Abstract
Background—The nature of the breakdown products produced in enterocytes during epithelial transport of intact proteins may be critical in determining the functional consequences of protein absorption. Aim—(a) To measure the transepithelial transport of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and to identify the nature of HRP breakdown products released on the basal side of enterocytes and (b) to assess the role of interferon γ (IFNγ) on HRP transport and processing. Methods—HT29-19A intestinal cells were used to assess transepithelial transport of HRP in Ussing chambers, and the nature of breakdown products in the basal compartment was analysed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Results—(1) In control conditions, [3H]HRP equivalent fluxes (3135 (219) ng/h per cm2; mean (SEM)) comprised 50% amino acids, 40% peptides, and 10% intact HRP. Steric exclusion HPLC of the breakdown products indicated a wide range of molecular masses including a major peptide of about 1150 Da. Lysosomal aspartyl and thiol proteases were expressed but no HLA-DR surface expression was noted. (2) At 48 to 72 hours after IFNγ stimulation, [3H]HRP equivalent fluxes increased significantly (7392 (1433) ng/h per cm2) without modification of the relative proportions of amino acids, peptides, and intact HRP, and without modification of the distribution of breakdown products in HPLC. Lysosomal protease activities were not modified by IFNγ but HLA-DR expression was increased. Conclusion—Intestinal cells are able to process HRP into peptides potentially capable of stimulating the immune system. IFNγ stimulates the transport and processing of HRP thus increasing the antigenic load in the intestinal mucosa.
Keywords: enterocyte; transcytosis; macromolecular degradation; HPLC; mucosal immunity
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (183.1 KB).
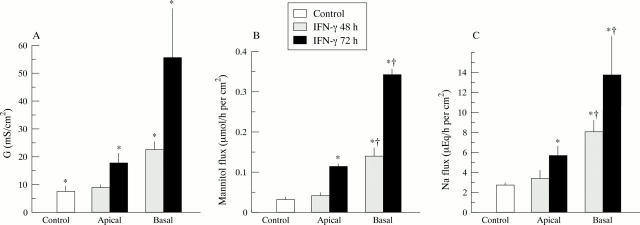
Figure 1 .
Effect on paracellular transport of placing interferon γ (IFNγ) on the basal or apical side of HT29-19A intestinal cell monolayers for 48 or 72 hours. Paracellular permeability was measured as (A) ionic conductance (G), and (B) mannitol and (C) Na fluxes. *Significantly different from untreated cells (p⩽0.02); †significantly different from time matched cells after IFNγ treatment on the apical side (p⩽0.03). n = 8 to 20 filter grown intestinal monolayers.
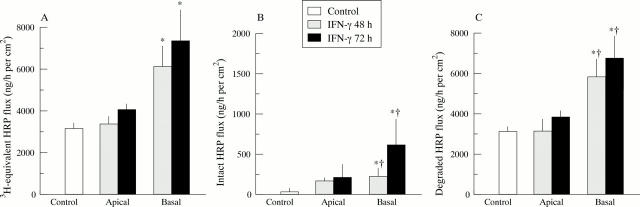
Figure 2 .
Effect of placing interferon γ (IFNγ) on the basal or apical side of HT29-19A intestinal cell monolayers for 48 or 72 hours, on the transepithelial transport of (A) 3H labelled horseradish peroxidase ([3H]HRP) in (B) intact or (C) degraded form. *Significantly different from untreated cells (p⩽0.008); †significantly different from time matched apical conditions (p⩽0.01). n = 8 to 17 filter grown monolayers.
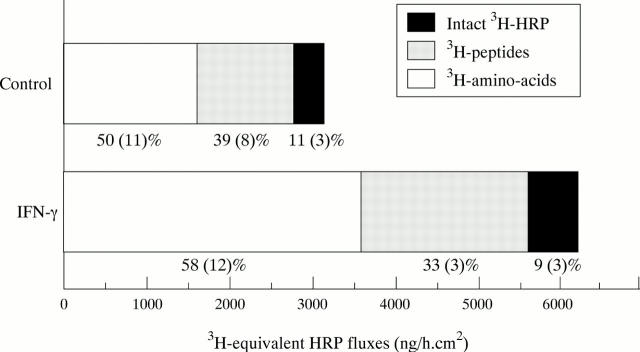
Figure 3 .
