Abstract
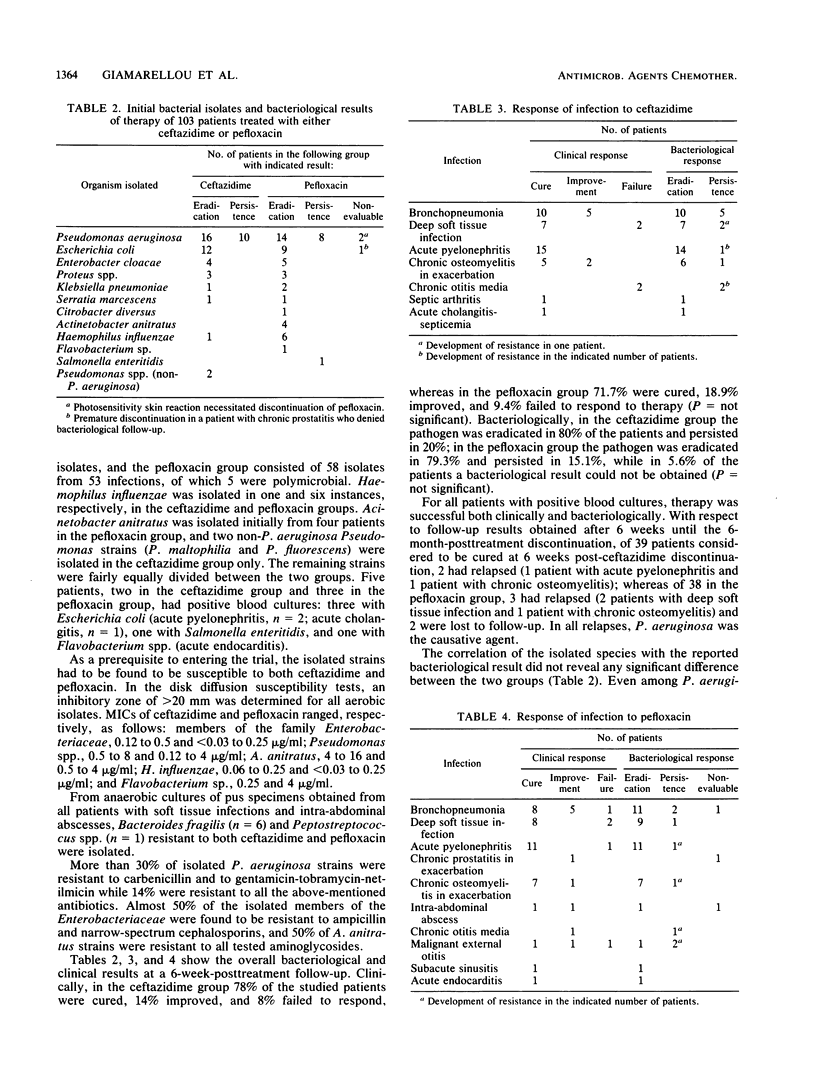
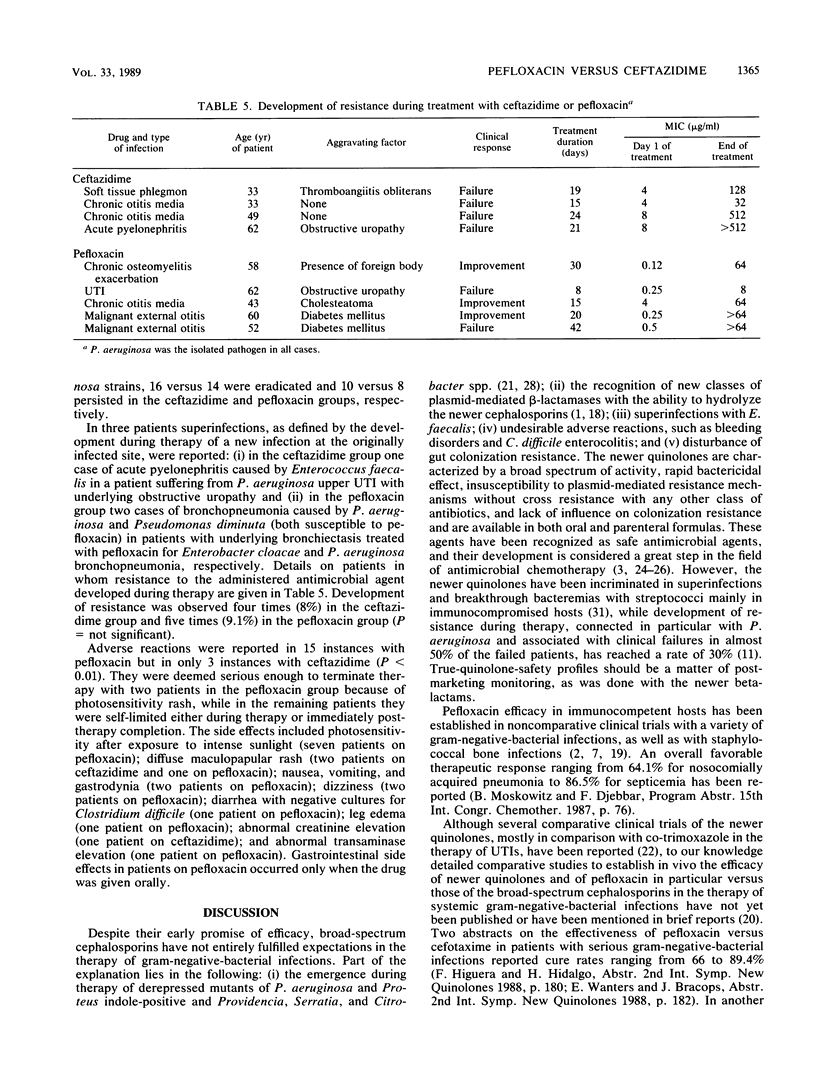
In a prospective open randomized trial, pefloxacin was given to 53 patients and ceftazidime was given to 50 patients suffering from bronchopneumonia (n = 29), deep soft tissue infection (n = 19), urinary tract infection (n = 28), chronic osteomyelitis in exacerbation (n = 15), chronic otitis media in exacerbation (n = 3), malignant external otitis (n = 3), abdominal abscess (n = 2), septic arthritis (n = 1), acute cholangitis (n = 1), bacterial endocarditis (n = 1), and subacute sinusitis (n = 1). Underlying aggravating factors coexisted in 45 and 41 patients in the pefloxacin and ceftazidime groups, respectively, with 32 and 33 infections characterized as nosocomial and severe in each group, respectively. Pefloxacin was given at a dose of 400 mg intravenously (i.v.) (n = 16) or per os (n = 23) every 8 or 12 h, as well as i.v. followed by per os (n = 14), for 7 to 180 days; and ceftazidime was given at 2 g i.v. every 8 h (n = 45) or 1 g intramuscularly every 8 h (n = 5) for 7 to 56 days. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and various members of the family Enterobacteriaceae predominated in culture specimens. Clinical cure was observed in 38 and 39 patients given pefloxacin and ceftazidime, respectively; 10 and 7 patients were improved; and in 5 and 4 patients treatment failed. Pathogen eradication was observed in 42 and 39 patients, respectively; persistence was observed in 8 and ll patients, respectively, followed by the emergence of resistance in five and four P. aeruginosa strains, respectively (P = not significant). With the exception of photosensitivity rash in seven patients given pefloxacin, all side effects observed in eight and three patients in the pefloxacin and ceftazidime groups, respectively (P < 0.01), were not important and were self-limited. It is concluded that pefloxacin is as effective as ceftazidime in moderate to severe gram-negative-bacterial infections, with similar trends toward development of resistance during therapy.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauernfeind A., Hörl G. Novel R-factor borne beta-lactamase of Escherichia coli confering resistance to cephalosporins. Infection. 1987 Jul-Aug;15(4):257–259. doi: 10.1007/BF01644127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerema J. B., Pauwels R., Scheepers J., Crombach W. Efficacy and safety of pefloxacin in the treatment of patients with complicated urinary tract infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17 (Suppl B):103–109. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.suppl_b.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clumeck N., Gordts B., Dab I., Jaspar N., Van Laethem Y., Butzler J. P. Ceftazidime as a single agent in the treatment of severe Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Jul;12 (Suppl A):207–211. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_a.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellamonica P., Bernard E., Etesse H., Garraffo R. The diffusion of pefloxacin into bone and the treatment of osteomyelitis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17 (Suppl B):93–102. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.suppl_b.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dournon E., Rajagopalan P., Vilde J. L., Pocidalo J. J. Efficacy of pefloxacin in comparison with erythromycin in the treatment of experimental guinea pig legionellosis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17 (Suppl B):41–48. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.suppl_b.