Abstract
Background—The clinical significance of a single assessment of circulating hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA and its relation to the level of intrahepatic HCV RNA remains unclear. Aims—To investigate the relation between intrahepatic HCV levels and clinicopathological characteristics of chronic HCV infection. Patients—Ninety eight consecutive patients with chronic HCV infection were studied; none had received α interferon therapy. Of these, 12 patients were repeatedly negative for HCV RNA in serum by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Methods—After diagnostic laparoscopy and liver biopsy, semiquantitative analysis of intrahepatic HCV RNA levels was carried out by limiting dilution of HCV cDNA. HCV genotypes were assessed in 96 patients by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of HCV cDNA. Results—Ten out of 12 patients who were RT-PCR negative for HCV RNA in serum were RT-PCR positive in liver; however, this group had a significantly lower intrahepatic HCV level and serum aminotransferase level than the remaining 86 patients. Histological severity (cirrhosis: n=10); histological activity index; HCV genotype (genotype 1: n=41; genotype 2: n=12; genotype 3: n=36; genotype 4: n=7); mode of infection (intravenous drug abuse: n=58; post-transfusion: n=10; haemophiliac: n=4; sporadic: n=26) and alcohol abuse did not affect the intrahepatic virus level. There was no correlation between patient age, duration of infection, and intrahepatic HCV level. Conclusions—Intrahepatic virus levels were not determined by host factors (age of patient, mode or duration of infection) or by virus factors (HCV genotype). Repeatedly negative RT-PCR for HCV RNA in serum does not indicate absence of HCV from the liver.
Keywords: intrahepatic hepatitis C virus; chronic hepatitis C virus infection
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (137.3 KB).
Figure 1 .
Intrahepatic virus levels in patients repeatedly HCV RNA positive (n=86) or negative (n=12) by RT-PCR.
Figure 2 .
Intrahepatic virus levels by HCV genotype. 1, genotype 1a (n=40); 2, genotype 1b (n=1); 3, genotype 2a (n=2); 4, genotype 2b (n=10); 5, genotype 3 (n=36); 6, genotype 4 (n=7).
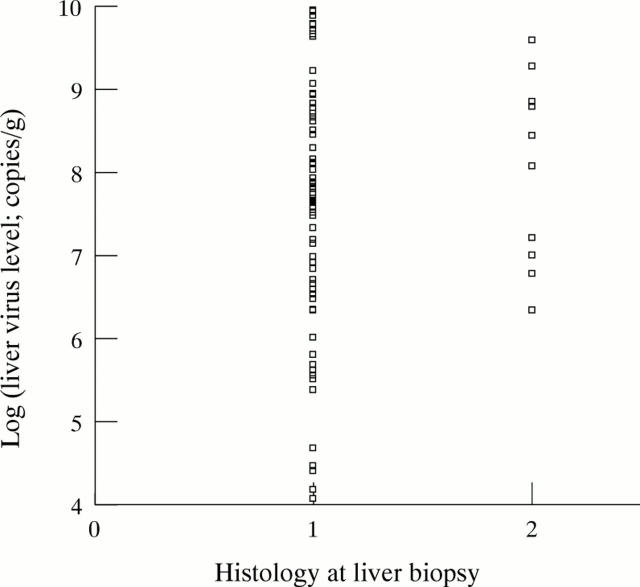
Figure 3 .
Intrahepatic virus levels by disease state. 1, Chronic hepatitis; 2, cirrhosis.
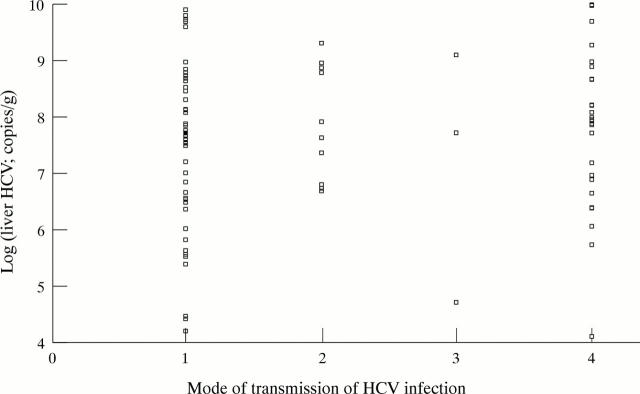
Figure 4 .
