Abstract
Background—Both proton pump inhibitor drug treatment and Helicobacter pylori infection cause hypergastrinaemia in man. Aims—To determine whether eradicating H pylori is a means of reducing hypergastrinaemia during subsequent proton pump inhibitor treatment. Methods—Patients with H pylori were randomised to treatment with either anti-H pylori or symptomatic treatment. One month later, all received four weeks treatment with omeprazole 40 mg/day for one month followed by 20 mg/day for six months. Serum gastrin concentrations were measured before and following each treatment. Results—In the patients randomised to anti-H pylori treatment, eradication of the infection lowered median fasting gastrin by 48% and meal stimulated gastrin by 46%. When gastrin concentrations one month following anti-H pylori/symptomatic treatment were used as baseline, omeprazole treatment produced a similar percentage increase in serum gastrin in the H pylori infected and H pylori eradicated patients. Consequently, in the patients in which H pylori was not eradicated, median fasting gastrin concentration was 38 ng/l (range 26-86) at initial presentation and increased to 64 ng/l (range 29-271) after seven months omeprazole, representing a median increase of 68% (p<0.005). In contrast, in the patients randomised to H pylori eradication, median fasting gastrin at initial presentation was 54 ng/l (range 17-226) and was unchanged after seven months omeprazole at 38 ng/l (range 17-95). Conclusion—Eradicating H pylori is a means of reducing the rise in gastrin during subsequent long term omeprazole treatment. In view of the potential deleterious effects of hypergastrinaemia it may be appropriate to render patients H pylori negative prior to commencing long term proton pump inhibitor treatment.
Keywords: hypergastrinaemia; Helicobacter pylori; omeprazole
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (131.8 KB).
Figure 1 .
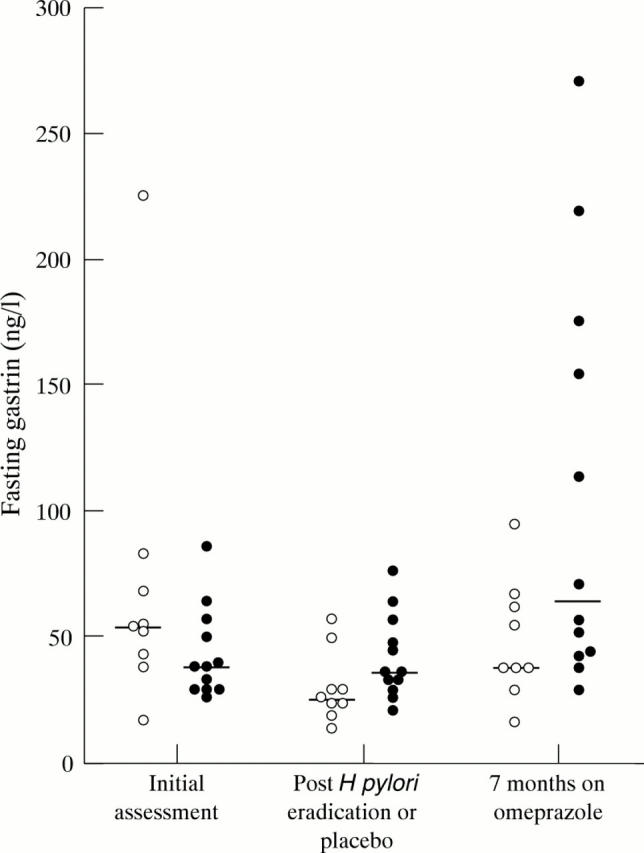
Fasting serum gastrin concentrations on initial assessment when all subjects were H pylori positive, following randomisation to H pylori eradication or no eradication, and following subsequent seven months' treatment with omeprazole. Subjects who had H pylori eradicated prior to omeprazole are represented by open circles.
Figure 2 .
