Abstract
Background—Liver disease in chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection ranges from minimal lesions to liver cirrhosis, eventually evolving to hepatocellular carcinoma. Whether and how HCV determines the different clinical and histological manifestations of the disease is not fully understood. Aims—To verify whether the amount of virus in individual patients could be related to the severity of liver injury. Patients and methods—Levels of HCV RNA were measured in serum in 96 consecutive patients with chronic hepatitis type C using a signal amplification assay. The relation between viraemic values and the corresponding viral load in the liver was assessed in a subgroup of 21 patients in whom HCV RNA was measured in serum samples and liver specimens obtained at the same time. Results—A positive correlation was observed between the amount of viral nucleic acid in the two compartments, indicating that levels of viraemia reflect the amount of virus present in the liver. Viral load did not correlate with aminotransferase activities nor with histological diagnosis, and serum and liver levels of HCV RNA were not significantly different in patients infected by the various HCV genotypes. Conclusions—Measurement of HCV replication in serum is a mirror of viral replication in the liver. The extent of replicative activity of HCV does not seem to play a role in the modulation of the associated hepatic disease.
Keywords: HCV RNA; bDNA assay; liver disease activity
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (109.3 KB).
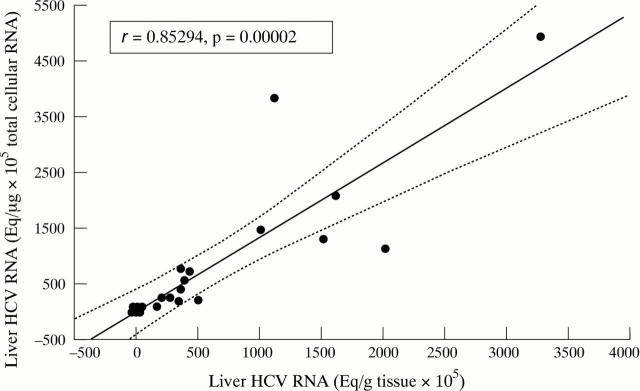
Figure 1 .
Relation between amount of HCV RNA in the liver expressed as Eq/g of tissue and Eq/µg of total cellular RNA.
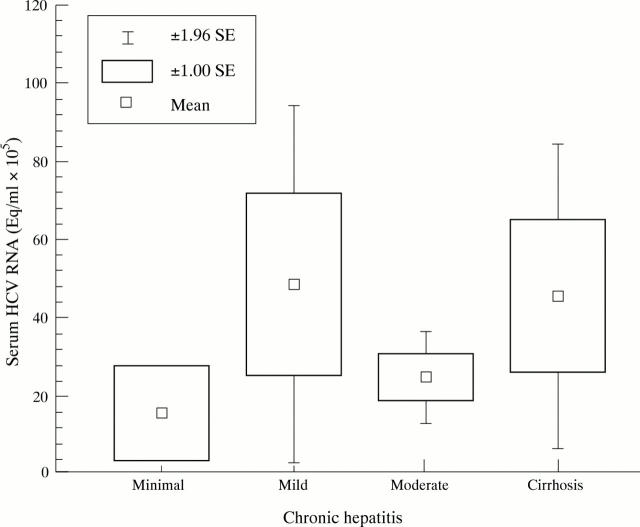
Figure 2 .
Viral load detected in serum in anti-HCV positive patients in relation to histological diagnosis.
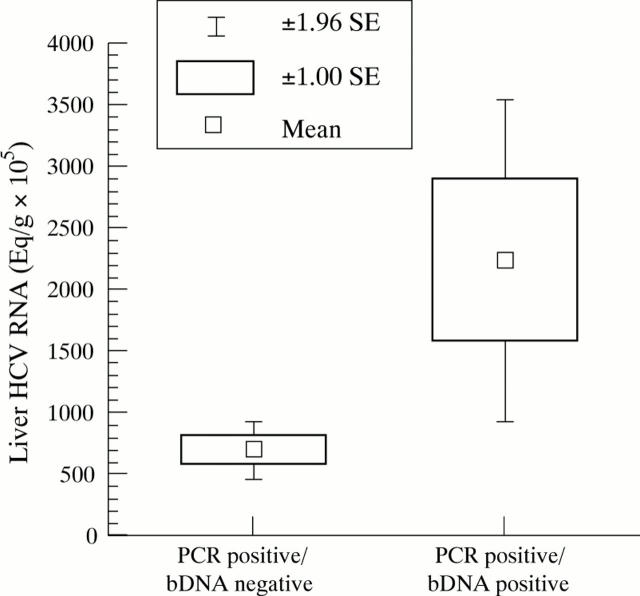
Figure 3 .