Intrahepatic virus levels according to mode of transmission of HCV. 1, IVDA (n=58); 2, post-transfusion (n=10); 3, haemophiliac (n=4); 4, sporadic (n=26).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti A., Morsica G., Chemello L., Cavalletto D., Noventa F., Pontisso P., Ruol A. Hepatitis C viraemia and liver disease in symptom-free individuals with anti-HCV. Lancet. 1992 Sep 19;340(8821):697–698. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92234-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberti A., Morsica G., Chemello L., Cavalletto D., Noventa F., Pontisso P., Ruol A. Hepatitis C viraemia and liver disease in symptom-free individuals with anti-HCV. Lancet. 1992 Sep 19;340(8821):697–698. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92234-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter H. J., Purcell R. H., Shih J. W., Melpolder J. C., Houghton M., Choo Q. L., Kuo G. Detection of antibody to hepatitis C virus in prospectively followed transfusion recipients with acute and chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 30;321(22):1494–1500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911303212202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blight K., Rowland R., Hall P. D., Lesniewski R. R., Trowbridge R., LaBrooy J. T., Gowans E. J. Immunohistochemical detection of the NS4 antigen of hepatitis C virus and its relation to histopathology. Am J Pathol. 1993 Dec;143(6):1568–1573. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth J. C., Brown J. L., Thomas H. C. The management of chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Gut. 1995 Oct;37(4):449–454. doi: 10.1136/gut.37.4.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. W., McOmish F., Holmes E. C., Dow B., Peutherer J. F., Follett E., Yap P. L., Simmonds P. Analysis of a new hepatitis C virus type and its phylogenetic relationship to existing variants. J Gen Virol. 1992 May;73(Pt 5):1131–1141. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-5-1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Weiner A. J., Overby L. R., Bradley D. W., Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):359–362. doi: 10.1126/science.2523562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courouce A. M., Bouchardeau F., Girault A., Le Marrec N. Significance of NS3 and NS5 antigens in screening for HCV antibody. Lancet. 1994 Apr 2;343(8901):853–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Bisceglie A. M., Hoofnagle J. H., Krawczynski K. Changes in hepatitis C virus antigen in liver with antiviral therapy. Gastroenterology. 1993 Sep;105(3):858–862. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90905-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban J. I., Esteban R., Viladomiu L., López-Talavera J. C., González A., Hernández J. M., Roget M., Vargas V., Genescà J., Buti M. Hepatitis C virus antibodies among risk groups in Spain. Lancet. 1989 Aug 5;2(8658):294–297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90485-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong T. L., Shindo M., Feinstone S. M., Hoofnagle J. H., Di Bisceglie A. M. Detection of replicative intermediates of hepatitis C viral RNA in liver and serum of patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):1058–1060. doi: 10.1172/JCI115368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunji T., Kato N., Hijikata M., Hayashi K., Saitoh S., Shimotohno K. Specific detection of positive and negative stranded hepatitis C viral RNA using chemical RNA modification. Arch Virol. 1994;134(3-4):293–302. doi: 10.1007/BF01310568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunji T., Kato N., Mori S., Ootsuyama Y., Hijikata M., Imawari M., Shimotohno K. Correlation between the serum level of hepatitis C virus RNA and disease activities in acute and chronic hepatitis C. Int J Cancer. 1992 Nov 11;52(5):726–730. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910520510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haruna Y., Hayashi N., Hiramatsu N., Takehara T., Hagiwara H., Sasaki Y., Kasahara A., Fusamoto H., Kamada T. Detection of hepatitis C virus RNA in liver tissues by an in situ hybridization technique. J Hepatol. 1993 Apr;18(1):96–100. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins A., Davidson F., Simmonds P. Comparison of plasma virus loads among individuals infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotypes 1, 2, and 3 by quantiplex HCV RNA assay versions 1 and 2, Roche Monitor assay, and an in-house limiting dilution method. J Clin Microbiol. 1997 Jan;35(1):187–192. doi: 10.1128/jcm.35.1.187-192.