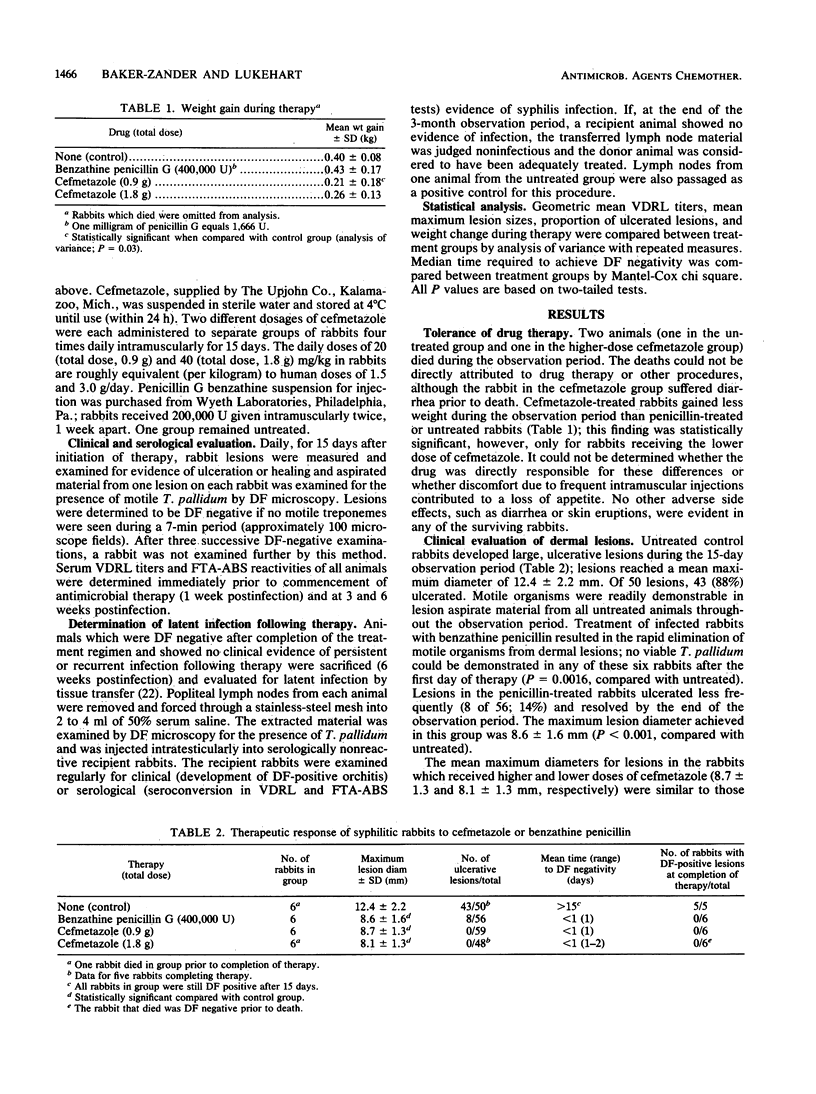
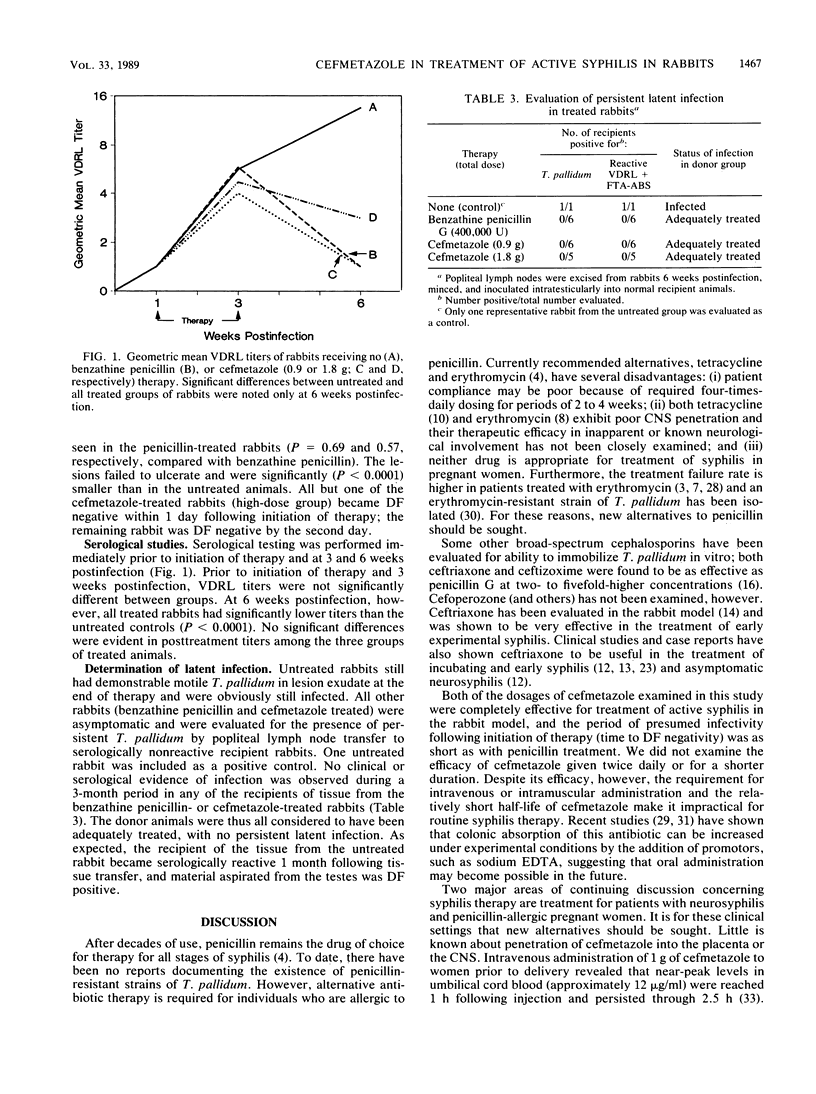
Abstract
Cefmetazole, a cephamycin-type antibiotic, was shown to be as effective as standard benzathine penicillin for therapy of active syphilis in the rabbit model. Four groups of six adult male rabbits were inoculated intradermally with 10(6) Treponema pallidum per site, producing primary syphilitic lesions. One week following infection, groups of rabbits were treated with benzathine penicillin (200,000 U intramuscularly weekly for 2 weeks) or cefmetazole (20 or 40 mg/kg per day intramuscularly in four divided doses for 15 days); one group was untreated. Daily dark-field microscopic examination of lesion aspirates demonstrated that the mean times to dark-field negativity were the same for benzathine penicillin- and two cefmetazole-treated groups (1.0. 1.0, and 1.17 days, respectively), while all untreated animals remained dark-field positive for greater than 15 days. Mean maximum lesion diameters in cefmetazole-treated animals (8.7 +/- 1.3 and 8.1 +/- 1.3 mm) were equivalent to those in penicillin-treated animals (8.6 +/- 1.6 mm) and were smaller than observed in untreated animals (12.4 +/- 2.2 mm; P less than 0.01); fewer lesions ulcerated in penicillin- or cefmetazole-treated rabbits than in untreated rabbits (P less than 0.001). Persistent infection was documented in lymph nodes of untreated rabbits; no evidence of latent infection was found in penicillin- or cefmetazole-treated animals.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baughn R. E., Musher D. M., Adams C. B., Knox J. M. Evaluation of rosaramicin phosphate in treatment of experimental syphilis in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):117–121. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry C. D., Hooton T. M., Collier A. C., Lukehart S. A. Neurologic relapse after benzathine penicillin therapy for secondary syphilis in a patient with HIV infection. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jun 18;316(25):1587–1589. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198706183162507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. T. Treatment of secondary syphilis. J Am Vener Dis Assoc. 1976 Dec;3(2 Pt 2):136–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK J. W., Jr, YOBS A. R. EFFECT OF ACTINOSPECTACIN IN EXPERIMENTAL SYPHILIS IN THE RABBIT. I. EARLY LESION SYPHILIS. Br J Vener Dis. 1963 Sep;39:184–189. doi: 10.1136/sti.39.3.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham W. B., Rake G. The Activity of Streptomycin in Experimental Syphilis. Science. 1946 Mar 22;103(2673):365–365. doi: 10.1126/science.103.2673.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott W. C. Treatment of primary syphilis. J Am Vener Dis Assoc. 