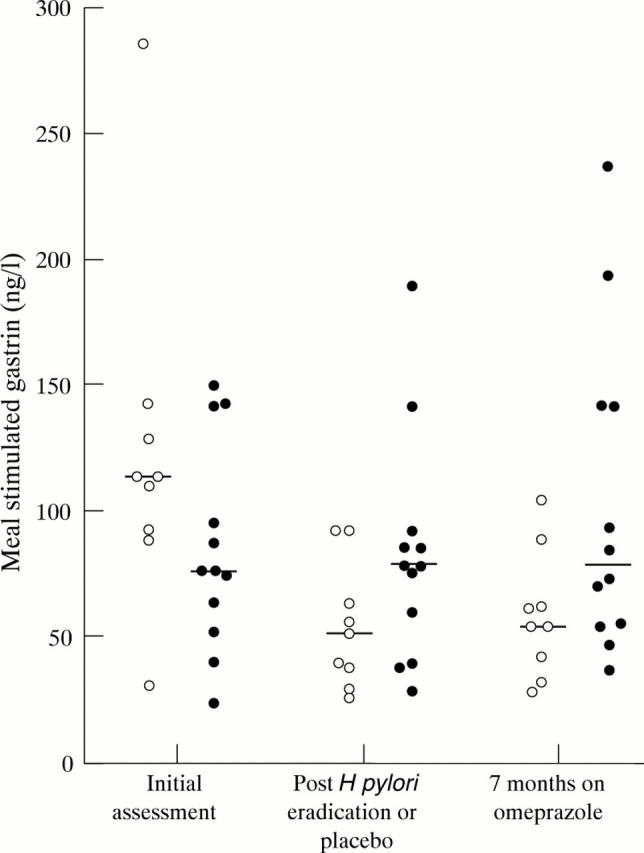
Meal stimulated gastrin concentrations on initial assessment when all subjects were H pylori positive, following randomisation to H pylori eradication or no eradication, and following subsequent seven months' treatment with omeprazole. Subjects who had H pylori eradicated prior to omeprazole are represented by open circles.
Figure 3 .
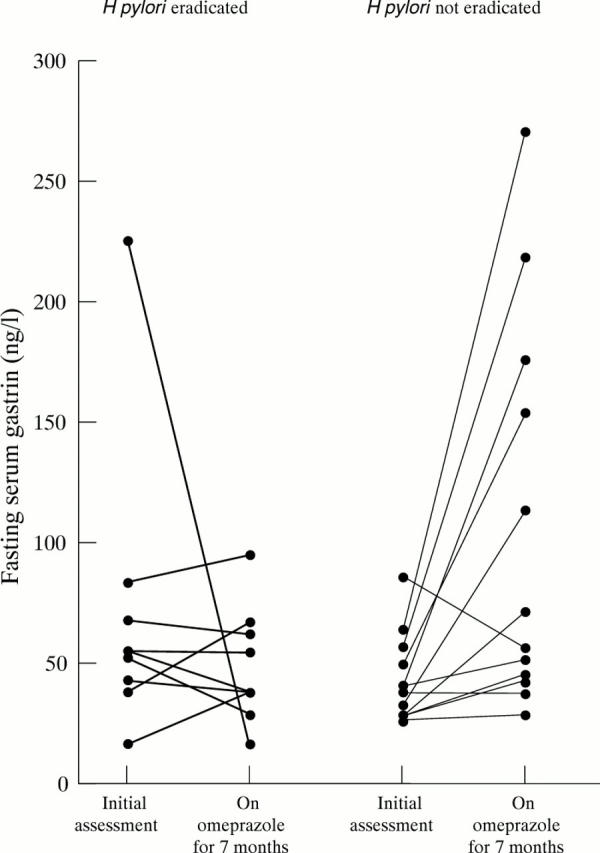
Fasting serum gastrin concentrations at initial assessment and after seven months omeprazole in subjects in whom H pylori was and was not eradicated prior to commencing proton pump inhibitor treatment.
Figure 4 .
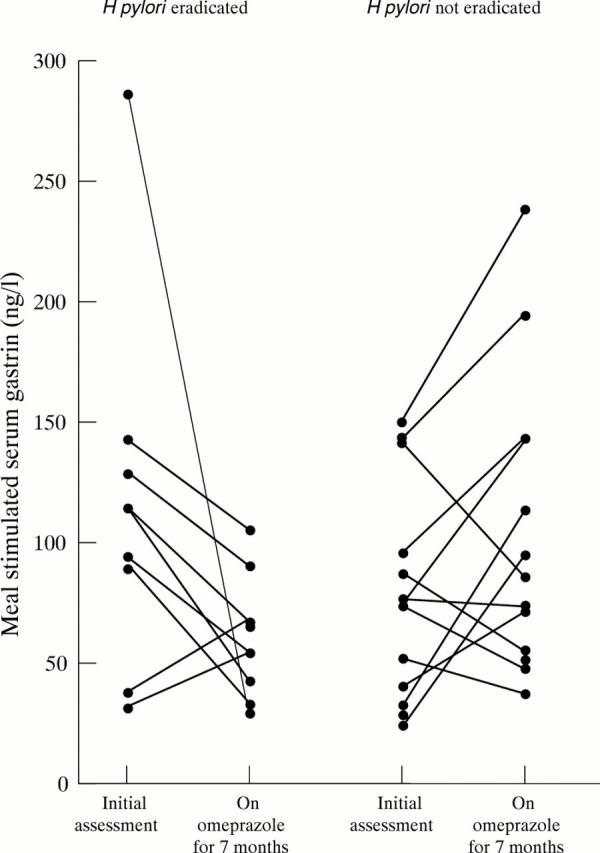
Meal stimulated gastrin concentrations at initial assessment and after seven months omeprazole in subjects in whom H pylori was and was not eradicated prior to commencing proton pump inhibitor treatment.