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi J., Kishihara Y., Yoshimura E., Tani Y., Yamaji K., Ikematsu H., Ishiko H., Kashiwagi S. Relationship of genotype to level of hepatitis C viraemia determined by competitive polymerase chain reaction. J Infect. 1995 May;30(3):235–239. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(95)90785-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiramatsu N., Hayashi N., Haruna Y., Kasahara A., Fusamoto H., Mori C., Fuke I., Okayama H., Kamada T. Immunohistochemical detection of hepatitis C virus-infected hepatocytes in chronic liver disease with monoclonal antibodies to core, envelope and NS3 regions of the hepatitis C virus genome. Hepatology. 1992 Aug;16(2):306–311. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu K. Q., Yu C. H., Vierling J. M. Direct detection of circulating hepatitis C virus RNA using probes from the 5' untranslated region. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;89(6):2040–2045. doi: 10.1172/JCI115815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving W. L., Neal K. R., Underwood J. C., Simmonds P. N., James V. Chronic hepatitis in United Kingdom blood donors infected with hepatitis C virus. Trent Regional Hepatitis C Virus Study Group. BMJ. 1994 Mar 12;308(6930):695–696. doi: 10.1136/bmj.308.6930.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis L. M., Watson H. G., McOmish F., Peutherer J. F., Ludlam C. A., Simmonds P. Frequent reinfection and reactivation of hepatitis C virus genotypes in multitransfused hemophiliacs. J Infect Dis. 1994 Oct;170(4):1018–1022. doi: 10.1093/infdis/170.4.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko S., Murakami S., Unoura M., Kobayashi K. Quantitation of hepatitis C virus RNA by competitive polymerase chain reaction. J Med Virol. 1992 Aug;37(4):278–282. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890370408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Hijikata M., Ootsuyama Y., Nakagawa M., Ohkoshi S., Sugimura T., Shimotohno K. Molecular cloning of the human hepatitis C virus genome from Japanese patients with non-A, non-B hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9524–9528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Yokosuka O., Hosoda K., Ito Y., Ohto M., Omata M. Quantification of hepatitis C virus by competitive reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction: increase of the virus in advanced liver disease. Hepatology. 1993 Jul;18(1):16–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knodell R. G., Ishak K. G., Black W. C., Chen T. S., Craig R., Kaplowitz N., Kiernan T. W., Wollman J. Formulation and application of a numerical scoring system for assessing histological activity in asymptomatic chronic active hepatitis. Hepatology. 1981 Sep-Oct;1(5):431–435. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Watanabe S., Konishi M., Yokoi M., Kakehashi R., Kaito M., Kondo M., Hayashi Y., Jomori T., Suzuki S. Quantitation and typing of serum hepatitis C virus RNA in patients with chronic hepatitis C treated with interferon-beta. Hepatology. 1993 Dec;18(6):1319–1325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo G., Choo Q. L., Alter H. J., Gitnick G. L., Redeker A. G., Purcell R. H., Miyamura T., Dienstag J. L., Alter M. J., Stevens C. E. An assay for circulating antibodies to a major etiologic virus of human non-A, non-B hepatitis. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):362–364. doi: 10.1126/science.2496467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Sureau C., Jacob J. R., White R., Fuerst T. R. Demonstration of in vitro infection of chimpanzee hepatocytes with hepatitis C virus using strand-specific RT/PCR. Virology. 1994 Aug 1;202(2):606–614. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau J. Y., Davis G. L., Kniffen J., Qian K. P., Urdea M. S., Chan C. S., Mizokami M., Neuwald P. D., Wilber J. C. Significance of serum hepatitis C virus RNA levels in chronic hepatitis C. Lancet. 1993 Jun 12;341(8859):1501–1504. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90635-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau J. Y., Mizokami M., Kolberg J. A., Davis G. L., Prescott L. E., Ohno T., Perrillo R. P., Lindsay K. L., Gish R. G., Qian K. P. Application of six hepatitis C virus genotyping systems to sera from chronic hepatitis C patients in the United States. J Infect Dis. 1995 Feb;171(2):281–289. doi: 10.1093/infdis/171.2.