Abstract
Background—Endotoxaemia is implicated in the pathophysiology of obstructive jaundice. The EndoCab enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a novel assay which measures endogenous antibody (IgG) to the inner core region of circulating endotoxins (ACGA). Aims—To investigate the significance of endotoxaemia in biliary obstruction using the EndoCab assay and assess the specificity of the humoral response to endotoxin compared with an exogenous antigenic challenge (tetanus toxoid, TT). Methods—Three groups of adult male Wistar rats were studied: no operation, sham operation, and bile duct ligation for 21 days (BDL). In the second study, rats rats received prior immunisation with TT. Results—In the preliminary experiment, plasma ACGA was significantly increased in the BDL group (306.6 (18.3)% versus 119.9(6.7)% and 105.2 (4.6)% in the sham and no operation groups, respectively; p<0.001). Although the mean endotoxin concentration in the BDL group was greater than that in the control groups this was not significant. There was a strong positive correlation between ACGA and endotoxin concentrations (p=0.0021). In the second study mean ACGA after 21 days of BDL was significantly elevated (267.1 (31.2)% versus 101.6 (21.2)% at baseline, p<0.0001). ACGA was unaffected in the other two groups. TT antibody concentrations fell in all three groups; only in the BDL group was the fall significant (97.6(5.3)% versus 78.8 (4.2)% at baseline, p<0.05). Conclusions—The specific rise in ACGA supports the hypothesis that endotoxin has an integral role in the pathophysiology of obstructive jaundice. The production of anticore glycolipid antibodies specifically reflects systemic endotoxaemia in this model. The EndoCab assay provides a novel, sensitive, and specific method for endotoxin detection.
Keywords: biliary obstruction; endotoxaemia; EndoCab assay
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (112.6 KB).
Figure 1 .
Summary of the important steps in experiment 2. The standard antibody response to TT is depicted in the upper frame.
Figure 2 .
Concentrations of anticore glycolipid antibody (IgG) in the three animal groups after 21 days.
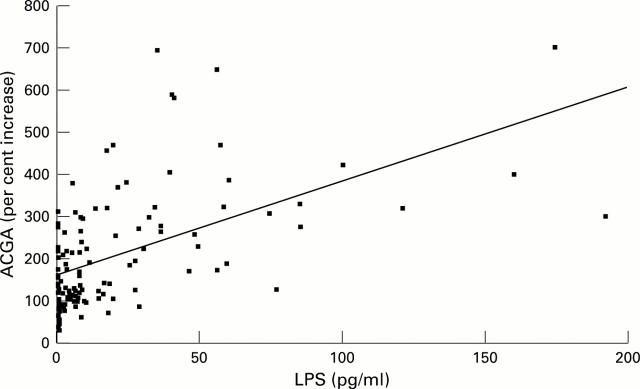
Figure 3 .
Correlation between ACGA and endotoxin concentrations.
Figure 4 .
Standard humoral antibody response (IgG and IgM) of adult male Wistar rats to tetanus toxoid over an 81 day period.
Figure 5 .
Change in plasma ACGA concentrations in the three animal groups over a 21 day period.
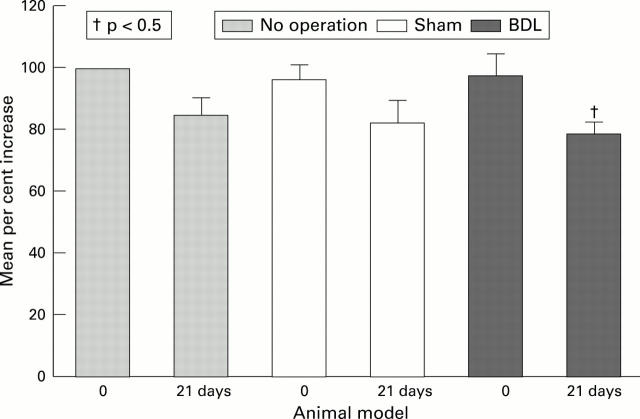
Figure 6 .
