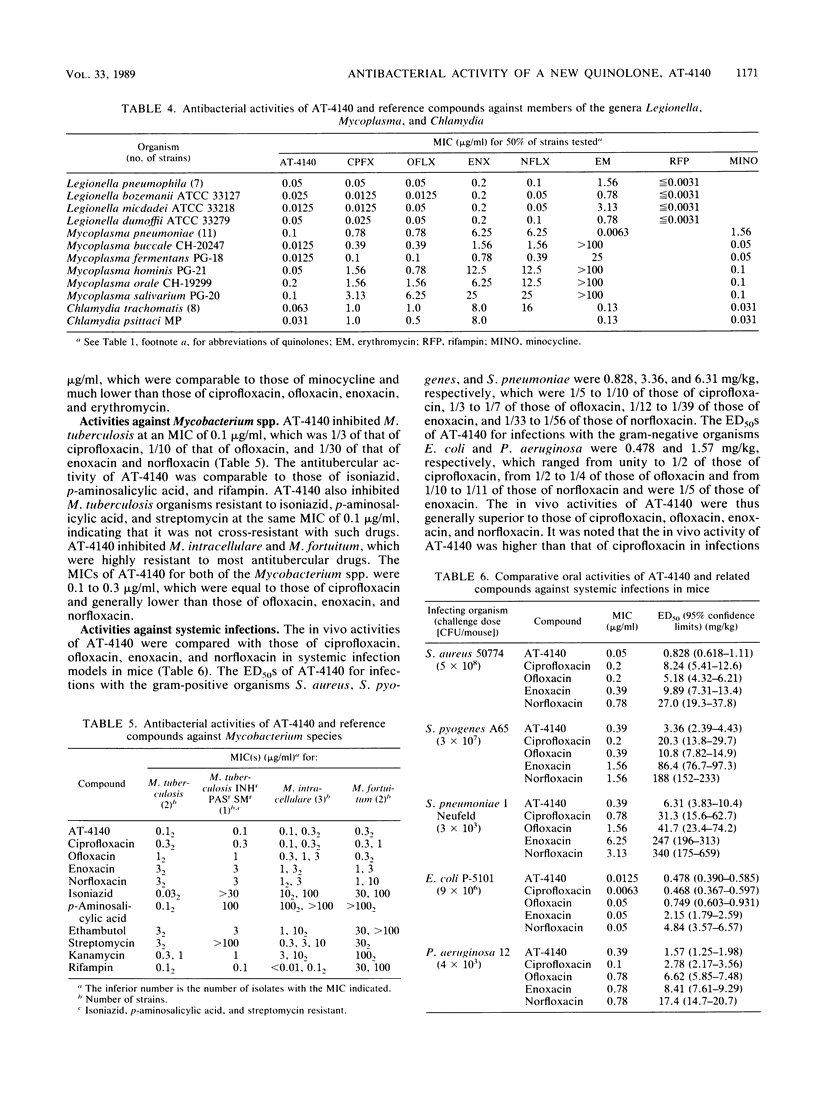
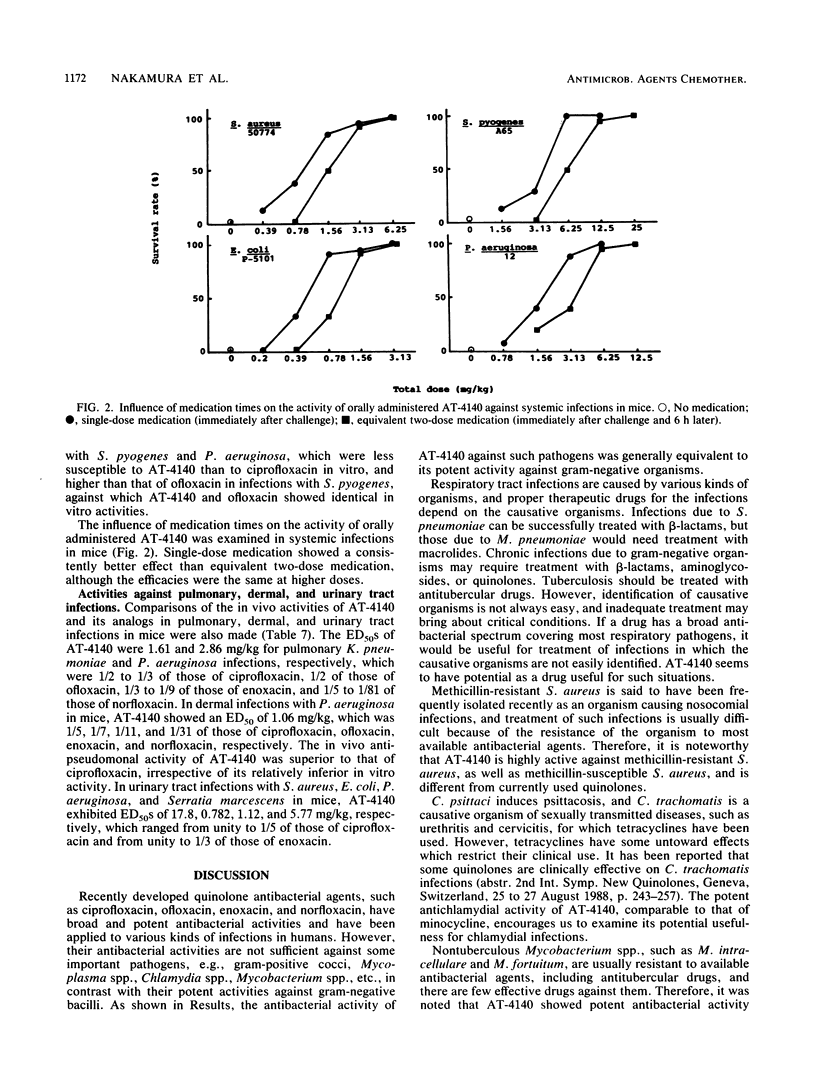
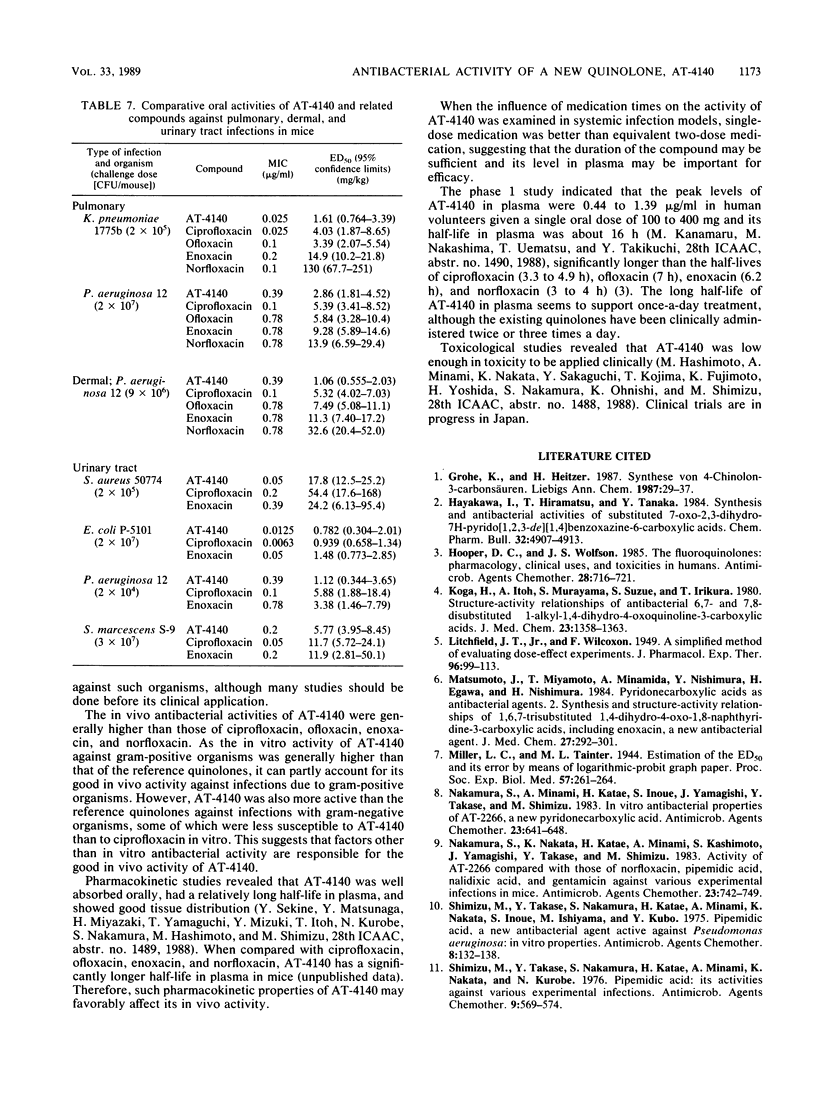
AT-4140, 5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-6,8-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-7-(cis-3,5- dimethyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid, showed broad and potent antibacterial activity. Its MICs for 90% of the strains tested were 0.1 to 0.78 micrograms/ml against gram-positive organisms, such as members of the genera Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and Enterococcus, and 0.0125 to 1.56 micrograms/ml against gram-negative organisms, such as members of the family Enterobacteriaceae and the genera Pseudomonas, Branhamella, Campylobacter, Haemophilus, and Neisseria. Its MICs were 0.025 to 0.78 micrograms/ml against glucose nonfermenters, such as members of the genera Xanthomonas, Acinetobacter, Alcaligenes, Moraxella, Flavobacterium, and Brucella; 0.2 to 0.78 micrograms/ml against anaerobes, such as Clostridium perfringens and Bacteroides fragilis; 0.0125 to 0.05 micrograms/ml against Legionella spp.; 0.0125 to 0.2 micrograms/ml against Mycoplasma spp.; 0.031 to 0.063 micrograms/ml against Chlamydia spp.; and 0.1 to 0.3 micrograms/ml against Mycobacterium spp. The potencies of AT-4140 against gram-negative organisms were comparable to those of ciprofloxacin and higher than those of ofloxacin, enoxacin, and norfloxacin. The potencies of AT-4140 against gram-positive organisms, glucose nonfermenters, anaerobes, Mycoplasma spp., Chlamydia spp., and Mycobacterium spp. were generally