Figure 5 .
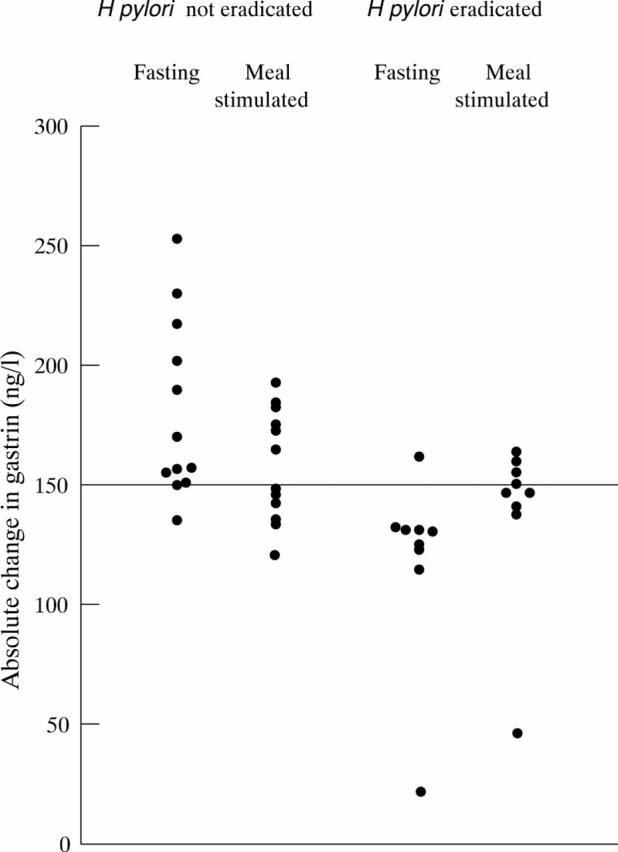
Absolute change in serum gastrin concentrations between initial assessment and end of seven months omeprazole in subjects in whom H pylori was or was not eradicated prior to proton pump inhibitor treatment.
Figure 6 .
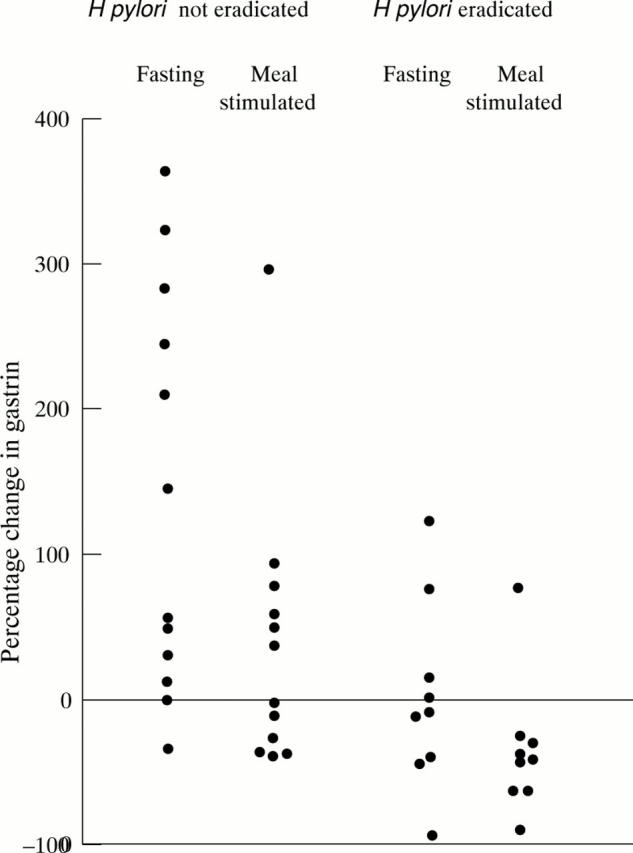
Percentage change in serum gastrin concentrations at initial assessment and after seven months omeprazole in subjects in whom H pylori was and was not eradicated prior to commencing proton pump inhibitor treatment.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee S., El-Omar E., Mowat A., Ardill J. E., Park R. H., Watson W., Beattie A. D., McColl K. E. Sucralfate suppresses Helicobacter pylori infection and reduces gastric acid secretion by 50% in patients with duodenal ulcer. Gastroenterology. 1996 Mar;110(3):717–724. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8608880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betton G. R., Dormer C. S., Wells T., Pert P., Price C. A., Buckley P. Gastric ECL-cell hyperplasia and carcinoids in rodents following chronic administration of H2-antagonists SK&F 93479 and oxmetidine and omeprazole. Toxicol Pathol. 1988;16(2):288–298. doi: 10.1177/019262338801600222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutzfeldt W., Lamberts R. Is hypergastrinaemia dangerous to man? Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1991;180:179–191. doi: 10.3109/00365529109093198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutzfeldt W., Stöckmann F., Conlon J. M., Fölsch U. R., Bonatz G., Wülfrath M. Effect of short- and long-term feeding of omeprazole on rat gastric endocrine cells. Digestion. 1986;35 (Suppl 1):84–97. doi: 10.1159/000199384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissele R., Patberg H., Koop H., Krack W., Lorenz W., McKnight A. T., Arnold R. Effect of gastrin receptor blockade on endocrine cells in rats during achlorhydria. Gastroenterology. 1992 Nov;103(5):1596–1601. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekman L., Hansson E., Havu N., Carlsson E., Lundberg C. Toxicological studies on omeprazole. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1985;108:53–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui W. M., Lam S. K., Ho J., Lai C. L., Lok A. S., Ng M. M., Lau W. Y., Branicki F. J. Effect of omeprazole on duodenal ulcer-associated antral gastritis and Helicobacter pylori. Dig Dis Sci. 1991 May;36(5):577–582. doi: 10.1007/BF01297022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka J., Martinez J., Townsend C. M., Jr, Thompson J. C. The effect of gastrin on growth of human stomach cancer cells. Ann Surg. 1992 May;215(5):528–534. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199205000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. B., Klinkenberg-Knol E. C., Meuwissen S. G., De Bruijne J. W., Festen H. P., Snel P., Lückers A. E., Biemond I., Lamers C. B. Effect of long-term treatment with omeprazole on serum gastrin and serum group A and C pepsinogens in patients with reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1990 Sep;99(3):621–628. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90946-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M., Lessells A. M., Eldridge J. Campylobacter like organisms on the gastric mucosa: culture, histological, and serological studies. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Sep;37(9):1002–1006. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.9.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko H., Nakada K., Mitsuma T., Uchida K., Furusawa A., Maeda Y., Morise K. Helicobacter pylori infection induces a decrease in immunoreactive-somatostatin concentrations of human stomach. Dig Dis Sci. 1992 Mar;37(3):409–416. doi: 10.1007/BF01307736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop H., Klein M., Arnold R. Serum gastrin levels during long-term omeprazole treatment. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1990 Apr;4(2):131–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1990.tb00457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop H., Klein M., Arnold R. Serum gastrin levels during long-term omeprazole treatment. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1990 Apr;4(2):131–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1990.tb00457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop H., Willemer S., Steinbach F., Eissele R., Tuch K., Arnold R. Influence of chronic drug-induced achlorhydria by substituted benzimidazoles on the endocrine stomach in rats. Gastroenterology. 1987 Feb;92(2):406–413. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90135-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers E. J., Lee A., Klinkenberg-Knol E. C., Meuwissen S. G. Review article: the development of atrophic gastritis--Helicobacter pylori and the effects of acid suppressive therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1995 Aug;9(4):331–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1995.tb00391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamberts R., Creutzfeldt W., Strüber H. G., Brunner G., Solcia E. Long-term omeprazole therapy in peptic ulcer disease: gastrin, endocrine cell growth, and gastritis. Gastroenterology. 1993 May;104(5):1356–1370. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90344-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson H., Carlsson E., Håkanson R., Mattsson H., Nilsson G., Seensalu R., Wallmark B., Sundler F. Time-course of development and reversal of gastric endocrine cell hyperplasia after inhibition of acid secretion. Studies with omeprazole and ranitidine in intact and antrectomized rats. Gastroenterology. 1988 Dec;95(6):1477–1486. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(88)80066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind T., Cederberg C., Idström J. P., Lönroth H., Olbe L., Lundell L. 24-hour intragastric acidity and plasma gastrin during long-term treatment with omeprazole or ranitidine in patients with reflux esophagitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1991 Jun;26(6):620–626. doi: 10.3109/00365529109043636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind T., Cederberg C., Idström J. P., Lönroth H., Olbe L., Lundell L. 24-hour intragastric acidity and plasma gastrin during long-term treatment with omeprazole or ranitidine in patients with reflux esophagitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1991 Jun;26(6):620–626. doi: 10.3109/00365529109043636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan R. P., Walker M. M., Misiewicz J. J., Gummett P. A., Karim Q. N., Baron J. H. Changes in the intragastric distribution of Helicobacter pylori during treatment with omeprazole. Gut. 1995 Jan;36(1):12–16. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucey M. R., Yamada T. Biochemistry and physiology of gastrointestinal somatostatin. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Mar;34(3 Suppl):5S–13S. doi: 10.1007/BF01536041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Warren J. R., Francis G. J., Langton S. R., Goodwin C. S., Blincow E. D. Rapid urease test in the management of Campylobacter pyloridis-associated gastritis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987 Mar;82(3):200–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McColl K. E., Fullarton G. M., Chittajalu R., el Nujumi A. M., MacDonald A. M., Dahill S. W., Hilditch T. E. Plasma gastrin, daytime intragastric pH, and nocturnal acid output before and at 1 and 7 months after eradication of Helicobacter pylori in duodenal ulcer subjects. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1991 Mar;26(3):339–346. doi: 10.3109/00365529109025052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McColl K. E., Nujumi A. M., Dorrian C. A., Macdonald A. M., Fullarton G. M., Harwood J. Helicobacter pylori and hypergastrinaemia during proton pump inhibitor therapy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1992;27(2):93–98. doi: 10.3109/00365529209165424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss S. F., Legon S., Bishop A. E., Polak J. M., Calam J. Effect of Helicobacter pylori on gastric somatostatin in duodenal ulcer disease. Lancet. 1992 Oct 17;340(8825):930–932. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92816-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulholland G., Ardill J. E., Fillmore D., Chittajallu R. S., Fullarton G. M., McColl K. E. Helicobacter pylori related hypergastrinaemia is the result of a selective increase in gastrin 17. Gut. 1993 Jun;34(6):757–761. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.6.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odum L., Petersen H. D., Andersen I. B., Hansen B. F., Rehfeld J. F. Gastrin and somatostatin in Helicobacter pylori infected antral mucosa. Gut. 1994 May;35(5):615–618. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.5.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penston J. G., Dixon J. S., Selway S. A., Wormsley K. G. Gastric histology and plasma gastrin response to a meal in patients with duodenal ulcer disease after five years treatment with ranitidine. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1990 Aug;4(4):381–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1990.tb00484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehfeld J. F. Gastrin and colorectal cancer: a never-ending dispute? Gastroenterology. 1995 Apr;108(4):1307–1310. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90234-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarnasky P. R., Kovacs T. O., Sytnik B., Walsh J. H. Asymptomatic H. pylori infection impairs pH inhibition of gastrin and acid secretion during second hour of peptone meal stimulation. Dig Dis Sci. 1993 Sep;38(9):1681–1687. doi: 10.1007/BF01303178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veenendaal R. A., Lichtendahl-Bernards A. T., Peña A. S., Endtz H. P., van Boven C. P., Lamers C. B. Effect of transport medium and transportation time on culture of Helicobacter pylori from gastric biopsy specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1993 Jun;46(6):561–563. doi: 10.1136/jcp.46.6.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldhuyzen van Zanten S. J., Pollak P. T., Best L. M., Bezanson G. S., Marrie T. Increasing prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection with age: continuous risk of infection in adults rather than cohort effect. J Infect Dis. 1994 Feb;169(2):434–437. doi: 10.1093/infdis/169.2.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdú E. F., Armstrong D., Fraser R., Viani F., Idström J. P., Cederberg C., Blum A. L. Effect of Helicobacter pylori status on intragastric pH during treatment with omeprazole. Gut. 1995 Apr;36(4):539–543. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdú E. F., Armstrong D., Idström J. P., Labenz J., Stolte M., Dorta G., Börsch G., Blum A. L. Effect of curing Helicobacter pylori infection on intragastric pH during treatment with omeprazole. Gut. 1995 Dec;37(6):743–748. doi: 10.1136/gut.37.6.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. A., Steele R. J. Gastrin antagonists in the treatment of gastric cancer. Anticancer Drugs. 1993 Dec;4(6):599–604. doi: 10.1097/00001813-199312000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil J., Bell G. D., Powell K., Morden A., Harrison G., Gant P. W., Jones P. H., Trowell J. E. Omeprazole and Helicobacter pylori: temporary suppression rather than true eradication. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1991 Jun;5(3):309–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1991.tb00032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


