Abstract
Background—Although fatty foods are commonly considered detrimental in patients with reflux disease, no objective data exist that substantiate this belief. Aims—To investigate the effect of fat on gastro-oesophageal reflux and lower oesophageal sphincter (LOS) motor activity. Subjects—Thirteen healthy subjects and 14 patients with reflux disease. Methods—Oesophageal pH, LOS, and oesophageal pressures were recorded for 180 minutes after a high fat (52% fat) and a balanced (24% fat) meal (both 3.18 MJ) on two different occasions. Eight controls and seven patients were studied in the recumbent position and the others in the sitting position. Results—The percentage of time at pH less than 4 and the rate of reflux episodes were higher (p<0.01) in the patients than in the healthy subjects (mean 14.1% versus 1.7% and 4.4/h versus 0.8/h respectively), as was the percentage of transient LOS relaxations associated with reflux (62% versus 32%, p<0.01). The high fat meal did not increase the rate of reflux episodes nor exposure to oesophageal acid in either group regardless of body posture.The rate of transient LOS relaxations, their association with reflux, and basal LOS pressure were also unaffected. Conclusions—Increasing fat intake does not affect gastro-oesophageal reflux or oesophagogastric competence for at least three hours after a meal.
Keywords: oesophagus; oesophagogastric junction; gastro-oesophageal reflux; fat
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (79.6 KB).
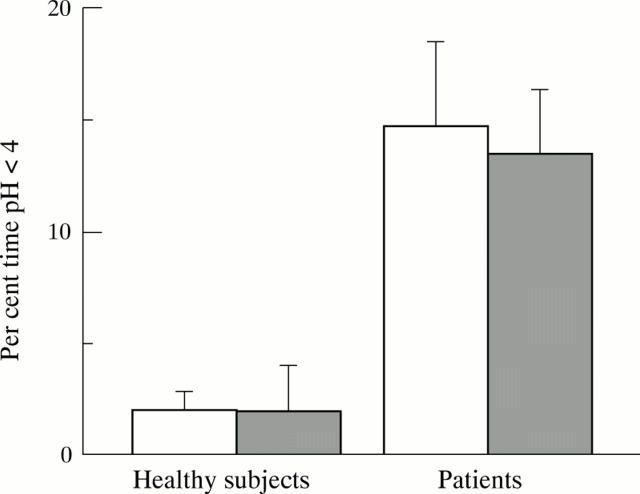
Figure 1 .
Oesophageal acid exposure after the balanced (open column) and the high fat meals (shaded column). Data are expressed as mean (SEM).
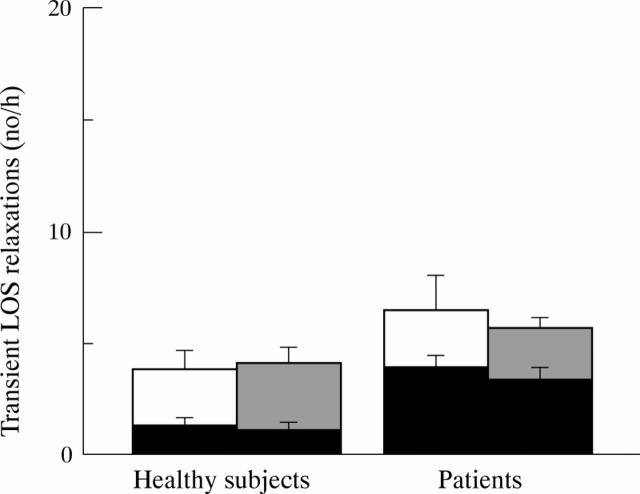
Figure 2 .
Rate of transient LOS relaxations and proportion associated with reflux, shown in black, after the balanced (open column) and the high fat meals (shaded column). Data are expressed as mean (SEM).
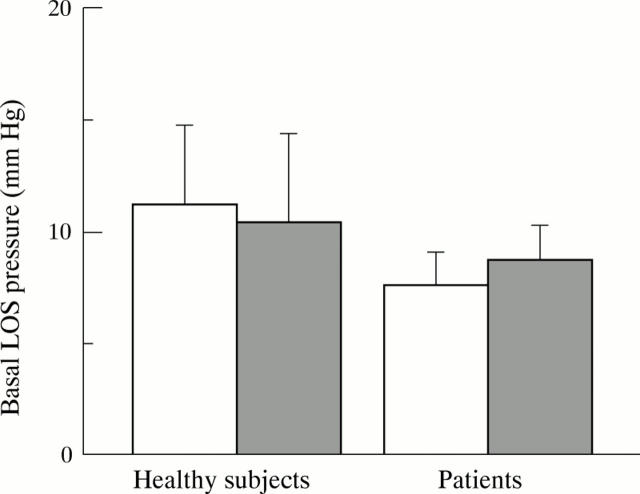
Figure 3 .
Basal LOS pressure after the balanced (open column) and the high fat meals (shaded column). Data are expressed as mean (SEM).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbera R., Feinle C., Read N. W. Abnormal sensitivity to duodenal lipid infusion in patients with functional dyspepsia. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1995 Nov;7(11):1051–1057. doi: 10.1097/00042737-199511000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker D. J., Sinclair J., Castell D. O., Wu W. C. A comparison of high and low fat meals on postprandial esophageal acid exposure. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989 Jul;84(7):782–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzi S. J., Martin C. J., Cox M. R., Dent J. Response of canine lower esophageal sphincter to gastric distension. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 1):G380–G385. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.3.G380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway R. H., Lyrenas E., Ireland A., Dent J. Effect of intraduodenal fat on lower oesophageal sphincter function and gastro-oesophageal reflux. Gut. 1997 Apr;40(4):449–453. doi: 10.1136/gut.40.4.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway R. H., Penagini R., Ireland A. C. Criteria for objective definition of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation. Am J Physiol. 1995 Jan;268(1 Pt 1):G128–G133. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1995.268.1.G128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. N., Knox M. T. A relation between the chain length of fatty acids and the slowing of gastric emptying. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(2):327–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. N., Pathak J. D. The osmotic effects of some simple molecules and ions on gastric emptying. J Physiol. 1960 Dec;154(2):254–269. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. N., Stubbs D. F. The volume and energy content of meals as determinants of gastric emptying. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(1):209–225. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal R. K., Holloway R. H., Penagini R., Blackshaw L. A., Dent J. Transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation. Gastroenterology. 1995 Aug;109(2):601–610. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebel O. T., Castell D. O. Lower esophageal sphincter pressure changes after food ingestion. Gastroenterology. 1972 Nov;63(5):778–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebel O. T., Fornes M. F., Castell D. O. Symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux: incidence and precipitating factors. Am J Dig Dis. 1976 Nov;21(11):953–956. doi: 10.1007/BF01071906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penagini R., Schoeman M. N., Dent J., Tippett M. D., Holloway R. H. Motor events underlying gastro-oesophageal reflux in ambulant patients with reflux oesophagitis. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 1996 Jun;8(2):131–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.1996.tb00253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeman M. N., Tippett M. D., Akkermans L. M., Dent J., Holloway R. H. Mechanisms of gastroesophageal reflux in ambulant healthy human subjects. Gastroenterology. 1995 Jan;108(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]