Abstract
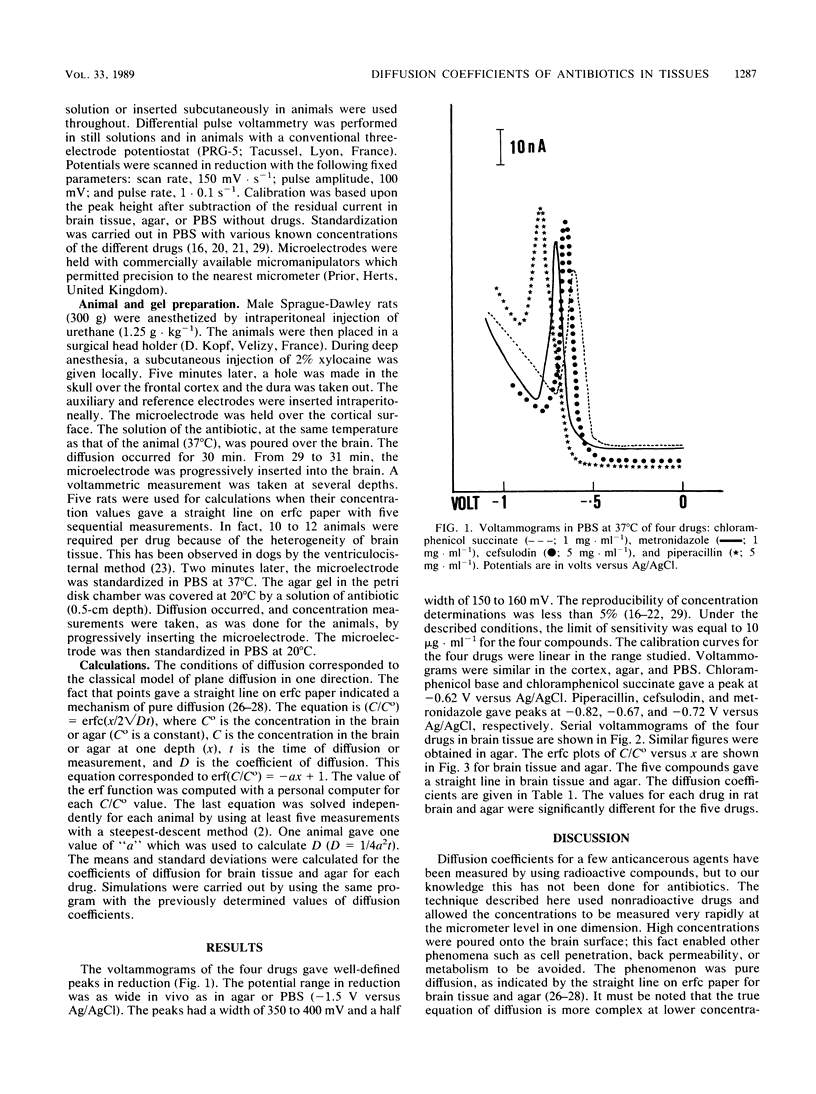
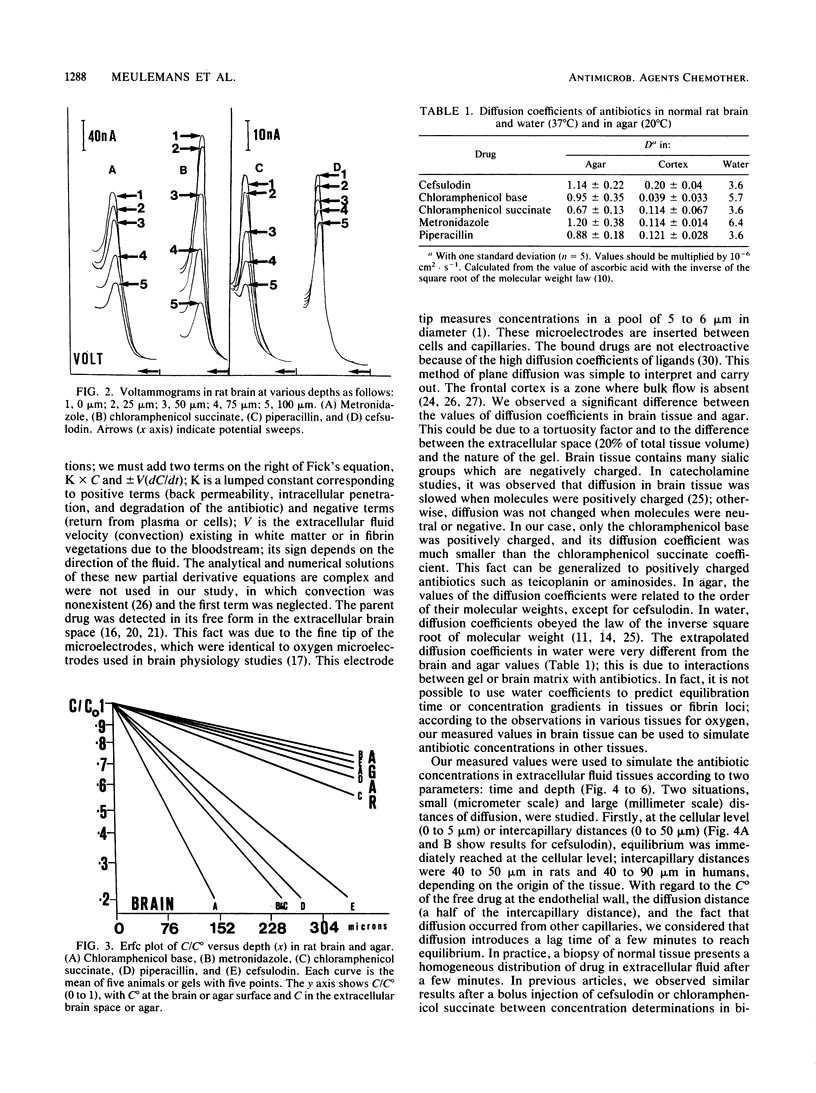
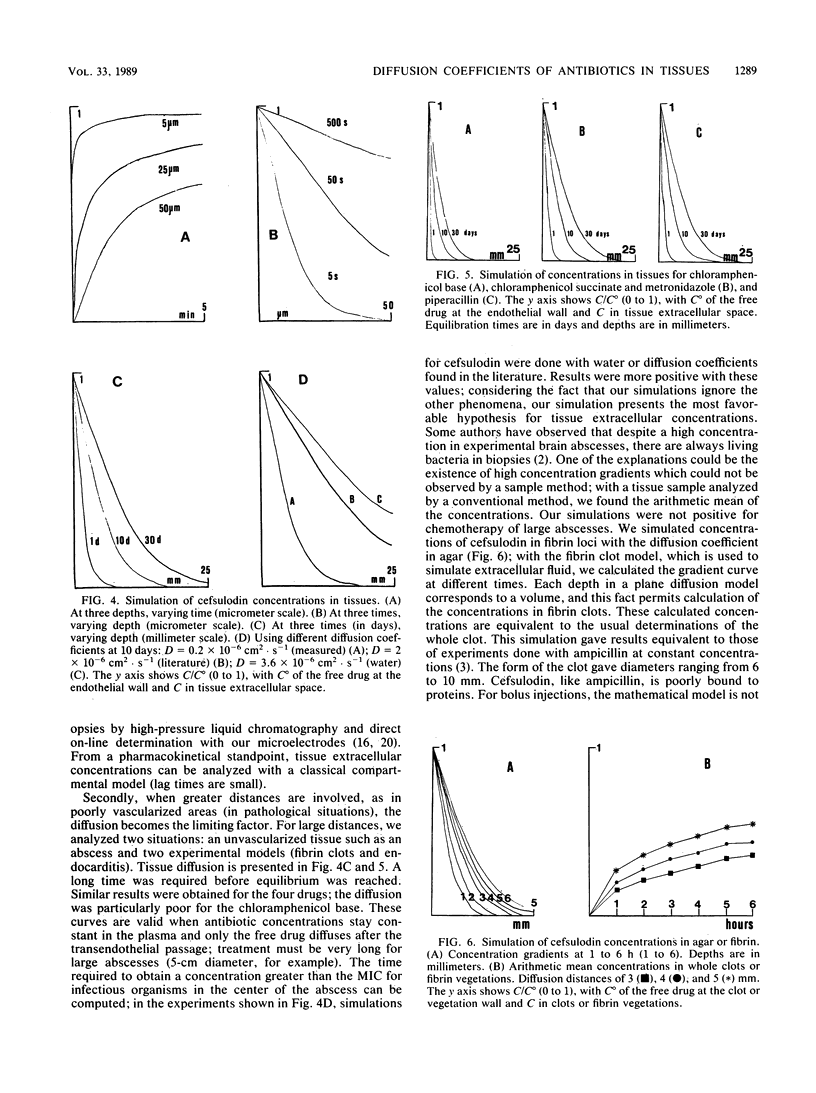
A method for determining diffusion coefficients of four antibiotics in extracellular tissue space according to Fick's law is described. This new method was applied to rat brain tissue and to agar. After diffusion of the antibiotic in one axis, the gradient concentration was determined with microvoltammetric electrodes. These microelectrodes (1 micron at the extreme tip) measured the free diffusible form of electroactive antibiotics in the extracellular brain space. Metronidazole, chloramphenicol succinate, cefsulodin, and piperacillin gave diffusion coefficients ranging from 0.1 x 10(-6) to 0.2 x 10(-6) cm2 . s-1 in tissue; chloramphenicol base, which is positively charged, gave a coefficient of 0.04 x 10(-6) cm2 . s-1. The coefficient ranged from 0.6 x 10(-6) to 1.2 x 10(-6) cm2 . s-1 in agar. These coefficients were used to simulate antibiotic concentrations in infectious sites and between capillaries by using a simple model of plane diffusion.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLUM J. J. Concentration profiles in and around capillaries. Am J Physiol. 1960 May;198:991–998. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.5.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks H. T., Kareiva P. Parameter estimation techniques for transport equations with application to population dispersal and tissue bulk flow models. J Math Biol. 1983;17(3):253–273. doi: 10.1007/BF00276516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barling R. W., Selkon J. B. The penetration of antibiotics into cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 May;4(3):203–227. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.3.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barza M., Brusch J., Bergeron M. G., Weinstein L. Penetration of antibiotics into fibrin loci in vivo. 3. Intermittent vs. continuous infusion and the effect of probenecid. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jan;129(1):73–78. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barza M., Cuchural G. General principles of antibiotic tissue penetration. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):59–75. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barza M., Weinstein L. Penetration of antibiotics into fibrin loci in vivo. I. Comparison of penetration of ampicillin into fibrin clots, abscesses, and "interstitial fluid". J Infect Dis. 1974 Jan;129(1):59–65. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergan T. Kinetics of tissue penetration. Are high plasma peak concentrations or sustained levels preferable for effective antibiotic therapy? Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):36–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergan T. Pharmacokinetics of tissue penetration of antibiotics. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):45–66. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron M. G. Tissue penetration of antibiotics. Clin Biochem. 1986 Apr;19(2):90–100. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(86)80054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasberg R. G., Patlak C., Fenstermacher J. D. Intrathecal chemotherapy: brain tissue profiles after ventriculocisternal perfusion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Oct;195(1):73–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klitzman B., Popel A. S., Duling B. R. Oxygen transport in resting and contracting hamster cremaster muscles: experimental and theoretical microvascular studies. Microvasc Res. 1983 Jan;25(1):108–131. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(83)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer F. Oxygen supply to tissues: the Krogh model and its assumptions. Experientia. 1982 Dec 15;38(12):1415–1426. doi: 10.1007/BF01955753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. P., Nicholls J. F. Diffusion of charged ions in mucus gel: effect of net charge. Biorheology. 1987;24(6):565–569. doi: 10.3233/bir-1987-24607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin V. A., Patlak C. S., Landahl H. D. Heuristic modeling of drug delivery to malignant brain tumors. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1980 Jun;8(3):257–296. doi: 10.1007/BF01059646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meulemans A., Henzel D., Brun-Pacaud M., Mohler J., Vicart P., Huy P. T. On-line pharmacokinetics of chloramphenicol in rat cortex by in vivo electrochemical detection. Chemotherapy. 1984;30(6):353–357. doi: 10.1159/000238293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meulemans A., Poulain B., Baux G., Tauc L. Changes in serotonin concentration in a living neurone: a study by on-line intracellular voltammetry. Brain Res. 1987 Jun 23;414(1):158–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91339-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meulemans A., Vicart P., Henzel D., Mohler J., Vulpillat M. Cefsulodin penetration into rat brain: extracellular versus total concentration. Chemotherapy. 