Abstract
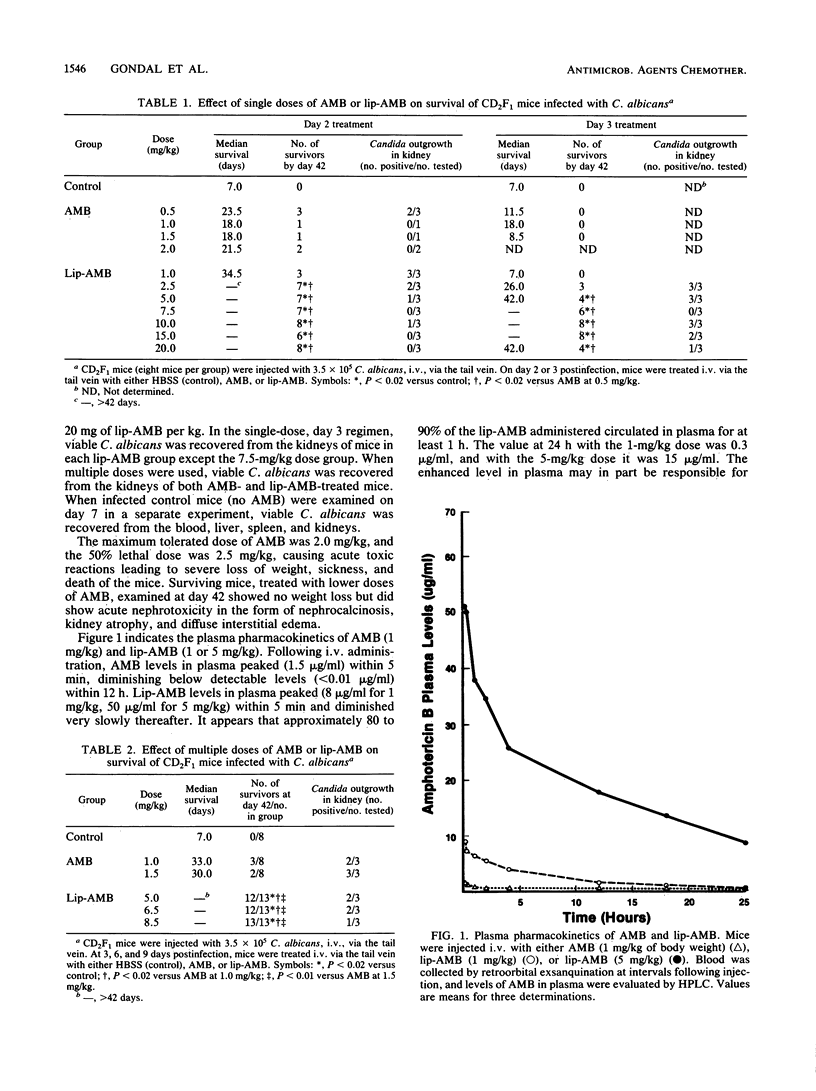
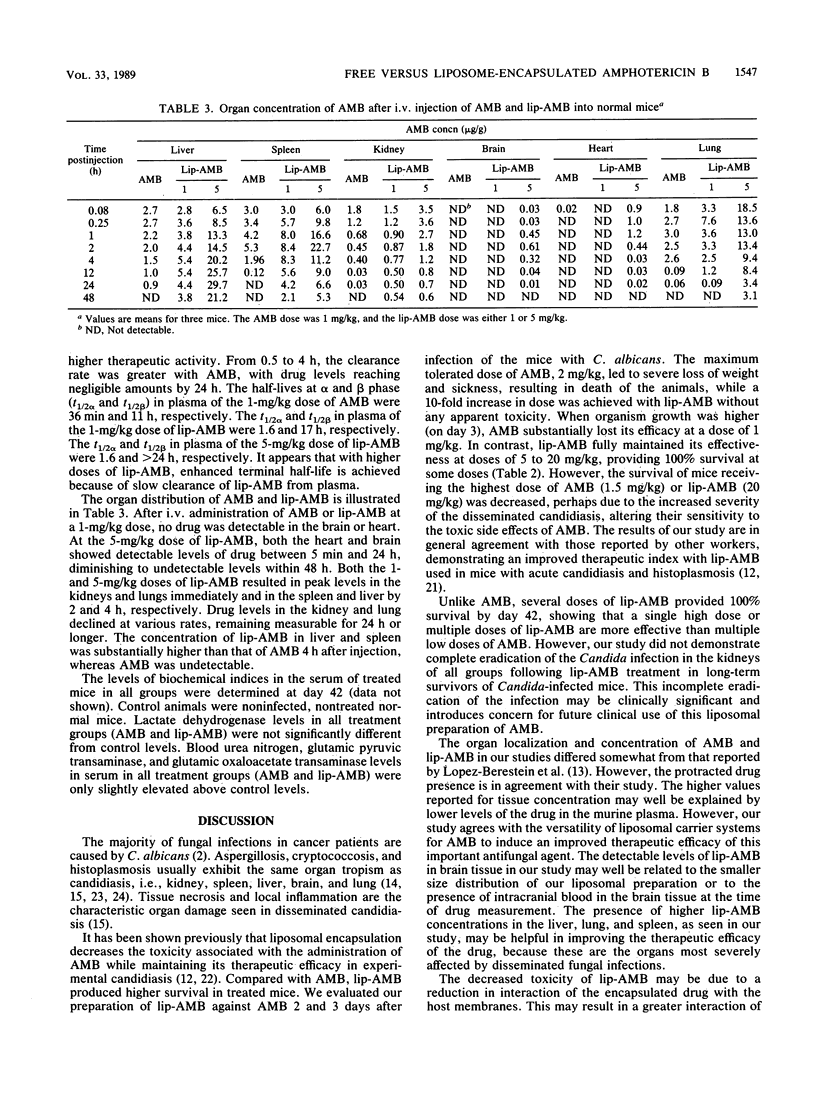
Various doses of amphotericin B encapsulated into unilamellar vesicles of 0.1 micron diameter (lip-AMB) (1.0 to 20.0 mg/kg of body weight) were compared with free amphotericin B (AMB) (0.5 to 2.0 mg/kg of body weight) in a murine model of disseminated candidiasis. CD2F1 mice injected intravenously with 3 x 10(5) Candida albicans cells were treated with either single- or multiple-dose regimens. Untreated infected mice had a median survival of 7 days, with all mice dead by 12 days. Single doses of AMB resulted in a median survival range from 18 to 23.5 days, with less than or equal to 38% survival by day 42. Single doses of lip-AMB resulted in 88 to 100% survival by day 42. The multiple-dose AMB regimen provided median survival of only 30 to 33 days, with less than or equal to 38% survival by day 42. The multiple-dose lip-AMB regimen resulted in greater than 90% survival by day 42. With single-dose regimens, lip-AMB levels in plasma were severalfold higher than AMB levels in plasma. By 10 h, at equivalent doses, lip-AMB levels in plasma were much higher, whereas AMB levels in plasma were not detectable. Compared with normal values, the blood urea nitrogen, serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase, serum glutamic oxaloacetate transaminase, and serum lactate dehydrogenase levels were not significantly altered by high doses of lip-AMB treatment. Viable C. albicans was recoverable from the kidneys of some of the lip-AMB-treated mice at day 42. Thus, encapsulation into unilamellar liposomes enhances the antifungal efficacy of amphotericin B while reducing the toxicity normally associated with administration of free amphotericin B.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreoli T. E. On the anatomy of amphotericin B-cholesterol pores in lipid bilayer membranes. Kidney Int. 1973 Nov;4(5):337–345. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. E., Jr, Lehrer R. I., Stiehm E. R., Fischer T. J., Young L. S. Severe candidal infections: clinical perspective, immune defense mechanisms, and current concepts of therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jul;89(1):91–106. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granich G. G., Kobayashi G. S., Krogstad D. J. Sensitive high-pressure liquid chromatographic assay for amphotericin B which incorporates an internal standard. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):584–588. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Craven P. C., Taylor R. L., Williams D. M., Magee W. E. Treatment of murine cryptococcosis with liposome-associated amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1982 May;145(5):748–752. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki J., Rodriguez V., Bodey G. P. Proceedings: Causes of death in cancer patients. Cancer. 1974 Feb;33(2):568–573. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197402)33:2<568::aid-cncr2820330236>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Hopfer R. L., Mehta R., Mehta K., Hersh E. M., Juliano R. L. Liposome-encapsulated amphotericin B for treatment of disseminated candidiasis in neutropenic mice. J Infect Dis. 1984 Aug;150(2):278–283. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.2.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Hopfer R. L., Mehta R., Mehta K., Hersh E. M., Juliano R. L. Prophylaxis of Candida albicans infection in neutropenic mice with liposome-encapsulated amphotericin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):366–367. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Mehta R., Hopfer R. L., Mills K., Kasi L., Mehta K., Fainstein V., Luna M., Hersh E. M., Juliano R. Treatment and prophylaxis of disseminated infection due to Candida albicans in mice with liposome-encapsulated amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):939–945. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Mehta R., Hopfer R., Mehta K., Hersh E. M., Juliano R. Effects of sterols on the therapeutic efficacy of liposomal amphotericin B in murine candidiasis. Cancer Drug Deliv. 1983;1(1):37–42. doi: 10.1089/cdd.1983.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Rosenblum M. G., Mehta R. Altered tissue distribution of amphotericin B by liposomal encapsulation: comparison of normal mice to mice infected with Candida albicans. Cancer Drug Deliv. 1984 Summer;1(3):199–205. doi: 10.1089/cdd.1984.1.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D., Young L. S., Armstrong D., Yu B. Aspergillosis complicating neoplastic disease. Am J Med. 1973 Jan;54(1):6–15. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Pazin G. J., Allen C. M. Disseminated candidiasis. Changes in incidence, underlying diseases, and pathology. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977 Jul;68(1):29–38. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/68.