Viral load in the liver in patients with HCV RNA detectable in the corresponding serum only by PCR and in those with viraemia detectable also by bDNA.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnaba V., Balsano F. Immunologic and molecular basis of viral persistence. The hepatitis B virus model. J Hepatol. 1992 Mar;14(2-3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(92)90189-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brillanti S., Foli M., Gaiani S., Masci C., Miglioli M., Barbara L. Persistent hepatitis C viraemia without liver disease. Lancet. 1993 Feb 20;341(8843):464–465. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90210-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerny A., McHutchison J. G., Pasquinelli C., Brown M. E., Brothers M. A., Grabscheid B., Fowler P., Houghton M., Chisari F. V. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to hepatitis C virus-derived peptides containing the HLA A2.1 binding motif. J Clin Invest. 1995 Feb;95(2):521–530. doi: 10.1172/JCI117694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coelho-Little E., Jeffers L. J., Bartholomew M., Reddy K. R., Schiff E. R., Dailey P. J. Correlation of HCV-RNA levels in serum and liver of patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 1995 Apr;22(4):508–508. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(95)80118-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmet V. J., Gerber M., Hoofnagle J. H., Manns M., Scheuer P. J. Classification of chronic hepatitis: diagnosis, grading and staging. Hepatology. 1994 Jun;19(6):1513–1520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari C., Valli A., Galati L., Penna A., Scaccaglia P., Giuberti T., Schianchi C., Missale G., Marin M. G., Fiaccadori F. T-cell response to structural and nonstructural hepatitis C virus antigens in persistent and self-limited hepatitis C virus infections. Hepatology. 1994 Feb;19(2):286–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gretch D. R., dela Rosa C., Carithers R. L., Jr, Willson R. A., Williams B., Corey L. Assessment of hepatitis C viremia using molecular amplification technologies: correlations and clinical implications. Ann Intern Med. 1995 Sep 1;123(5):321–329. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-123-5-199509010-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gretch D., Corey L., Wilson J., dela Rosa C., Willson R., Carithers R., Jr, Busch M., Hart J., Sayers M., Han J. Assessment of hepatitis C virus RNA levels by quantitative competitive RNA polymerase chain reaction: high-titer viremia correlates with advanced stage of disease. J Infect Dis. 1994 Jun;169(6):1219–1225. doi: 10.1093/infdis/169.6.1219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara H., Hayashi N., Mita E., Naito M., Kasahara A., Fusamoto H., Kamada T. Quantitation of hepatitis C virus RNA in serum of asymptomatic blood donors and patients with type C chronic liver disease. Hepatology. 1993 Apr;17(4):545–550. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840170404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko S., Murakami S., Unoura M., Kobayashi K. Quantitation of hepatitis C virus RNA by competitive polymerase chain reaction. J Med Virol. 1992 Aug;37(4):278–282. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890370408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Tanaka E., Sodeyama T., Urushihara A., Matsumoto A., Kiyosawa K. The natural course of chronic hepatitis C: a comparison between patients with genotypes 1 and 2 hepatitis C viruses. Hepatology. 1996 Apr;23(4):695–699. doi: 10.1053/jhep.1996.v23.pm0008666319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koziel M. J., Dudley D., Wong J. T., Dienstag J., Houghton M., Ralston R., Walker B. D. Intrahepatic cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for hepatitis C virus in persons with chronic hepatitis. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 15;149(10):3339–3344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawczynski K., Beach M. J., Bradley D. W., Kuo G., di Bisceglie A. M., Houghton M., Reyes G. R., Kim J. P., Choo Q. L., Alter M. J. Hepatitis C virus antigen in hepatocytes: immunomorphologic detection and identification. Gastroenterology. 1992 Aug;103(2):622–629. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90856-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau J. Y., Davis G. L., Kniffen J., Qian K. P., Urdea M. S., Chan C. S., Mizokami M., Neuwald P. D., Wilber J. C. Significance of serum hepatitis C virus RNA levels in chronic hepatitis C. Lancet. 1993 Jun 12;341(8859):1501–1504. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90635-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau J. Y., Davis G. L., Prescott L. E., Maertens G., Lindsay K. L., Qian K., Mizokami M., Simmonds P. Distribution of hepatitis C virus genotypes determined by line probe assay in patients with chronic hepatitis C seen at tertiary referral centers in the United States. Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group. Ann Intern Med. 1996 May 15;124(10):868–876. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-124-10-199605150-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau J. Y., Simmonds P., Urdea M. S. Implications of variations of "conserved" regions of hepatitis C virus genome. Lancet. 1995 Aug 12;346(8972):425–426. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)92786-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzin A., Bagnarelli P., Menzo S., Giostra F., Brugia M., Francesconi R., Bianchi F. B., Clementi M. Quantitation of hepatitis C virus genome molecules in plasma samples. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Aug;32(8):1939–1944. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.8.1939-1944.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuinness P. H., Bishop G. A., Painter D. M., Chan R., McCaughan G. W. Intrahepatic hepatitis C RNA levels do not correlate with degree of liver injury in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 1996 Apr;23(4):676–687. doi: 10.1002/hep.510230404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon A., Shepherd R. W., Faoagali J. L., Balderson G., Ong T. H., Patrick M., Cleghorn G. J., Lynch S., Strong R. Cytomegalovirus infection after liver transplantation in children. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1993 Nov-Dec;8(6):540–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1993.tb01649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito M., Hayashi N., Hagiwara H., Hiramatsu N., Kasahara A., Fusamoto H., Kamada T. Serum hepatitis C virus RNA quantity and histological features of hepatitis C virus carriers with persistently normal ALT levels. Hepatology. 1994 Apr;19(4):871–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nousbaum J. B., Pol S., Nalpas B., Landais P., Berthelot P., Bréchot C. Hepatitis C virus type 1b (II) infection in France and Italy. Collaborative Study Group. Ann Intern Med. 1995 Feb 1;122(3):161–168. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-122-3-199502010-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontisso P., Ruvoletto M. G., Nicoletti M., Tisminetzky S., Gerotto M., Levrero M., Artini M., Baldi M., Ballardini G., Barbara L. Distribution of three major hepatitis C virus genotypes in Italy. A multicentre study of 495 patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Viral Hepat. 1995;2(1):33–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.1995.tb00069.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prati D., Capelli C., Zanella A., Mozzi F., Bosoni P., Pappalettera M., Zanuso F., Vianello L., Locatelli E., de Fazio C. Influence of different hepatitis C virus genotypes on the course of asymptomatic hepatitis C virus infection. Gastroenterology. 1996 Jan;110(1):178–183. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8536854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto N., Enomoto N., Kurosaki M., Marumo F., Sato C. Detection and quantification of hepatitis C virus RNA replication in the liver. J Hepatol. 1994 May;20(5):593–597. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80345-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silini E., Bono F., Cividini A., Cerino A., Bruno S., Rossi S., Belloni G., Brugnetti B., Civardi E., Salvaneschi L. Differential distribution of hepatitis C virus genotypes in patients with and without liver function abnormalities. Hepatology. 1995 Feb;21(2):285–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds P. Variability of hepatitis C virus. Hepatology. 1995 Feb;21(2):570–583. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840210243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrault N. A., Dailey P. J., Ferrell L., Collins M. L., Wilber J. C., Urdea M. S., Bhandari B. N., Wright T. L. Hepatitis C virus: quantitation and distribution in liver. J Med Virol. 1997 Mar;51(3):217–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. C., Jacyna M., Waters J., Main J. Virus-host interaction in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Semin Liver Dis. 1988 Nov;8(4):342–349. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukiyama-Kohara K., Iizuka N., Kohara M., Nomoto A. Internal ribosome entry site within hepatitis C virus RNA. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1476–1483. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1476-1483.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urdea M. S., Horn T., Fultz T. J., Anderson M., Running J. A., Hamren S., Ahle D., Chang C. A. Branched DNA amplification multimers for the sensitive, direct detection of human hepatitis viruses. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1991;(24):197–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Le S. Y., Ali N., Siddiqui A. An RNA pseudoknot is an essential structural element of the internal ribosome entry site located within the hepatitis C virus 5' noncoding region. RNA. 1995 Jul;1(5):526–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Kakumu S., Yoshioka K., Higashi Y., Tanaka K., Ishikawa T., Takayanagi M. Hepatitis C virus genotypes are not responsible for development of serious liver disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1994 Feb;39(2):234–239. doi: 10.1007/BF02090191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]