Abstract
Background/Aims—Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIPO) reflects a dysfunction of the visceral smooth muscle or the enteric nervous system. Gastrointestinal manifestations are common in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) but CIPO has not been reported. Features of CIPO are reported in five patients with SLE. Methods—From 1988 to 1993, five patients with SLE or SLE-like syndrome were hospitalised for gastrointestinal manometric studies. CIPO was the onset feature in two cases. Antroduodenal manometry (three hours fasting, two hours fed) was performed in all patients, and oesophageal manometry in four. Results—Intestinal hypomotility associated with reduced bladder capacity and bilateral ureteral distension was found in four patients and aperistalsis of the oesophagus in three. Treatment, which consisted of high dose corticosteroids, parenteral nutrition, promotility agents, and antibiotics, led to remission of both CIPO and urinary abnormalities in all cases. Antroduodenal manometry performed in two patients after remission showed increased intestinal motility. One patient died, and postmortem examination showed intestinal vasculitis. Conclusions—CIPO in SLE is a life threatening situation that can be reversed by treatment. It may be: (a) a complication or onset feature of the disease; (b) secondary to smooth muscle involvement; (c) associated with ureteral and vesical involvement; (d) the result of intestinal vasculitis.
Keywords: chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction; systemic lupus erythematosus
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (174.6 KB).
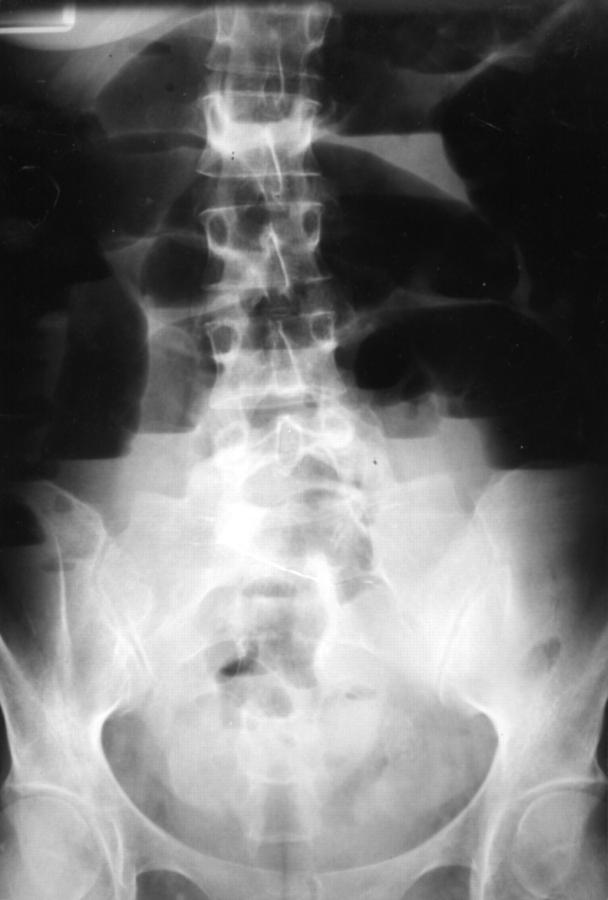
Figure 1 .
Plain abdominal radiograph (upright film). Gaseous distension of the small bowel with the presence of fluid in the bowel loops is observed.
Figure 2 .
Urinary involvement during systemic lupus erythematosus and chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (intravenous urography). There is an increase in the thickness of the bladder wall with marked reduction in capacity associated with bilateral ureteral distension (patient 1).
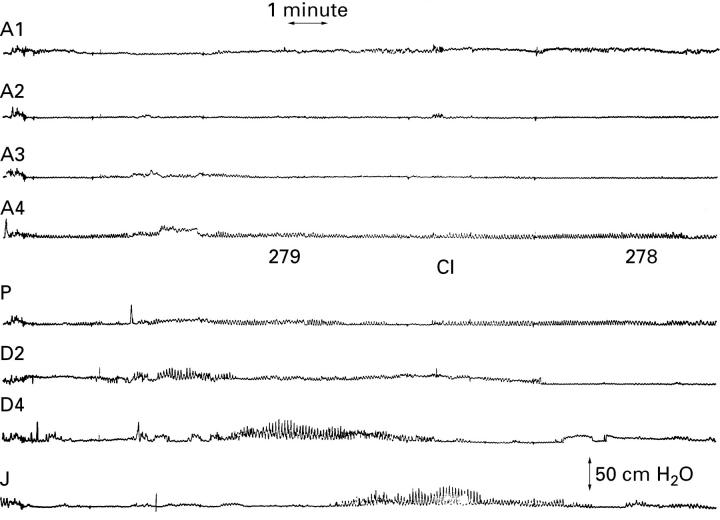
Figure 3 .
Fasting gastrointestinal motility tracings in patient 5. Intestinal hypomotility is observed with weak distal antral, duodenal, and jejunal contractions suggestive of a myopathic disorder. A, antrum (1 to 4, proximal to distal); P, pylorus; D2, descending duodenum; D4, distal duodenum; J, jejunum.
