Abstract
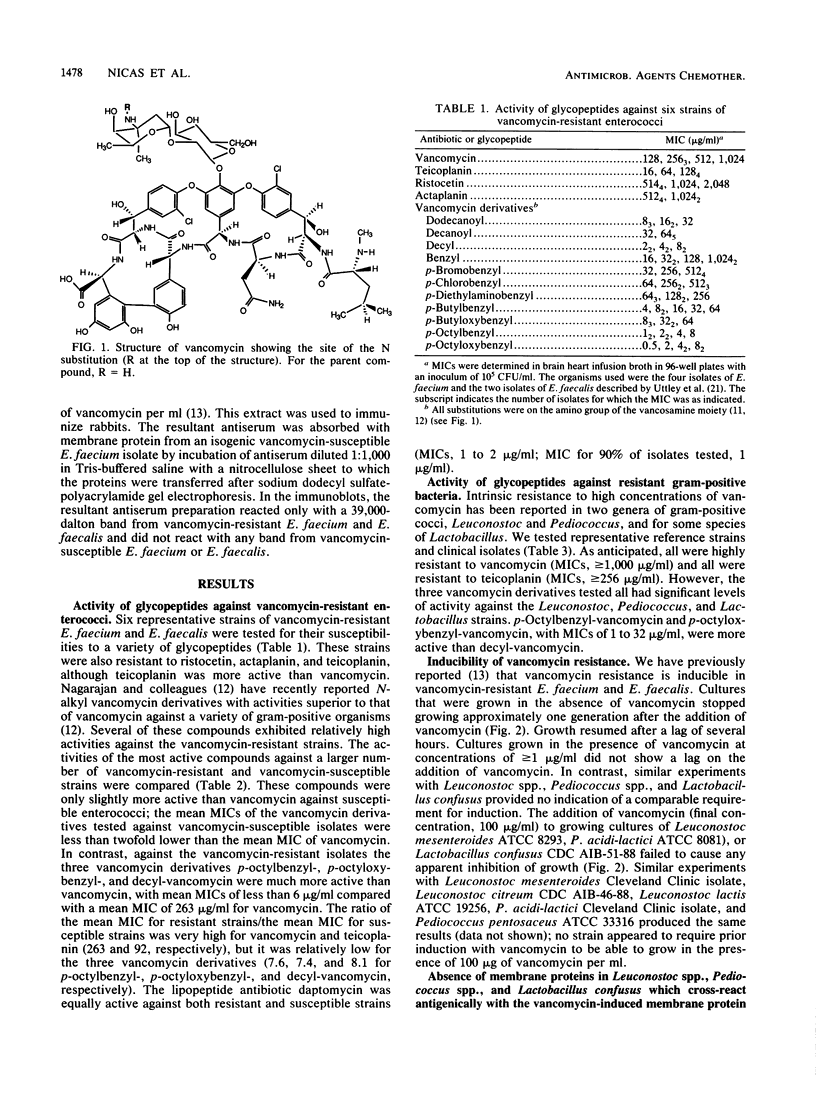
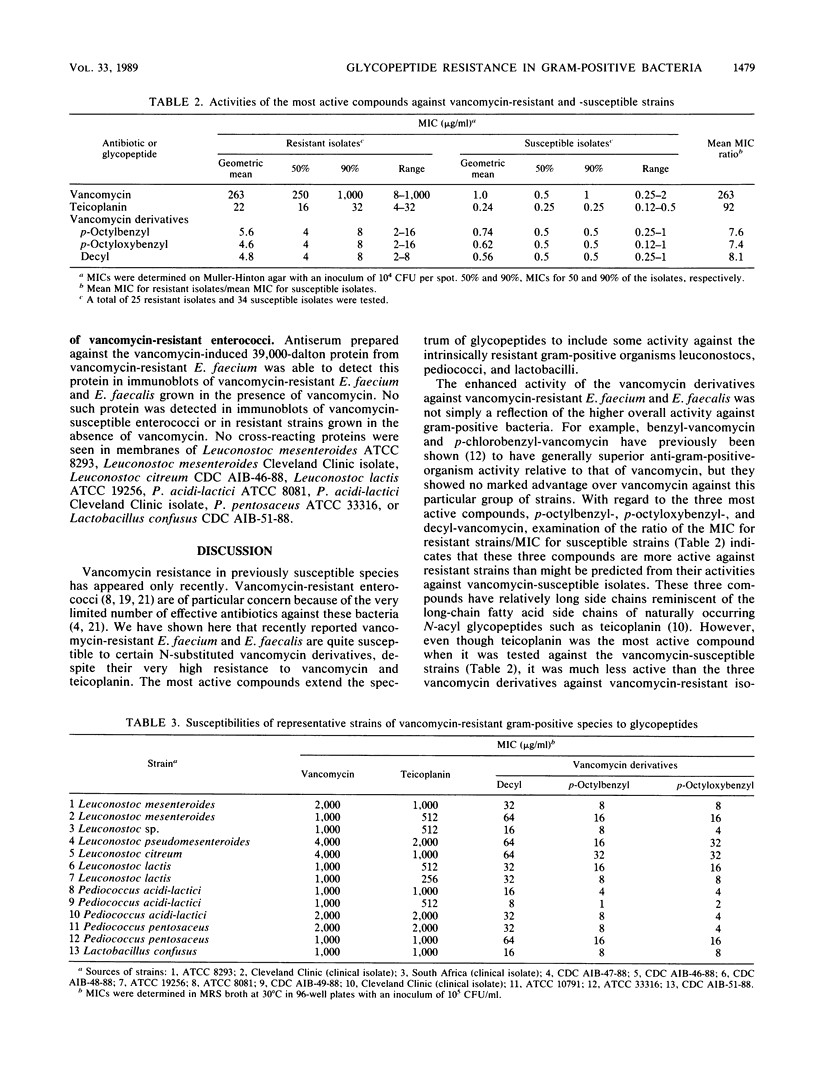
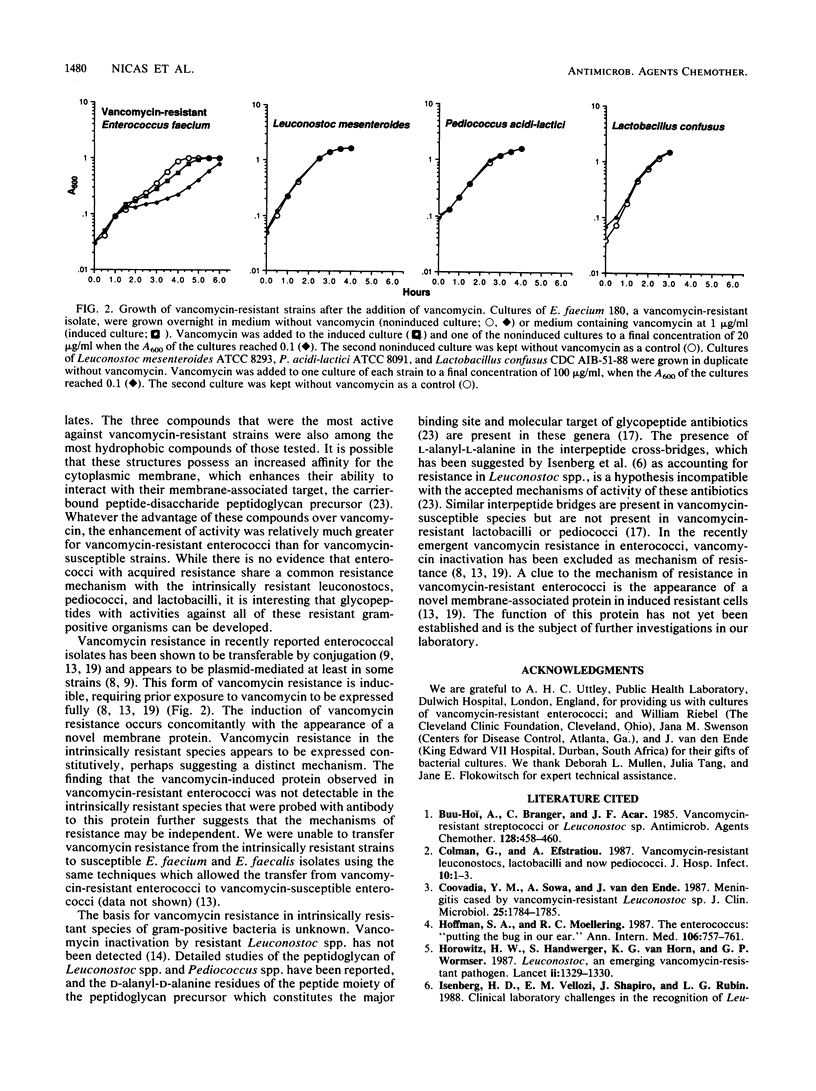
Gram-positive bacteria resistant to vancomycin are rare; but they include members of the genera Leuconostoc, Lactobacillus, and Pediococcus, as well as recently emerging vancomycin-resistant strains of Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis. Vancomycin, teicoplanin, and several vancomycin derivatives were tested for their activities against vancomycin-resistant gram-positive bacteria. Vancomycin-resistant E. faecium and E. faecalis were generally cross-resistant to other glycopeptides, but some N-substituted vancomycin derivatives were active against the resistant strains, with MICs of 2 to 32 micrograms/ml. These vancomycin derivatives also had significant levels of activity against intrinsically vancomycin-resistant organisms such as Leuconostoc sp. While vancomycin resistance in E. faecium and E. faecalis was inducible, resistance in members of the genera Leuconostoc, Lactobacillus, and Pediococcus appeared to be expressed constitutively. Antibody to a vancomycin-induced membrane protein found in membranes of resistant enterococci did not detect a cross-reacting protein in other vancomycin-resistant species.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buu-Hoï A., Branger C., Acar J. F. Vancomycin-resistant streptococci or Leuconostoc sp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):458–460. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman G., Efstratiou A. Vancomycin-resistant leuconostocs, lactobacilli and now pediococci. J Hosp Infect. 1987 Jul;10(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(87)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coovadia Y. M., Solwa Z., van den Ende J. Meningitis caused by vancomycin-resistant Leuconostoc sp. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1784–1785. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1784-1785.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann S. A., Moellering R. C., Jr The enterococcus: "putting the bug in our ears". Ann Intern Med. 1987 May;106(5):757–761. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-5-757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz H. W., Handwerger S., van Horn K. G., Wormser G. P. Leuconostoc, an emerging vancomycin-resistant pathogen. Lancet. 1987 Dec 5;2(8571):1329–1330. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91217-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg H. D., Vellozzi E. M., Shapiro J., Rubin L. G. Clinical laboratory challenges in the recognition of Leuconostoc spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):479–483. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.479-483.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. H., Gilligan P. H., Facklam R. R. Recovery of resistant enterococci during vancomycin prophylaxis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1216–1218. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1216-1218.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq R., Derlot E., Duval J., Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated resistance to vancomycin and teicoplanin in Enterococcus faecium. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jul 21;319(3):157–161. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198807213190307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq R., Derlot E., Weber M., Duval J., Courvalin P. Transferable vancomycin and teicoplanin resistance in Enterococcus faecium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):10–15. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malabarba A., Strazzolini P., Depaoli A., Landi M., Berti M., Cavalleri B. Teicoplanin, antibiotics from Actinoplanes teichomyceticus nov. sp. VI. Chemical degradation: physico-chemical and biological properties of acid hydrolysis products. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1984 Sep;37(9):988–999. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.37.988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagarajan R., Schabel A. A., Occolowitz J. L., Counter F. T., Ott J. L., Felty-Duckworth A. M. Synthesis and antibacterial evaluation of N-alkyl vancomycins. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1989 Jan;42(1):63–72. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.42.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagarajan R., Schabel A. A., Occolowitz J. L., Counter F. T., Ott J. L. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of N-acyl vancomycins. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1988 Oct;41(10):1430–1438. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.41.1430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Wu C. Y., Hobbs J. N., Jr, Preston D. A., Allen N. E. Characterization of vancomycin resistance in Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jul;33(7):1121–1124. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.7.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orberg P. K., Sandine W. E. Common occurrence of plasmid DNA and vancomycin resistance in Leuconostoc spp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Dec;48(6):1129–1133. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.6.1129-1133.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. G., Vellozzi E., Shapiro J., Isenberg H. D. Infection with vancomycin-resistant "streptococci" due to Leuconostoc species. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):216–216. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff K. L., Kuritzkes D. R., Wolfson J. S., Ferraro M. J. Vancomycin-resistant gram-positive bacteria isolated from human sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2064–2068. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2064-2068.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kandler O. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):407–477. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.407-477.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe R. S., Stapleton J. T., Gilligan P. H. Emergence of vancomycin resistance in coagulase-negative staphylococci. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 9;316(15):927–931. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704093161507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlaes D. M., Bouvet A., Devine C., Shlaes J. H., al-Obeid S., Williamson R. Inducible, transferable resistance to vancomycin in Enterococcus faecalis A256. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Feb;33(2):198–203. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.2.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlaes D. M., Marino J., Jacobs M. R. Infection caused by vancomycin-resistant Streptococcus sanguis II. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):527–528. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uttley A. H., Collins C. H., Naidoo J., George R. C. Vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Lancet. 1988 Jan 2;1(8575-6):57–58. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vescovo M., Morelli L., Bottazzi V. Drug resistance plasmids in Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus reuteri. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):50–56. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.50-56.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. H., Waltho J. P. Molecular basis of the activity of antibiotics of the vancomycin group. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 1;37(1):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90765-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


