Abstract
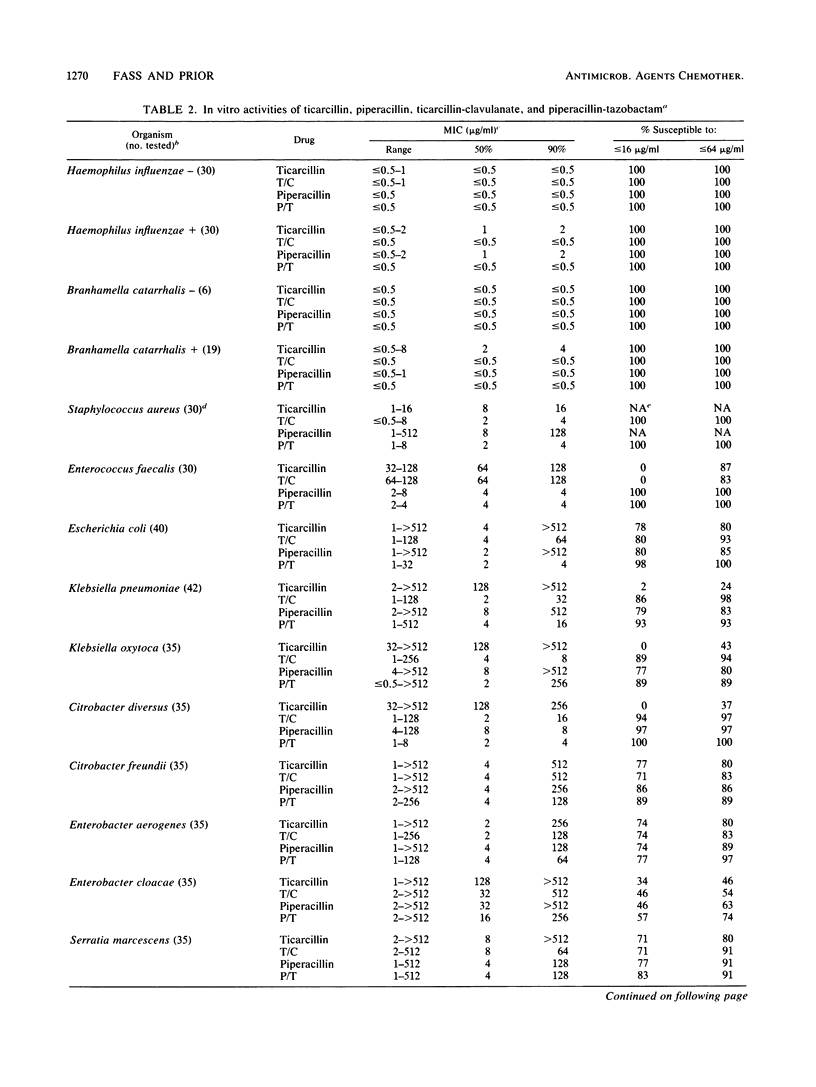
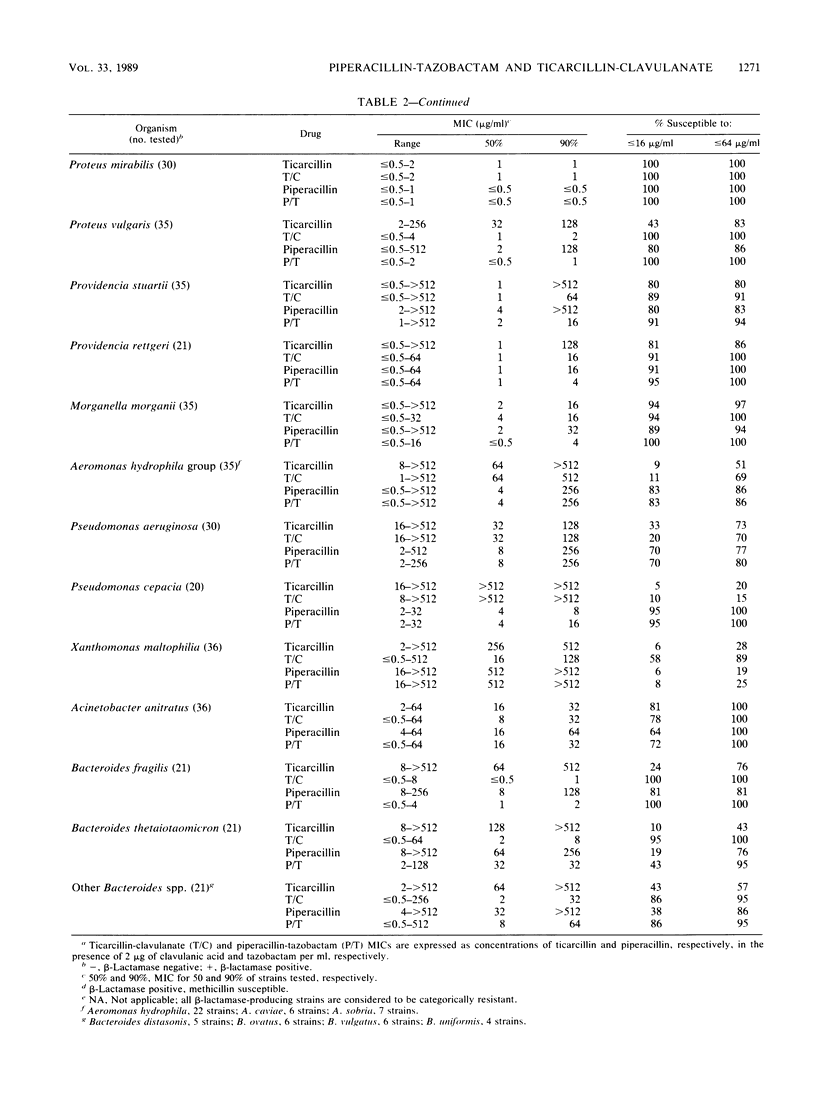
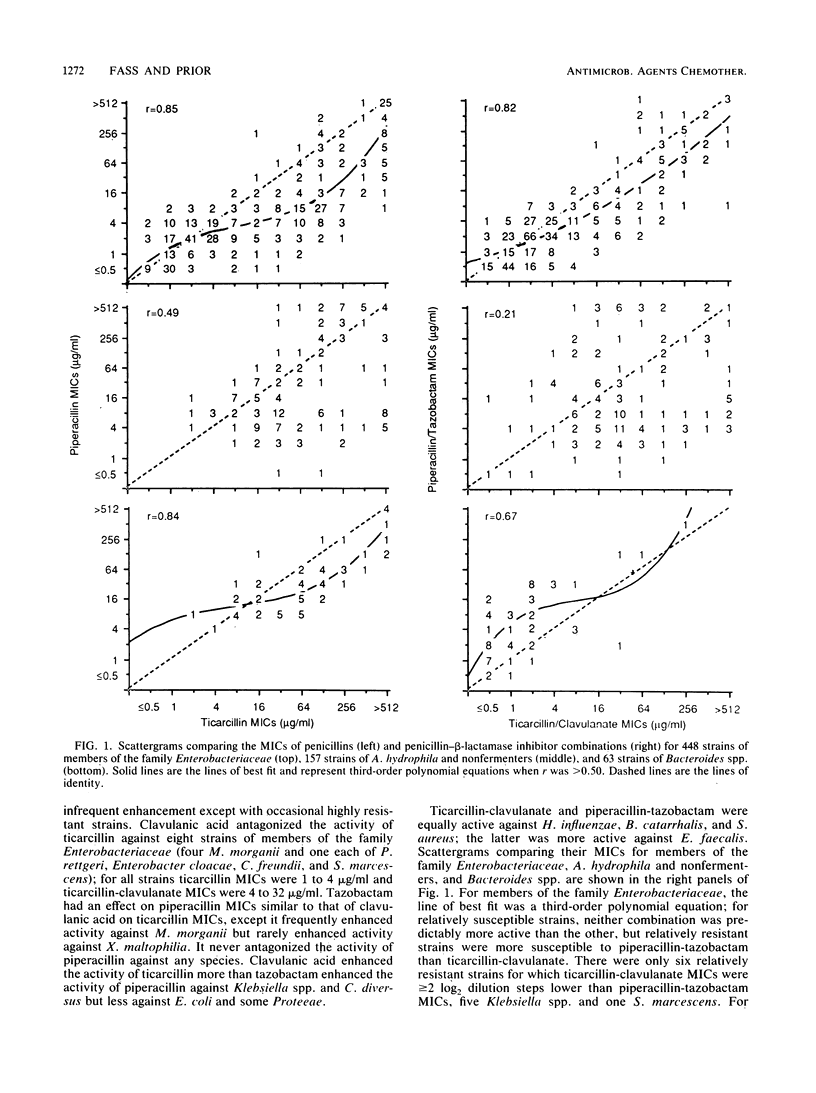
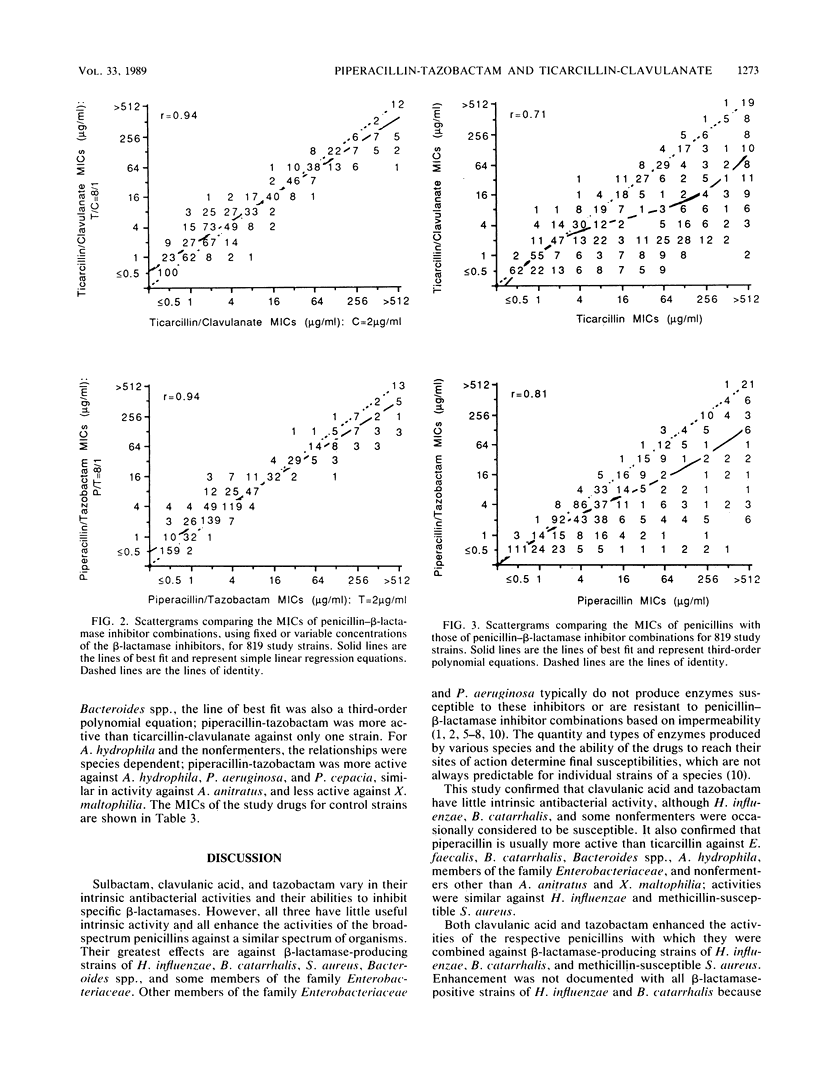
The in vitro activities of ticarcillin, piperacillin, clavulanic acid, tazobactam, ticarcillin-clavulanate, and piperacillin-tazobactam against 819 bacterial isolates were compared. The two beta-lactamase inhibitors, clavulanic acid and tazobactam, had little useful antibacterial activity but enhanced the activities of the penicillins against beta-lactamase-producing strains of Haemophilus influenzae, Branhamella catarrhalis, and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus; all strains were susceptible to both combinations. Both enzyme inhibitors also enhanced the activities of the penicillins against most strains of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp., Citrobacter diversus, Proteus spp., Providencia spp., and Bacteroides spp. and against occasional strains of Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter spp., and Serratia marcescens. Clavulanic acid frequently enhanced the activity of ticarcillin against Xanthomonas maltophilia, and tazobactam frequently enhanced the activity of piperacillin against Morganella morganii. Enhancement was observed primarily with strains relatively resistant to the penicillins. In general, clavulanic acid was more effective than tazobactam in enhancing penicillin activity against Klebsiella spp., C. diversus, X. maltophilia, and