Processing of 3H labelled horseradish peroxidase ([3H]HRP) during transport. Incubation for 48 hours with interferon γ (IFNγ) increased 3H equivalent HRP transport (total HRP) without significantly modifying the percentages of amino acids, peptides, and intact HRP. n = 5 to 6 separate experiments.
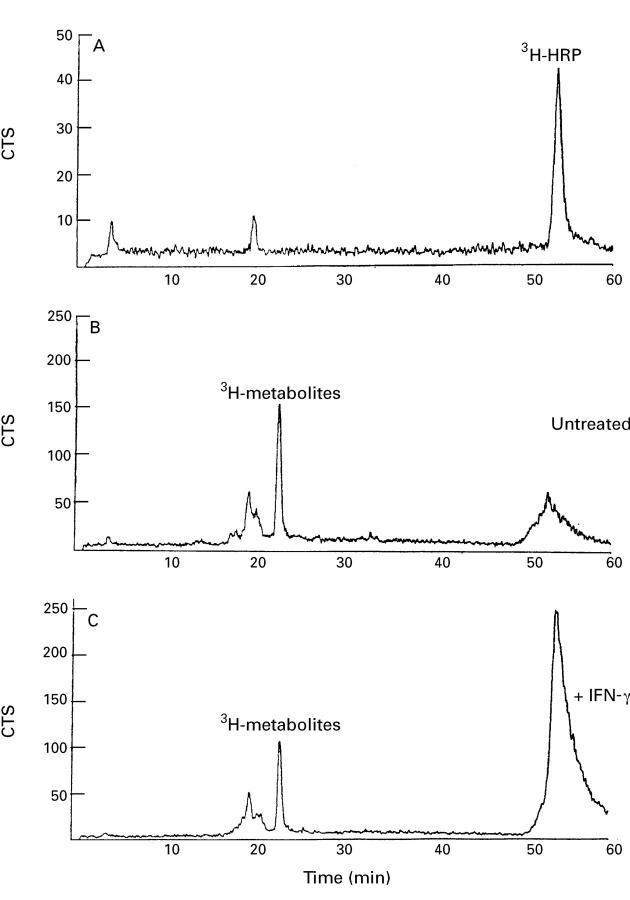
Figure 4 .
3H labelled metabolites formed after transepithelial transport of 3H labelled horseradish peroxidase ([ 3H]HRP) across intestinal HT29-19A cells, as shown by reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC). [3H]HRP before transport (A), and 3H labelled metabolites and [3H]HRP after transport in untreated cells (B) and in cells treated with interferon γ (IFNγ) for 48 hours (C). This elution profile is representative of two separate experiments.
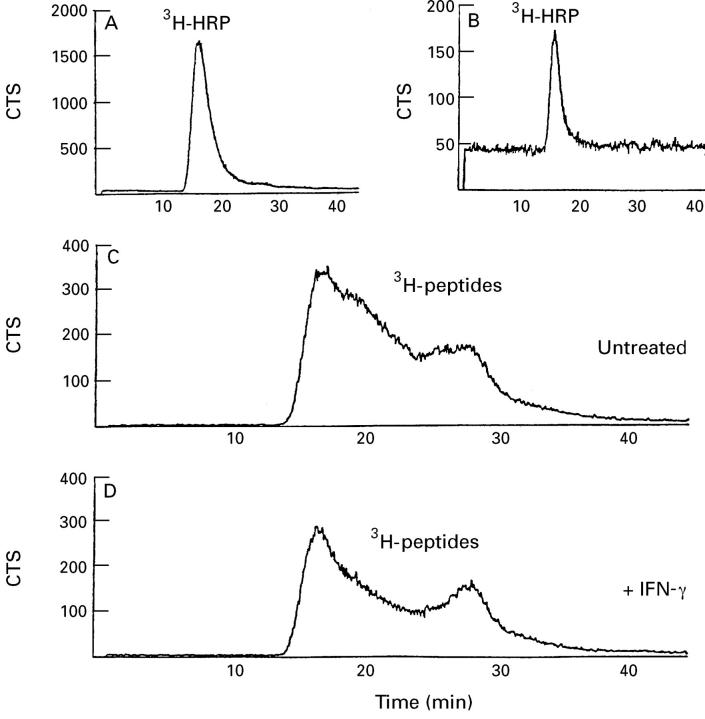
Figure 5 .
3H labelled peptides formed during transepithelial transport of 3H labelled horseradish peroxidase ([ 3H]HRP) across intestinal HT29-19A cells as shown by steric exclusion HPLC. [3H]HRP before transport (A),[3H]HRP after 4.5 hours in the apical compartment (B),[3H]metabolites after transepithelial transport in the basal compartment, in untreated cells (C) and cells treated with interferon γ (IFNγ) (D). This chromatogram is representative of two separate experiments.