higher than those of the quinolones with which AT-4140 was compared. AT-4140 showed good oral efficacy against systemic infections with Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice. Its efficacy was better when a daily dose was given once than when it was given in two doses. Good efficacies of the orally administered drug were also observed in pulmonary, dermal, and urinary tract infection models in mice. The in vivo efficacies of AT-4140 were equal to or better than those of ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, enoxacin, and norfloxacin.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hayakawa I., Hiramitsu T., Tanaka Y. Synthesis and antibacterial activities of substituted 7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7H-pyrido[1,2,3-de][1,4]benzoxazine-6-carboxyl ic acids. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1984 Dec;32(12):4907–4913. doi: 10.1248/cpb.32.4907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S. The fluoroquinolones: pharmacology, clinical uses, and toxicities in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):716–721. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga H., Itoh A., Murayama S., Suzue S., Irikura T. Structure-activity relationships of antibacterial 6,7- and 7,8-disubstituted 1-alkyl-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acids. J Med Chem. 1980 Dec;23(12):1358–1363. doi: 10.1021/jm00186a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto J., Miyamoto T., Minamida A., Nishimura Y., Egawa H., Nishimura H. Pyridonecarboxylic acids as antibacterial agents. 2. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 1,6,7-trisubstituted 1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acids, including enoxacin, a new antibacterial agent. J Med Chem. 1984 Mar;27(3):292–301. doi: 10.1021/jm00369a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Minami A., Katae H., Inoue S., Yamagishi J., Takase Y., Shimizu M. In vitro antibacterial properties of AT-2266, a new pyridonecarboxylic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 May;23(5):641–648. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.5.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Nakata K., Katae H., Minami A., Kashimoto S., Yamagishi J., Takase Y., Shimizu M. Activity of AT-2266 compared with those of norfloxacin, pipemidic acid, nalidixic acid, and gentamicin against various experimental infections in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 May;23(5):742–749. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.5.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu M., Takase Y., Nakamura S., Katae H., Minami A. Pipemidic acid, a new antibacterial agent active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: in vitro properties. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Aug;8(2):132–138. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.2.132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu M., Takdase Y., Nakamura S., Katae H., Minami A. Pipemidic acid: its activities against various experimental infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):569–574. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


