Abstract
Background—Due to the expression of urease, Helicobacter pylori is able to establish itself in the human stomach under acidic conditions. A novel host defence mechanism was recently proposed, suggesting that the formation of salivary nitrite in symbiosis with facultative anaerobic bacteria in the oropharynx, is aimed at enhancing the antimicrobial activity of gastric juice. Aims—To investigate whether the addition of nitrite in physiological concentrations influences the resistance of H pylori to acid. Methods—H pylori cultured from fresh gastric biopsy specimens was exposed for 30 minutes to normal saline and to HCl/KCl buffer (0.2M) at pH 2 with urea (5 mM) added. The influence of potassium nitrite (50-1000 µmol/l) on bacterial survival was determined. Results—Addition of nitrite (1 mM) to acidic solutions (pH 2) resulted in complete kill of H pylori within 30 minutes exposure time whereas acid alone allowed the organism to survive (p<0.001). The antimicrobial effect of nitrite at pH 2 against H pylori was dose dependent and complete kill of organisms occurred at concentrations ⩾500 µmol/l. Conclusion—Acidified nitrite has antibacterial activity against H pylori. This should prompt further research into the effect of salivary nitrite on the survival of H pylori in the human stomach.
Keywords: nitrite; Helicobacter pylori; acidic conditions
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (103.6 KB).
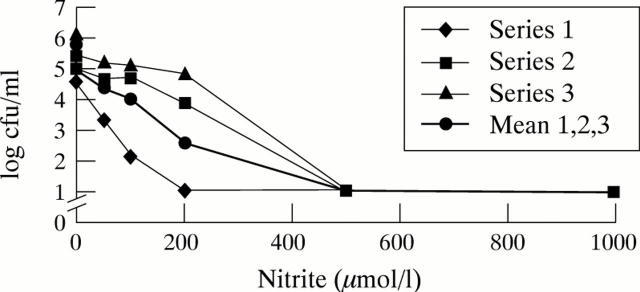
Figure 1 .
Antibacterial activity of nitrite against H pylori at pH 2 after 30 minutes' exposure. Experiments were carried out in triplicate (series 1, 2, and 3). No survival was detected at concentrations of nitrite ⩾500 µmol/l.
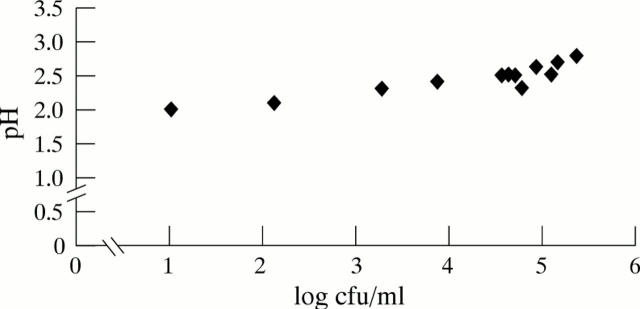
Figure 2 .