1976 Dec;3(2 Pt 2):128–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett E. D., Strausbaugh L. J. Antimicrobial agents and the central nervous system. Neurosurgery. 1980 Jun;6(6):691–714. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198006000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashira S., Matsueda Y., Fujii R. [Laboratory and clinical evaluation of cefmetazole in the newborn infants (author's transl)]. Jpn J Antibiot. 1981 Jun;34(6):864–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. W., 3rd, Baker-Zander S. A., Moskovitz B. L., Lukehart S. A., Handsfield H. H. Ceftriaxone therapy for asymptomatic neurosyphilis. Case report and Western blot analysis of serum and cerebrospinal fluid IgG response to therapy. Sex Transm Dis. 1986 Jul-Sep;13(3 Suppl):185–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. W., 3rd, Roddy R. E., Handsfield H. H. Ceftriaxone therapy for incubating and early syphilis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):881–884. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Bey R. F., Wolgamot S. J. Comparison of the activities of ceftriaxone and penicillin G against experimentally induced syphilis in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):984–989. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Barry A. L., Fuchs P. C., Thornsberry C. Antimicrobial activity of cefmetazole (CS-1170) and recommendations for susceptibility testing by disk diffusion, dilution, and anaerobic methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):1055–1059. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.1055-1059.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korting H. C., Walther D., Riethmüller U., Meurer M. Comparative in vitro susceptibility of Treponema pallidum to ceftizoxime, ceftriaxone and penicillin G. Chemotherapy. 1986;32(4):352–355. doi: 10.1159/000238434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwahara S., Zenyoji H. Cephaloridine treatment of experimental rabbit syphilis. Postgrad Med J. 1967 Aug;43(Suppl):130–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Baker-Zander S. A., Holmes K. K. Efficacy of aztreonam in treatment of experimental syphilis in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):390–391. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Baker-Zander S. A. Roxithromycin (RU 965): effective therapy for experimental syphilis infection in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):187–190. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Baker-Zander S. A., Sell S. Characterization of lymphocyte responsiveness in early experimental syphilis. I. In vitro response to mitogens and Treponema pallidum antigens. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):454–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Hook E. W., 3rd, Baker-Zander S. A., Collier A. C., Critchlow C. W., Handsfield H. H. Invasion of the central nervous system by Treponema pallidum: implications for diagnosis and treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Dec 1;109(11):855–862. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-11-855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorthy T. T., Lee C. T., Lim K. B., Tan T. Ceftriaxone for treatment of primary syphilis in men: a preliminary study. Sex Transm Dis. 1987 Apr-Jun;14(2):116–118. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198704000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao H., Yanagisawa H., Shimizu B., Kaneko M., Nagano M. A new semisynthetic 7alpha-methoxycephalosporin, CS-1170: 7beta-((cyanomethyl)thio)acetamido)-7alpha-methoxy-3-((1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)thio)methyl)-3-cephem-4-carboxylic acid. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 May;29(5):554–558. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Edmondson D. G. In vitro culture system to determine MICs and MBCs of antimicrobial agents against Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum (Nichols strain). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):68–74. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya S., Yamazaki M., Sugawara S., Tamaki S., Matsuhashi M. New cephamycin antibiotic, CS-1170: binding affinity to penicillin-binding proteins and inhibition of peptidoglycan cross-linking reactions in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Nov;14(5):780–785. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.5.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeter A. L., Lucas J. B., Price E. V., Falcone V. H. Treatment for early syphilis and reactivity of serologic tests. JAMA. 1972 Jul 31;221(5):471–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiga M., Hayashi M., Horie T., Awazu S. Differences in the promotion mechanism of the colonic absorption of antipyrine, phenol red and cefmetazole. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1987 Feb;39(2):118–123. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1987.tb06956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Stapleton J. T., Bassford P. J., Jr In vitro assay to demonstrate high-level erythromycin resistance of a clinical isolate of Treponema pallidum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Feb;32(2):164–169. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.2.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuka T., Furuya A., Kamada A., Nishihata T. Effect of phenothiazines, disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and diethyl maleate on in vitro rat colonic transport of cefmetazole and inulin. J Pharmacobiodyn. 1987 Feb;10(2):63–71. doi: 10.1248/bpb1978.10.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