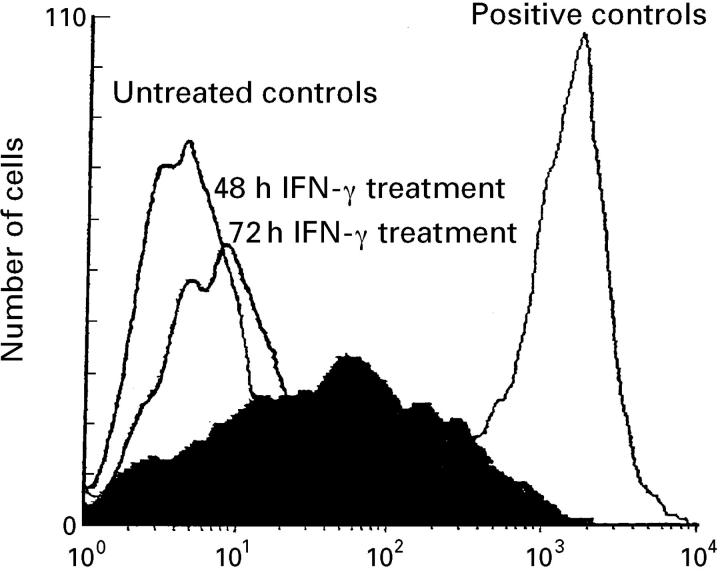
Figure 6 .
HLA-DR molecule expression on the surface of untreated intestinal HT29-19A cells, and cells treated on their basal side with 100 U/ml recombinant human interferon γ (IFNγ) for 48 or 72 hours. A monoclonal antibody recognising HLA-DR (clone L243) was used. Untreated cells did not express HLA-DR. After 48 hours of IFNγ treatment, HLA-DR expression was significant, and after 72 hours, it had greatly increased. A positive control was run with EBV-B cells.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. B., Planchon S. M., Roche J. K. IFN-gamma modulation of epithelial barrier function. Time course, reversibility, and site of cytokine binding. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2356–2363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augeron C., Laboisse C. L. Emergence of permanently differentiated cell clones in a human colonic cancer cell line in culture after treatment with sodium butyrate. Cancer Res. 1984 Sep;44(9):3961–3969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland P. W., Whiting C. V. Antigen processing by isolated rat intestinal villus enterocytes. Immunology. 1989 Dec;68(4):497–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Guagliardi L. E. The cell biology of antigen processing and presentation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:707–744. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth J., Duncan J. J. The hydrolysis of N-benzoyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-valyl-L-arginine-p-nitroanilide and its use as a substrate for the assay of cathepsin B. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 15;106(1):156–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerf-Bensussan N., Quaroni A., Kurnick J. T., Bhan A. K. Intraepithelial lymphocytes modulate Ia expression by intestinal epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2244–2252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colgan S. P., Morales V. M., Madara J. L., Polischuk J. E., Balk S. P., Blumberg R. S. IFN-gamma modulates CD1d surface expression on intestinal epithelia. Am J Physiol. 1996 Jul;271(1 Pt 1):C276–C283. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1996.271.1.C276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Paolo M. C., Merrett M. N., Crotty B., Jewell D. P. 5-Aminosalicylic acid inhibits the impaired epithelial barrier function induced by gamma interferon. Gut. 1996 Jan;38(1):115–119. doi: 10.1136/gut.38.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fais S., Capobianchi M. R., Pallone F., Di Marco P., Boirivant M., Dianzani F., Torsoli A. Spontaneous release of interferon gamma by intestinal lamina propria lymphocytes in Crohn's disease. Kinetics of in vitro response to interferon gamma inducers. Gut. 1991 Apr;32(4):403–407. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.4.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A., Weiner H. L. Induction of anergy or active suppression following oral tolerance is determined by antigen dosage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6688–6692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Margulies D. H. The biochemistry and cell biology of antigen processing and presentation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:403–450. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonnella P. A., Wilmore D. W. Co-localization of class II antigen and exogenous antigen in the rat enterocyte. J Cell Sci. 1993 Nov;106(Pt 3):937–940. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.3.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman M., Ducroc R., Desjeux J. F., Morgat J. L. Horseradish peroxidase transport across adult rabbit jejunum in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jun;242(6):G558–G564. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1982.242.6.G558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiribarren A., Heyman M., L'Helgouac'h A., Desjeux J. F. Effect of cytokines on the epithelial function of the human colon carcinoma cell line HT29 cl 19A. Gut. 1993 May;34(5):616–620. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.5.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockett R. D., Cook J. R., Findlay K., Harding C. V. Interferon-gamma differentially regulates antigen-processing functions in distinct endocytic compartments of macrophages with constitutive expression of class II major histocompatibility complex molecules. Immunology. 1996 May;88(1):68–75. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1996.d01-632.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D., Walker-Smith J. A., Phillips A. D. Macromolecular absorption by histologically normal and abnormal small intestinal mucosa in childhood: an in vitro study using organ culture. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1983 May;2(2):235–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiserlian D., Vidal K., Revillard J. P. Murine enterocytes can present soluble antigen to specific class II-restricted CD4+ T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Aug;19(8):1513–1516. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin N., Mitchell D. J., Brocke S., Ling N., Steinman L. Reversal of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by a soluble peptide variant of a myelin basic protein epitope: T cell receptor antagonism and reduction of interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha production. J Exp Med. 1994 Dec 1;180(6):2227–2237. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.6.2227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lah T. T., Hawley M., Rock K. L., Goldberg A. L. Gamma-interferon causes a selective induction of the lysosomal proteases, cathepsins B and L, in macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1995 Apr 17;363(1-2):85–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00287-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAEHLY A. C., CHANCE B. The assay of catalases and peroxidases. Methods Biochem Anal. 1954;1:357–424. doi: 10.1002/9780470110171.ch14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Stafford J. Interferon-gamma directly affects barrier function of cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):724–727. doi: 10.1172/JCI113938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malin M., Isolauri E., Pikkarainen P., Karikoski R., Isolauri J. Enhanced absorption of macromolecules. A secondary factor in Crohn's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1996 Jul;41(7):1423–1428. doi: 10.1007/BF02088568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L., Eisenhardt D., Salomon P., Bauer W., Plous R., Piccinini L. Expression of class II molecules on intestinal epithelial cells in humans. Differences between normal and inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jan;100(1):3–12. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90575-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler S. G., Rankin B. M., Moran-Davis P., Cleaveland J. S., Kiener P. A. Effect of interferon-gamma on antigen processing in human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Dec;24(12):3124–3130. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez G. M., Diment S. Role of cathepsin D in antigen presentation of ovalbumin. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 1;149(9):2894–2898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro L., Reboul A., Journet A. M., Colomb M. G. Major involvement of cathepsin B in the intracellular proteolytic processing of exogenous IgGs in U937 cells. Mol Immunol. 1993 Aug;30(11):1033–1039. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(93)90128-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby W. S., Janossy G., Mason D. Y., Jewell D. P. Expression of HLA-DR antigens by colonic epithelium in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Sep;53(3):614–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh B., Lee K. C., Fraga E., Wilkinson A., Wong M., Barton M. A. Minimum peptide sequences necessary for priming and triggering of humoral and cell-mediated immune responses in mice: use of synthetic peptide antigens of defined structure. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1336–1343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soloway P., Fish S., Passmore H., Gefter M., Coffee R., Manser T. Regulation of the immune response to peptide antigens: differential induction of immediate-type hypersensitivity and T cell proliferation due to changes in either peptide structure or major histocompatibility complex haplotype. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):847–858. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M., Walker W. A. Food proteins and gut mucosal barrier I. Binding and uptake of cow's milk proteins by adult rat jejunum in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 1):G556–G562. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.5.G556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis S., Menzies I. Intestinal permeability: functional assessment and significance. Clin Sci (Lond) 1992 May;82(5):471–488. doi: 10.1042/cs0820471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Bennink J. R. The binary logic of antigen processing and presentation to T cells. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90356-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z. Y., Michael J. G. Orally inducible immune unresponsiveness is abrogated by IFN-gamma treatment. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4163–4165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer K. P., Poremba C., Weber P., Ciclitira P. J., Harms E. Translocation of gliadin into HLA-DR antigen containing lysosomes in coeliac disease enterocytes. Gut. 1995 May;36(5):703–709. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.5.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Elburg R. M., Uil J. J., de Monchy J. G., Heymans H. S. Intestinal permeability in pediatric gastroenterology. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1992;194:19–24. doi: 10.3109/00365529209096021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]