Abstract
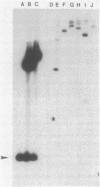
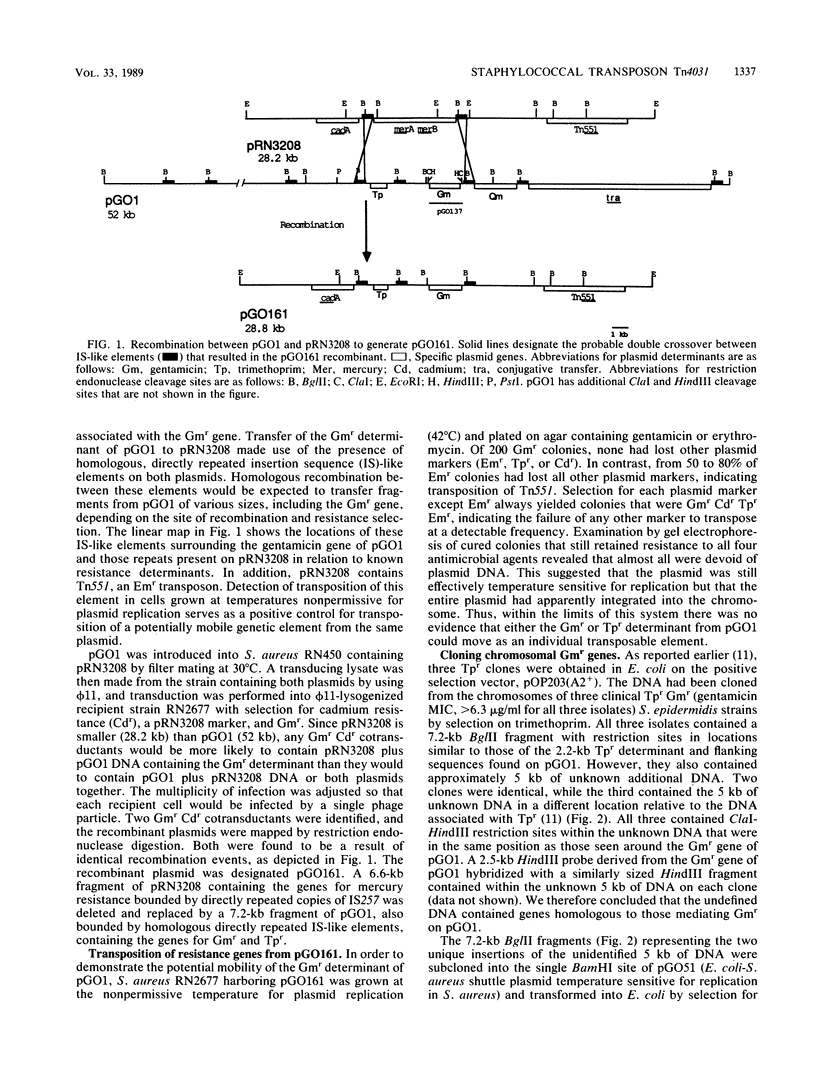
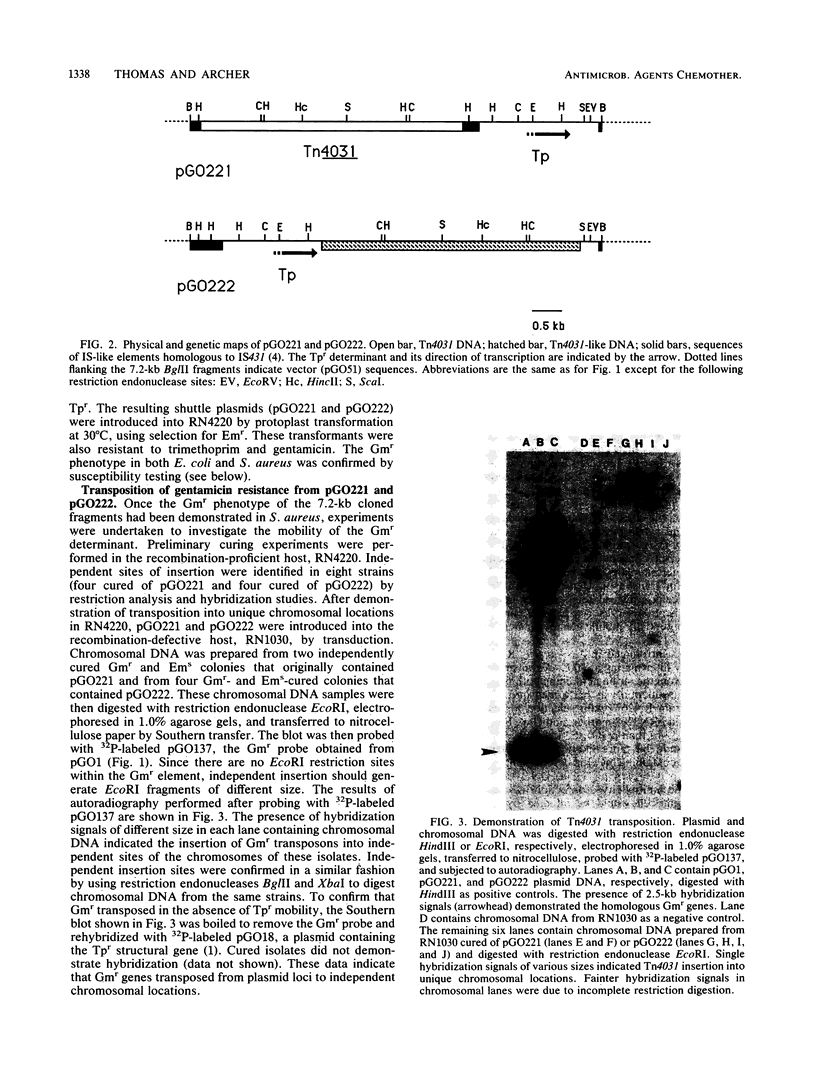
Homologous genes encoding resistance to gentamicin, tobramycin, and kanamycin through the bifunctional acetylating [AAC(6')] and phosphorylating [APH(2")] aminoglycoside-modifying enzyme were identified in staphylococci isolated from patients in the United States. The mobility of gentamicin resistance (Gmr) genes found on a prototype conjugative plasmid (pGO1) was compared with that of genes cloned from chromosomal sites. Plasmid-encoded Gmr genes and flanking sequences were introduced onto a temperature-sensitive plasmid (pRN3208) from pGO1 by homologous recombination between insertion sequence-like elements present on both replicons. Growth of Staphylococcus aureus strains containing the temperature-sensitive recombinant (pGO161) at the nonpermissive temperature for plasmid replication (42 degrees C) revealed no translocation of Gmr from its plasmid location. A transposon (Tn551) resident on the same replicon did translocate. Chromosomal Gmr determinants were cloned, together with the gene for trimethoprim resistance (dfrA), from three geographically distinct S. epidermidis isolates; two were subcloned onto temperature-sensitive Escherichia coli-S. aureus shuttle plasmids as 7.2-kilobase BglII fragments. Growth of both recombination-deficient and-proficient S. aureus strains containing the cloned genes at 42 degrees C allowed detection of transposition of Gmr sequences and identification of insertion into random chromosomal sites. We have designated this 5-kilobase transposon from S. epidermidis as Tn4031.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer G. L., Coughter J. P., Johnston J. L. Plasmid-encoded trimethoprim resistance in staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):733–740. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer G. L., Dietrick D. R., Johnston J. L. Molecular epidemiology of transmissible gentamicin resistance among coagulase-negative staphylococci in a cardiac surgery unit. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):243–251. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer G. L., Johnston J. L. Self-transmissible plasmids in staphylococci that encode resistance to aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):70–77. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barberis-Maino L., Berger-Bächi B., Weber H., Beck W. D., Kayser F. H. IS431, a staphylococcal insertion sequence-like element related to IS26 from Proteus vulgaris. Gene. 1987;59(1):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S., Cohen S. N. High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00267940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Wong E. S., Falkow S. Common R-plasmids in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis during a nosocomial Staphylococcus aureus outbreak. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):210–215. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley K., Loesch D., Landesman B., Mead K., Chern M., Strate R. An outbreak of infections caused by strains of Staphylococcus aureus resistant to methicillin and aminoglycosides. I. Clinical studies. J Infect Dis. 1979 Mar;139(3):273–279. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.3.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden H., Neter E., McLaughlin S., Giacoia G. Gentamicin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Emergence in an intensive care nursery. JAMA. 1979 Jan 12;241(2):143–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froggatt J. W., Johnston J. L., Galetto D. W., Archer G. L. Antimicrobial resistance in nosocomial isolates of Staphylococcus haemolyticus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):460–466. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galetto D. W., Johnston J. L., Archer G. L. Molecular epidemiology of trimethoprim resistance among coagulase-negative staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1683–1688. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie M. T., May J. W., Skurray R. A. Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus isolated at an Australian hospital between 1946 and 1981. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Apr;19(2):137–147. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-2-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goering R. V., Ruff E. A. Comparative analysis of conjugative plasmids mediating gentamicin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Sep;24(3):450–452. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.3.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. S., Huang R. T., Davies J. Aminocyclitol resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: presence of plasmids and aminocyclitol-modifying enzymes. Plasmid. 1983 Mar;9(2):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenhood G. P., Hill D. L., Dixon R. E., Carter M. J., Kanto W. P. Changing phage typing patterns of epidemic gentamicin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Evidence for transmission of gentamicin resistance. Lancet. 1979 Feb 10;1(8111):289–291. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90703-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinsted J., Bennett P. M., Higginson S., Richmond M. H. Regional preference of insertion of Tn501 and Tn802 into RP1 and its derivatives. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 9;166(3):313–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00267624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzman R. S., Florman A. L., Lyman M. Gentamicin resistant and sensitive strains of S. aureus. Factors affecting colonization and virulence for infants in a special care nursery. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Sep;112(3):352–361. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe H. W., Sweeney H. M., Weinstein R. A., Kabins S. A., Nathan C., Cohen S. Structural and phenotypic varieties of gentamicin resistance plasmids in hospital strains of Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 May;21(5):773–779. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.5.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiswirth B. N., Löfdahl S., Betley M. J., O'Reilly M., Schlievert P. M., Bergdoll M. S., Novick R. P. The toxic shock syndrome exotoxin structural gene is not detectably transmitted by a prophage. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):709–712. doi: 10.1038/305709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon B. R., Gillespie M. T., Byrne M. E., May J. W., Skurray R. A. Plasmid-mediated resistance to gentamicin in Staphylococcus aureus: the involvement of a transposon. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Mar;23(2):101–110. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-2-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon B. R., Gillespie M. T., Skurray R. A. Detection and characterization of IS256, an insertion sequence in Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Nov;133(11):3031–3038. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-11-3031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon B. R., Skurray R. Antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus: genetic basis. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):88–134. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.88-134.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Novick R. P. Site-specific recombination between plasmids of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):316–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.316-326.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Adler G. K., Projan S. J., Carleton S., Highlander S. K., Gruss A., Khan S. A., Iordanescu S. Control of pT181 replication I. The pT181 copy control function acts by inhibiting the synthesis of a replication protein. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2399–2405. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. Properties of a cryptic high-frequency transducing phage in Staphylococcus aureus. Virology. 1967 Sep;33(1):155–166. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porthouse A., Brown D. F., Smith R. G., Rogers T. Gentamicin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1976 Jan 3;1(7949):20–21. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92912-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouch D. A., Byrne M. E., Kong Y. C., Skurray R. A. The aacA-aphD gentamicin and kanamycin resistance determinant of Tn4001 from Staphylococcus aureus: expression and nucleotide sequence analysis. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Nov;133(11):3039–3052. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-11-3039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaberg D. R., Power G., Betzold J., Forbes B. A. Conjugative R plasmids in antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus causing nosocomial infections. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soussy C. J., Bouanchaud D. H., Fouace J., Dublanchet A., Duval J. A gentamycin resistance plasmid in Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1975 Jul-Aug;126B(1):91–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speller D. C., Raghunath D., Stephens M., Viant A. C., Reeves D. S., Wilkinson P. J., Broughall J. M., Holt H. A. Epidemic infection by a gentamicin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in three hospitals. Lancet. 1976 Feb 28;1(7957):464–466. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91485-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storrs M. J., Courvalin P., Foster T. J. Genetic analysis of gentamicin resistance in methicillin- and gentamicin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus isolated in Dublin hospitals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Aug;32(8):1174–1181. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.8.1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. D., Jr, Archer G. L. Identification and cloning of the conjugative transfer region of Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pGO1. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):684–691. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.684-691.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend D. E., Ashdown N., Greed L. C., Grubb W. B. Transposition of gentamicin resistance to staphylococcal plasmids encoding resistance to cationic agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Aug;14(2):115–124. doi: 10.1093/jac/14.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend D. E., Bolton S., Ashdown N., Grubb W. B. Transfer of plasmid-borne aminoglycoside-resistance determinants in staphylococci. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Oct;20(2):169–185. doi: 10.1099/00222615-20-2-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel L., Nathan C., Sweeney H. M., Kabins S. A., Cohen S. Infections due to gentamicin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain in a nursery for neonatal infants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):466–472. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein R. A., Kabins S. A., Nathan C., Sweeney H. M., Jaffe H. W., Cohen S. Gentamicin-resistant staphylococci as hospital flora: epidemiology and resistance plasmids. J Infect Dis. 1982 Mar;145(3):374–382. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.3.374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Solh N., Moreau N., Ehrlich S. D. Molecular cloning and analysis of Staphylococcus aureus chromosomal aminoglycoside resistance genes. Plasmid. 1986 Mar;15(2):104–118. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(86)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]