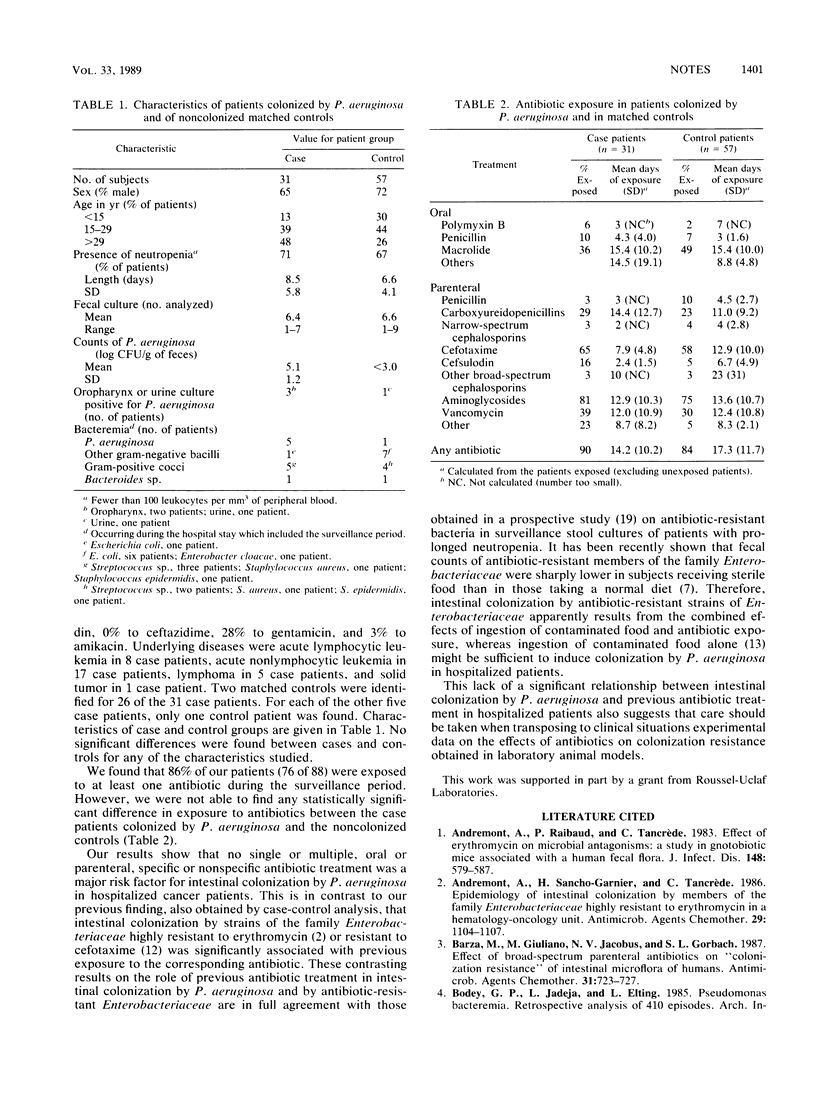
Abstract
To determine whether antibiotic treatment increases the risk of colonization by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, we performed a case-control study comparing antibiotic exposure in cancer patients colonized by P. aeruginosa and in noncolonized controls. Of 88 patients, 76 had been exposed to at least one antibiotic, but colonization was not statistically associated with exposure to any specific antibiotic treatment, administered orally or parenterally, alone or in combination.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andremont A., Raibaud P., Tancrède C. Effect of erythromycin on microbial antagonisms: a study in gnotobiotic mice associated with a human fecal flora. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):579–587. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andremont A., Sancho-Garnier H., Tancrede C. Epidemiology of intestinal colonization by members of the family Enterobacteriaceae highly resistant to erythromycin in a hematology-oncology unit. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1104–1107. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barza M., Giuliano M., Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L. Effect of broad-spectrum parenteral antibiotics on "colonization resistance" of intestinal microflora of humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 May;31(5):723–727. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.5.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck A. C., Cooke E. M. The fate of ingested Pseudomonas aeruginosa in normal persons. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Nov 4;2(4):521–525. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-4-521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corpet D. E. Antibiotic resistance from food. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 5;318(18):1206–1207. doi: 10.1056/nejm198805053181818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentges D. J., Stein A. J., Casey S. W., Que J. U. Protective role of intestinal flora against infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice: influence of antibiotics on colonization resistance. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):118–122. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.118-122.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecquet S., Andremont A., Tancrède C. Selective antimicrobial modulation of the intestinal tract by norfloxacin in human volunteers and in gnotobiotic mice associated with a human fecal flora. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1047–1052. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prevot M. H., Andremont A., Sancho-Garnier H., Tancrede C. Epidemiology of intestinal colonization by members of the family Enterobacteriaceae resistant to cefotaxime in a hematology-oncology unit. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):945–947. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Schimpff S. C. Occasional notes. Please don't eat the salads. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 12;304(7):433–435. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102123040730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimpff S. C., Young V. M., Greene W. H., Vermeulen G. D., Moody M. R., Wiernik P. H. Origin of infection in acute nonlymphocytic leukemia. Significance of hospital acquisition of potential pathogens. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Nov;77(5):707–714. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-77-5-707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tancrède C. H., Andremont A. O. Bacterial translocation and gram-negative bacteremia in patients with hematological malignancies. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):99–103. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingard J. R., Dick J., Charache P., Saral R. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria in surveillance stool cultures of patients with prolonged neutropenia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Sep;30(3):435–439. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.3.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