Change in plasma TAB concentrations in the three animal groups over a 21 day period.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. P., Dixon J. M., Taylor T. V., Davies G. C. Surgical experience of deeply jaundiced patients with bile duct obstruction. Br J Surg. 1984 Mar;71(3):234–238. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800710326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnaud J. P., Humbert W., Eloy M. R., Adloff M. Effect of obstructive jaundice on wound healing. An experimental study in rats. Am J Surg. 1981 May;141(5):593–596. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(81)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANG F. B. A bacterial disease of Limulus polyphemus. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1956 May;98(5):325–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakkevold K. E., Kambestad B. Morbidity and mortality after radical and palliative pancreatic cancer surgery. Risk factors influencing the short-term results. Ann Surg. 1993 Apr;217(4):356–368. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199304000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barclay G. R., Scott B. B., Wright I. H., Rogers P. N., Smith D. G., Poxton I. R. Changes in anti-endotoxin-IgG antibody and endotoxaemia in three cases of gram-negative septic shock. Circ Shock. 1989 Oct;29(2):93–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bemelmans M. H., Gouma D. J., Greve J. W., Buurman W. A. Cytokines tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 in experimental biliary obstruction in mice. Hepatology. 1992 Jun;15(6):1132–1136. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blamey S. L., Fearon K. C., Gilmour W. H., Osborne D. H., Carter D. C. Prediction of risk in biliary surgery. Br J Surg. 1983 Sep;70(9):535–538. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800700910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradfield J. W. Control of spillover. The importance of Kupffer-cell function in clinical medicine. Lancet. 1974 Oct 12;2(7885):883–886. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso V., Pimenta A., da Fonseca J. C., Rodrigues J. S., Vaz M. J. The effect of cholestasis on hepatic clearance of bacteria. World J Surg. 1982 May;6(3):330–334. doi: 10.1007/BF01653550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements W. D., Diamond T., McCrory D. C., Rowlands B. J. Biliary drainage in obstructive jaundice: experimental and clinical aspects. Br J Surg. 1993 Jul;80(7):834–842. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800800707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements W. D., Halliday M. I., McCaigue M. D., Barclay R. G., Rowlands B. J. Effects of extrahepatic obstructive jaundice on Kupffer cell clearance capacity. Arch Surg. 1993 Feb;128(2):200–205. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1993.01420140077012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements W. D., Parks R., Erwin P., Halliday M. I., Barr J., Rowlands B. J. Role of the gut in the pathophysiology of extrahepatic biliary obstruction. Gut. 1996 Oct;39(4):587–593. doi: 10.1136/gut.39.4.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J., McConnell J. S. Observations on the measurement and evaluation of endotoxemia by a quantitative limulus lysate microassay. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):916–924. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curley P. J., McMahon M. J., Lancaster F., Banks R. E., Barclay G. R., Shefta J., Boylston A. W., Whicher J. T. Reduction in circulating levels of CD4-positive lymphocytes in acute pancreatitis: relationship to endotoxin, interleukin 6 and disease severity. Br J Surg. 1993 Oct;80(10):1312–1315. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800801031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitch E. A., Sittig K., Li M., Berg R., Specian R. D. Obstructive jaundice promotes bacterial translocation from the gut. Am J Surg. 1990 Jan;159(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(05)80610-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond T., Dolan S., Thompson R. L., Rowlands B. J. Development and reversal of endotoxemia and endotoxin-related death in obstructive jaundice. Surgery. 1990 Aug;108(2):370–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond T., Rowlands B. J. Endotoxaemia in obstructive jaundice. HPB Surg. 1991 Jun;4(2):81–94. doi: 10.1155/1991/48672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding J. W., Andersson R., Soltesz V., Willén R., Bengmark S. Obstructive jaundice impairs reticuloendothelial function and promotes bacterial translocation in the rat. J Surg Res. 1994 Aug;57(2):238–245. doi: 10.1006/jsre.1994.1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. M., Armstrong C. P., Duffy S. W., Elton R. A., Davies G. C. Upper gastrointestinal bleeding. A significant complication after surgery for relief of obstructive jaundice. Ann Surg. 1984 Mar;199(3):271–275. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198403000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. C., Lehr L., Urbaschek R. M., Kozak J. Limulus amebocyte lysate test for endotoxemia: investigations with a femtogram sensitive spectrophotometric assay. Klin Wochenschr. 1981 Mar 2;59(5):213–218. doi: 10.1007/BF01476578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M. S., Westwick J., Kakkar V. V. Endotoxin, prostaglandins and renal fibrin deposition in obstructive jaundice. Br J Surg. 1982 Oct;69(10):625–629. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800691022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K. R., Halliday M. I., Barclay G. R., Milne L., Brown D., Stephens S., Maxwell R. J., Rowlands B. J. Significance of systemic endotoxaemia in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1995 Jun;36(6):897–901. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.6.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldie A. S., Fearon K. C., Ross J. A., Barclay G. R., Jackson R. E., Grant I. S., Ramsay G., Blyth A. S., Howie J. C. Natural cytokine antagonists and endogenous antiendotoxin core antibodies in sepsis syndrome. The Sepsis Intervention Group. JAMA. 1995 Jul 12;274(2):172–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig J. D., Krukowski Z. H., Matheson N. A. Surgical morbidity and mortality in one hundred and twenty-nine patients with obstructive jaundice. Br J Surg. 1988 Mar;75(3):216–219. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800750309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve J. W., Gouma D. J., Soeters P. B., Buurman W. A. Suppression of cellular immunity in obstructive jaundice is caused by endotoxins: a study with germ-free rats. Gastroenterology. 1990 Feb;98(2):478–485. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90841-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. R., Allison M. E., Prentice C. R., Blumgart L. H. Endotoxemia, disturbance of coagulation, and obstructive jaundice. Am J Surg. 1982 Sep;144(3):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(82)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. R. The identification of risk factors and their application to the management of obstructive jaundice. Aust N Z J Surg. 1980 Oct;50(5):476–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1980.tb04173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanaga S., Morita T., Harada T., Nakamura S., Niwa M., Takada K., Kimura T., Sakakibara S. Chromogenic substrates for horseshoe crab clotting enzyme. Its application for the assay of bacterial endotoxins. Haemostasis. 1978;7(2-3):183–188. doi: 10.1159/000214260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob A. I., Goldberg P. K., Bloom N., Degenshein G. A., Kozinn P. J. Endotoxin and bacteria in portal blood. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jun;72(6):1268–1270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S., Grosfeld J. L., Gross K., Plager D. A., Ross D., Rosenthal R. S., Hull M., Weber T. R. Impaired bacterial clearance and trapping in obstructive jaundice. Ann Surg. 1984 Jan;199(1):14–20. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198401000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmings A. N., van Deventer S. J., Obertop H., Rauws E. A., Gouma D. J. Inflammatory and immunologic effects of obstructive jaundice: pathogenesis and treatment. J Am Coll Surg. 1995 Dec;181(6):567–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocsár L. T., Bertók L., Várterész V. Effect of bile acids on the intestinal absorption of endotoxin in rats. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):220–223. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.220-223.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E. C., Chu K. M., Lo C. Y., Mok F. P., Fan S. T., Lo C. M., Wong J. Surgery for malignant obstructive jaundice: analysis of mortality. Surgery. 1992 Nov;112(5):891–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. The effect of obstructive jaundice on the migration of reticulo-endothelial cells and fibroblasts into early experimental granulomata. Br J Surg. 1972 Nov;59(11):875–877. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800591107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liehr H., Englisch G., Rasenack U. Lactulose--a drug with antiendotoxin effect. Hepatogastroenterology. 1980 Oct;27(5):356–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura K., Ishida T., Setoguchi M., Higuchi Y., Akizuki S., Yamamoto S. Upregulation of mouse CD14 expression in Kupffer cells by lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1994 May 1;179(5):1671–1676. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.5.1671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mythen M. G., Barclay G. R., Purdy G., Hamilton-Davies C., Mackie I. J., Webb A. R., Machin S. J. The role of endotoxin immunity, neutrophil degranulation and contact activation in the pathogenesis of post-operative organ dysfunction. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1993 Dec;4(6):999–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriishi T., Sata M., Toyonaga A., Sasaki E., Tanikawa K. Evaluation of intestinal permeability in patients with inflammatory bowel disease using lactulose and measuring antibodies to lipid A. Gut. 1995 Jun;36(6):891–896. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.6.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain J. A., Bailey M. E. Experimental and clinical study of lactulose in obstructive jaundice. Br J Surg. 1986 Oct;73(10):775–778. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800731003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt H. A., Cameron J. L., Postier R. G., Gadacz T. R. Factors affecting mortality in biliary tract surgery. Am J Surg. 1981 Jan;141(1):66–72. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(81)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughneen P. T., Kumar S. C., Pellis N. R., Rowlands B. J. Endotoxemia and cholestasis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1988 Sep;167(3):205–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott-Conner C. E., Grogan J. B. The pathophysiology of biliary obstruction and its effect on phagocytic and immune function. J Surg Res. 1994 Aug;57(2):316–336. doi: 10.1006/jsre.1994.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott B. B., Barclay G. R. Endotoxin-polymyxin complexes in an improved enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for IgG antibodies in blood donor sera to gram-negative endotoxin core glycolipids. Vox Sang. 1987;52(4):272–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1987.tb04893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikora S. S., Kapoor R., Pradeep R., Kapoor V. K., Saxena R., Kaushik S. P. Palliative surgical treatment of malignant obstructive jaundice. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1994 Oct;20(5):580–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarnes R. C. The inactivation of endotoxin after interaction with certain proteins of normal serum. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):644–662. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su C. H., P'eng F. K., Lui W. Y. Factors affecting morbidity and mortality in biliary tract surgery. World J Surg. 1992 May-Jun;16(3):536–540. doi: 10.1007/BF02104465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. N., Cohen J., Blenkharn J. I., McConnell J. S., Barr J., Blumgart L. H. A randomized clinical trial of oral ursodeoxycholic acid in obstructive jaundice. Br J Surg. 1986 Aug;73(8):634–636. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800730819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy T. F., Jr, Fox E. S. CD14-lipopolysaccharide receptor activity in hepatic macrophages after cholestatic liver injury. Surgery. 1995 Aug;118(2):371–377. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6060(05)80347-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trede M., Schwall G. The complications of pancreatectomy. Ann Surg. 1988 Jan;207(1):39–47. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198801000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane D. W., Redlich P., Weber T., Leapman S., Siddiqui A. R., Grosfeld J. L. Impaired immune function in obstructive jaundice. J Surg Res. 1988 Sep;45(3):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(88)90077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle E. N. Fibrinogen in liver disease. Arch Surg. 1974 Dec;109(6):741–746. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1974.01360060011003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle E. N., Wright N. A. Endotoxin and acute renal failure associated with obstructive jaundice. Br Med J. 1970 Nov 21;4(5733):472–474. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5733.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells C. L., Maddaus M. A., Simmons R. L. Proposed mechanisms for the translocation of intestinal bacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Sep-Oct;10(5):958–979. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.5.958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windsor J. A., Fearon K. C., Ross J. A., Barclay G. R., Smyth E., Poxton I., Garden O. J., Carter D. C. Role of serum endotoxin and antiendotoxin core antibody levels in predicting the development of multiple organ failure in acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1993 Aug;80(8):1042–1046. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800800840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D. Multiple receptors for endotoxin. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90082-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]