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Ehle I., Yoshikawa T. T., Edwards J. E., Schotz M. C., Guze L. B. Quantitation of amphotericin B with use of high-pressure liquid chromatography. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):414–422. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman A., White G., More N., Schein P. S. Pharmacological, toxicological, and therapeutic evaluation in mice of doxorubicin entrapped in cardiolipin liposomes. Cancer Res. 1985 Feb;45(2):796–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sculier J. P., Coune A., Meunier F., Brassinne C., Laduron C., Hollaert C., Collette N., Heymans C., Klastersky J. Pilot study of amphotericin B entrapped in sonicated liposomes in cancer patients with fungal infections. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1988 Mar;24(3):527–538. doi: 10.1016/s0277-5379(98)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer C., Kaplan M. H., Armstrong D. Bacteremia and fungemia complicating neoplastic disease. A study of 364 cases. Am J Med. 1977 May;62(5):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90876-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szoka F. C., Jr, Milholland D., Barza M. Effect of lipid composition and liposome size on toxicity and in vitro fungicidal activity of liposome-intercalated amphotericin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Mar;31(3):421–429. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.3.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. L., Williams D. M., Craven P. C., Graybill J. R., Drutz D. J., Magee W. E. Amphotericin B in liposomes: a novel therapy for histoplasmosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 May;125(5):610–611. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.5.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay C., Barza M., Fiore C., Szoka F. Efficacy of liposome-intercalated amphotericin B in the treatment of systemic candidiasis in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):170–173. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Krick J. A., Remington J. S. Pulmonary infection in the compromised host: part I. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Aug;114(2):359–394. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.2.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S. Nosocomial infections in the immunocompromised adult. Am J Med. 1981 Feb;70(2):398–404. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90779-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