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dow J., Chazal J., Frydman A. M., Janny P., Woehrle R., Djebbar F., Gaillot J. Transfer kinetics of pefloxacin into cerebro-spinal fluid after one hour i.v. infusion of 400 mg in man. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17 (Suppl B):81–87. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.suppl_b.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eron L. J., Park C. H., Hixon D. L., Goldenberg R. I., Poretz D. M. Ceftazidime in patients with Pseudomonas infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Jul;12 (Suppl A):161–169. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_a.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giamarellou H., Galanakis N., Dendrinos C., Stefanou J., Daphnis E., Daikos G. K. Evaluation of ciprofloxacin in the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;5(2):232–235. doi: 10.1007/BF02013996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giamarellou H., Galanakis N., Douzinas E., Petrikkos G., El Messidi M., Papoulias G., Daikos G. K. Evaluation of aztreonam in difficult-to-treat infections with prolonged posttreatment follow-up. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):245–249. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giamarellou H., Touliatou K., Koratzanis G., Petrikkos G., Kanellakopoulou K., Lelekis M., Pagona A., Tsagarakis J., Symeonides J., Falagas M. Nosocomial consequences of antibiotic usage. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1986;49:182–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A., Phillips I. The comparative in-vitro activity of pefloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17 (Suppl B):1–10. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.suppl_b.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliebe C., Nies B. A., Meyer J. F., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Evolution of plasmid-coded resistance to broad-spectrum cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):302–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauwers S., Vincken W., Naessens A., Pierard D. Efficacy and safety of pefloxacin in the treatment of severe infections in patients hospitalized in intensive care units. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17 (Suppl B):111–115. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.suppl_b.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore D. M. Clinical significance of beta-lactamase induction and stable derepression in gram-negative rods. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;6(4):439–445. doi: 10.1007/BF02013107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord C. E., Edlund C., Lahnborg G. The efficacy of pefloxacin in comparison to gentamicin in the treatment of experimentally induced peritonitis in rats. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17 (Suppl B):59–63. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.suppl_b.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Type I beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria: interactions with beta-lactam antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1986 Nov;154(5):792–800. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.5.792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist L. In-vitro activity of pefloxacin against micro-organisms multiply resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics and aminoglycosides. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17 (Suppl B):11–17. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.suppl_b.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