pH in universal containers at the end of the experiment versus number of surviving H pylori (starting pH=2 in all experiments).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benjamin N., O'Driscoll F., Dougall H., Duncan C., Smith L., Golden M., McKenzie H. Stomach NO synthesis. Nature. 1994 Apr 7;368(6471):502–502. doi: 10.1038/368502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunelli L., Crow J. P., Beckman J. S. The comparative toxicity of nitric oxide and peroxynitrite to Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1995 Jan 10;316(1):327–334. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1995.1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campylobacter-like organisms in the stomach of patients and healthy individuals. Lancet. 1984 Jun 16;1(8390):1348–1349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groote M. A., Fang F. C. NO inhibitions: antimicrobial properties of nitric oxide. Clin Infect Dis. 1995 Oct;21 (Suppl 2):S162–S165. doi: 10.1093/clinids/21.supplement_2.s162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groote M. A., Granger D., Xu Y., Campbell G., Prince R., Fang F. C. Genetic and redox determinants of nitric oxide cytotoxicity in a Salmonella typhimurium model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 3;92(14):6399–6403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.14.6399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougall H. T., Smith L., Duncan C., Benjamin N. The effect of amoxycillin on salivary nitrite concentrations: an important mechanism of adverse reactions? Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1995 Apr;39(4):460–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1995.tb04479.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C., Dougall H., Johnston P., Green S., Brogan R., Leifert C., Smith L., Golden M., Benjamin N. Chemical generation of nitric oxide in the mouth from the enterosalivary circulation of dietary nitrate. Nat Med. 1995 Jun;1(6):546–551. doi: 10.1038/nm0695-546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykhuizen R. S., Frazer R., Duncan C., Smith C. C., Golden M., Benjamin N., Leifert C. Antimicrobial effect of acidified nitrite on gut pathogens: importance of dietary nitrate in host defense. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996 Jun;40(6):1422–1425. doi: 10.1128/aac.40.6.1422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Broitman S. A., Zamcheck N. Gastric acid barrier to ingested microorganisms in man: studies in vivo and in vitro. Gut. 1972 Apr;13(4):251–256. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.4.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. Y., Lew G. M., Klein P. D., Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Saeed Z. A., Malaty H. M. Effect of treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection on the long-term recurrence of gastric or duodenal ulcer. A randomized, controlled study. Ann Intern Med. 1992 May 1;116(9):705–708. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-9-705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. L., Lehninger A. L. Sites of inhibition of mitochondrial electron transport in macrophage-injured neoplastic cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):527–535. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins R. J., Vial P. A., Ferreccio C., Ovalle J., Prado P., Sotomayor V., Russell R. G., Wasserman S. S., Morris J. G., Jr Seroprevalence of Helicobacter pylori in Chile: vegetables may serve as one route of transmission. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jul;168(1):222–226. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.1.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. O., Weitzberg E., Lundberg J. M., Alving K. Intragastric nitric oxide production in humans: measurements in expelled air. Gut. 1994 Nov;35(11):1543–1546. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.11.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Barrett L. J., Prakash C., McCallum R. W., Guerrant R. L. Urea protects Helicobacter (Campylobacter) pylori from the bactericidal effect of acid. Gastroenterology. 1990 Sep;99(3):697–702. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90957-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. M., Smith L. M., Drummond R. S., Duncan C. W., Golden M., Benjamin N. Chemical synthesis of nitric oxide in the stomach from dietary nitrate in humans. Gut. 1997 Feb;40(2):211–214. doi: 10.1136/gut.40.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mégraud F., Brassens-Rabbé M. P., Denis F., Belbouri A., Hoa D. Q. Seroepidemiology of Campylobacter pylori infection in various populations. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1870–1873. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1870-1873.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaki T., Nakayama M., Kato R. Inhibition by nitric oxide and nitric oxide-producing vasodilators of DNA synthesis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Dec 15;189(6):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(90)90031-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3051–3064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J. Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1993 Mar;22(1):89–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snepar R., Poporad G. A., Romano J. M., Kobasa W. D., Kaye D. Effect of cimetidine and antacid on gastric microbial flora. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):518–524. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.518-524.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdu E., Viani F., Armstrong D., Fraser R., Siegrist H. H., Pignatelli B., Idström J. P., Cederberg C., Blum A. L., Fried M. Effect of omeprazole on intragastric bacterial counts, nitrates, nitrites, and N-nitroso compounds. Gut. 1994 Apr;35(4):455–460. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.4.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wink D. A., Darbyshire J. F., Nims R. W., Saavedra J. E., Ford P. C. Reactions of the bioregulatory agent nitric oxide in oxygenated aqueous media: determination of the kinetics for oxidation and nitrosation by intermediates generated in the NO/O2 reaction. Chem Res Toxicol. 1993 Jan-Feb;6(1):23–27. doi: 10.1021/tx00031a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L., Gunn C., Beckman J. S. Bactericidal activity of peroxynitrite. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Nov 1;298(2):452–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90434-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]