1986;32(5):393–398. doi: 10.1159/000238441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meulemans A., Vicart P., Mohler J., Henzel D., Vulpillat M. Permeability of nitroimidazoles in rat cortex. Chemotherapy. 1986;32(6):486–493. doi: 10.1159/000238457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meulemans A., Vicart P., Mohler J., Vulpillat M. Determination of antibiotic lipophilicity with a micromethod: application to brain permeability in man and rats. Chemotherapy. 1988;34(2):90–95. doi: 10.1159/000238553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak C. S., Fenstermacher J. D. Measurements of dog blood-brain transfer constants by ventriculocisternal perfusion. Am J Physiol. 1975 Oct;229(4):877–884. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.4.877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport S. I., Ohno K., Pettigrew K. D. Drug entry into the brain. Brain Res. 1979 Aug 24;172(2):354–359. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90546-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice M. E., Gerhardt G. A., Hierl P. M., Nagy G., Adams R. N. Diffusion coefficients of neurotransmitters and their metabolites in brain extracellular fluid space. Neuroscience. 1985 Jul;15(3):891–902. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg G. A., Kyner W. T., Estrada E. Bulk flow of brain interstitial fluid under normal and hyperosmolar conditions. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jan;238(1):F42–F49. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.1.F42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg G. A., Kyner W. T. Gray and white matter brain-blood transfer constants by steady-state tissue clearance in cat. Brain Res. 1980 Jul 7;193(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90945-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHANTZ E. J., LAUFFER M. A. Diffusion measurements in agar gel. Biochemistry. 1962 Jul;1:658–663. doi: 10.1021/bi00910a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder S., Voigt R., Horn G., Sestakova I., Skarka P. Pulspolarografische Bestimmung von Piperacillin (Pipril) im Serum und Urin. Pharmazie. 1985 May;40(5):333–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squella J. A., Becerra R., Nunez-Vergara L. J. Polarography: a new tool in the elucidation of drug-albumin interactions. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Oct 15;36(20):3531–3533. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90337-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