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuinness P. H., Bishop G. A., Painter D. M., Chan R., McCaughan G. W. Intrahepatic hepatitis C RNA levels do not correlate with degree of liver injury in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 1996 Apr;23(4):676–687. doi: 10.1002/hep.510230404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McOmish F., Chan S. W., Dow B. C., Gillon J., Frame W. D., Crawford R. J., Yap P. L., Follett E. A., Simmonds P. Detection of three types of hepatitis C virus in blood donors: investigation of type-specific differences in serologic reactivity and rate of alanine aminotransferase abnormalities. Transfusion. 1993 Jan;33(1):7–13. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1993.33193142314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McOmish F., Yap P. L., Dow B. C., Follett E. A., Seed C., Keller A. J., Cobain T. J., Krusius T., Kolho E., Naukkarinen R. Geographical distribution of hepatitis C virus genotypes in blood donors: an international collaborative survey. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Apr;32(4):884–892. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.4.884-892.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon A., Shepherd R. W., Faoagali J. L., Balderson G., Ong T. H., Patrick M., Cleghorn G. J., Lynch S., Strong R. Cytomegalovirus infection after liver transplantation in children. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1993 Nov-Dec;8(6):540–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1993.tb01649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa H., Shimomura H., Hasui T., Tsuji H., Tsuji T. Quantitative detection of hepatitis C virus genome in liver tissue and circulation by competitive reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Dig Dis Sci. 1994 Feb;39(2):225–233. doi: 10.1007/BF02090190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao T., Enomoto N., Takada N., Takada A., Date T. Typing of hepatitis C virus genomes by restriction fragment length polymorphism. J Gen Virol. 1991 Sep;72(Pt 9):2105–2112. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-9-2105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nouri Aria K. T., Sallie R., Sangar D., Alexander G. J., Smith H., Byrne J., Portmann B., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Detection of genomic and intermediate replicative strands of hepatitis C virus in liver tissue by in situ hybridization. J Clin Invest. 1993 May;91(5):2226–2234. doi: 10.1172/JCI116449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto N., Enomoto N., Kurosaki M., Marumo F., Sato C. Detection and quantification of hepatitis C virus RNA replication in the liver. J Hepatol. 1994 May;20(5):593–597. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80345-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds P., Balfe P., Peutherer J. F., Ludlam C. A., Bishop J. O., Brown A. J. Human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals contain provirus in small numbers of peripheral mononuclear cells and at low copy numbers. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):864–872. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.864-872.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds P., Smith D. B., McOmish F., Yap P. L., Kolberg J., Urdea M. S., Holmes E. C. Identification of genotypes of hepatitis C virus by sequence comparisons in the core, E1 and NS-5 regions. J Gen Virol. 1994 May;75(Pt 5):1053–1061. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-75-5-1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds P., Zhang L. Q., Watson H. G., Rebus S., Ferguson E. D., Balfe P., Leadbetter G. H., Yap P. L., Peutherer J. F., Ludlam C. A. Hepatitis C quantification and sequencing in blood products, haemophiliacs, and drug users. Lancet. 1990 Dec 15;336(8729):1469–1472. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93179-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobler L. H., Busch M. P., Wilber J., Dinello R., Quan S., Polito A., Kochesky R., Bahl C., Nelles M., Lee S. R. Evaluation of indeterminate c22-3 reactivity in volunteer blood donors. Transfusion. 1994 Feb;34(2):130–134. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1994.34294143940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Kakumu S., Yoshioka K., Higashi Y., Tanaka K., Ishikawa T., Takayanagi M. Hepatitis C virus genotypes are not responsible for development of serious liver disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1994 Feb;39(2):234–239. doi: 10.1007/BF02090191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuki N., Hayashi N., Kamada T. HCV viraemia and liver injury in symptom-free blood donors. Lancet. 1993 Aug 14;342(8868):444–444. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92863-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]