Bacteroides spp., whereas tazobactam was more effective against Escherichia coli and Proteeae. There was little or no enhancement of activity against Enterococcus faecalis, Aeromonas hydrophila, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas cepacia, or Acinetobacter anitratus. Clavulanic acid occasionally antagonized the activity of ticarcillin against ticarcillin-susceptible members of the family Enterobacteriaceae, but those strains were still considered susceptible to the combination. Tazobactam never antagonized the activity of piperacillin. In a direct comparison of the activities of ticarcillin-clavulanate and piperacillin-tazobactam, the two were equally active against H. influenzae, B. catarrhalis, and S. aureus; the latter was more active against E. faecalis. For relatively susceptible strains of members of the family Enterobacteriaceae, neither combination was predictably more active than the other, but relatively resistant strains were generally more susceptible to piperacillin-tazobactam. Piperacillin-tazobactam was more active than ticarcillin-clavulanate against A. hydrophila, P. aeruginosa, and P. cepacia, similar in activity against A. anitratus, and less active against X. maltophilia and Bacteroides spp.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelbaum P. C., Jacobs M. R., Spangler S. K., Yamabe S. Comparative activity of beta-lactamase inhibitors YTR 830, clavulanate, and sulbactam combined with beta-lactams against beta-lactamase-producing anaerobes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):789–791. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronoff S. C., Jacobs M. R., Johenning S., Yamabe S. Comparative activities of the beta-lactamase inhibitors YTR 830, sodium clavulanate, and sulbactam combined with amoxicillin or ampicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Oct;26(4):580–582. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.4.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doern G. V., Jorgensen J. H., Thornsberry C., Preston D. A., Tubert T., Redding J. S., Maher L. A. National collaborative study of the prevalence of antimicrobial resistance among clinical isolates of Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Feb;32(2):180–185. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.2.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J., Helsel V. L., Barnishan J., Ayers L. W. In vitro susceptibilities of four species of coagulase-negative staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Oct;30(4):545–552. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.4.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Kitzis M. D., Yamabe S., Acar J. F. Comparative evaluation of a new beta-lactamase inhibitor, YTR 830, combined with different beta-lactam antibiotics against bacteria harboring known beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):955–957. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. R., Aronoff S. C., Johenning S., Shlaes D. M., Yamabe S. Comparative activities of the beta-lactamase inhibitors YTR 830, clavulanate, and sulbactam combined with ampicillin and broad-spectrum penicillins against defined beta-lactamase-producing aerobic gram-negative bacilli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):980–985. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. R., Aronoff S. C., Johenning S., Yamabe S. Comparative activities of the beta-lactamase inhibitors YTR 830, clavulanate and sulbactam combined with extended-spectrum penicillins against ticarcillin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae and pseudomonads. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Aug;18(2):177–184. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Iaconis J. P., Bodey G. P., Samonis G. Resistance to ticarcillin-potassium clavulanate among clinical isolates of the family Enterobacteriaceae: role of PSE-1 beta-lactamase and high levels of TEM-1 and SHV-1 and problems with false susceptibility in disk diffusion tests. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Sep;32(9):1365–1369. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.9.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobberingh E. E., Davies B. I., van Boven C. P. Branhamella catarrhalis: antibiotic sensitivities and beta-lactamases. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Jan;13(1):55–64. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