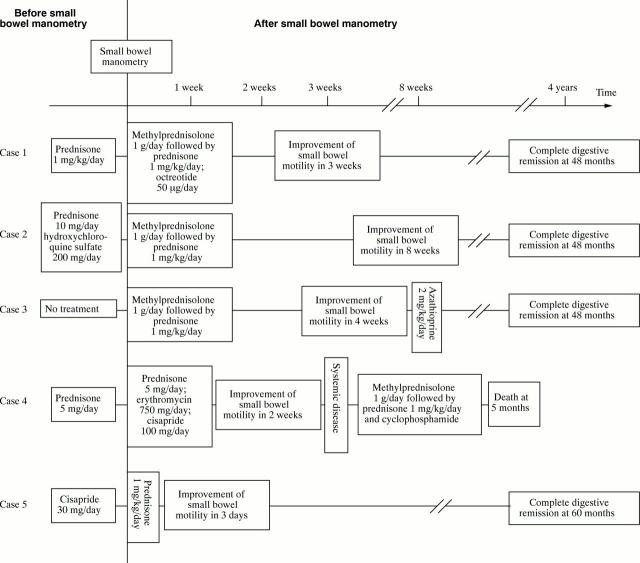
Figure 4 .
Treatment of patients and outcomes.
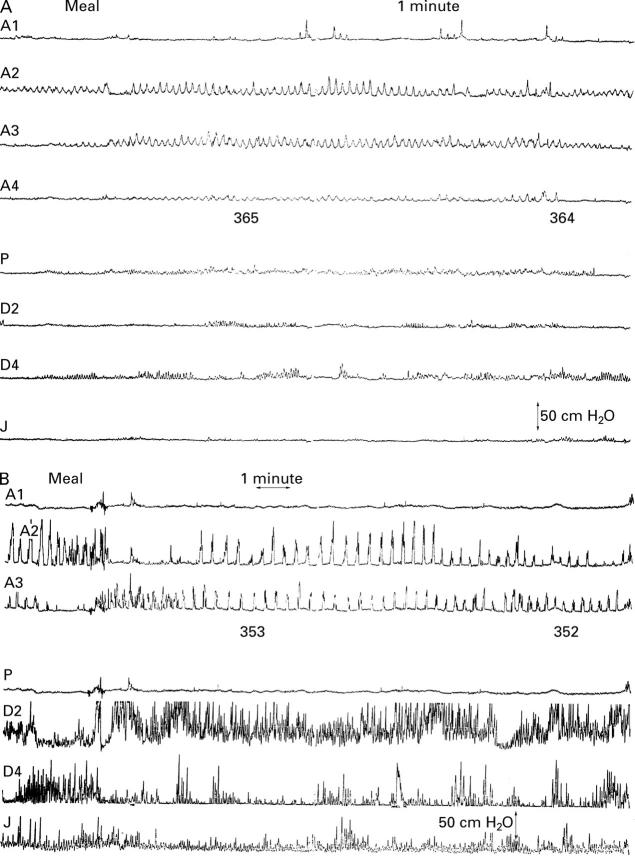
Figure 5 .
(A) Postprandial motility tracings before treatment (patient 1): a reduction in amplitude of gastrointestinal contractions can be seen. (B) Postprandial motility tracings after one year of treatment (patient 1): increased antral and intestinal motility can be seen. A, antrum (1 to 4, proximal to distal); P, pylorus; D2, descending duodenum; D4, distal duodenum; J, jejunum.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annese V., Janssens J., Vantrappen G., Tack J., Peeters T. L., Willemse P., Van Cutsem E. Erythromycin accelerates gastric emptying by inducing antral contractions and improved gastroduodenal coordination. Gastroenterology. 1992 Mar;102(3):823–828. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90164-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN C. H., HASERICK J. R., SHIREY E. K. Gastrointestinal manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Gastroenterology. 1956 Dec;31(6):649-64; discussion, 664-6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cacoub P., Benhamou Y., Barbet P., Piette J. C., Le Cae A., Chaussade S., Cadranel J. F., Callard P., Opolon P., Godeau P. Systemic lupus erythematosus and chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction. J Rheumatol. 1993 Feb;20(2):377–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilleri M., Pusey C. D., Chadwick V. S., Rees A. J. Gastrointestinal manifestations of systemic vasculitis. Q J Med. 1983 Spring;52(206):141–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaussade S., Grandjouan S., Couturier D., Thierman-Duffaud D., Henry J. F. Induction of phase 3 of the migrating motor complex in human small intestine by trimebutine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1987;32(6):615–618. doi: 10.1007/BF02455998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Haynes B., Katz P. The spectrum of vasculitis: clinical, pathologic, immunologic and therapeutic considerations. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Nov;89(5 Pt 1):660–676. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-5-660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk D. L., Anuras S., Christensen J. Chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction. Gastroenterology. 1978 May;74(5 Pt 1):922–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greydanus M. P., Camilleri M. Abnormal postcibal antral and small bowel motility due to neuropathy or myopathy in systemic sclerosis. Gastroenterology. 1989 Jan;96(1):110–115. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90770-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez F., Valenzuela J. E., Ehresmann G. R., Quismorio F. P., Kitridou R. C. Esophageal dysfunction in patients with mixed connective tissue diseases and systemic lupus erythematosus. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Jul;27(7):592–597. doi: 10.1007/BF01297214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner F. S. Dermatomyositis and its manifestations in the gastrointestinal tract. Am J Gastroenterol. 1970 Feb;53(2):141–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laing T. J. Gastrointestinal vasculitis and pneumatosis intestinalis due to systemic lupus erythematosus: successful treatment with pulse intravenous cyclophosphamide. Am J Med. 1988 Oct;85(4):555–558. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(88)80096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S. D., Debinski H. S., Kamm M. A. Clinical characteristics of chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in adults. Gut. 1997 Nov;41(5):675–681. doi: 10.1136/gut.41.5.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meulders Q., Michel C., Marteau P., Grange J. D., Mougenot B., Ronco P., Mignon F. Association of chronic interstitial cystitis, protein-losing enteropathy and paralytic ileus with seronegative systemic lupus erythematosus: case report and review of the literature. Clin Nephrol. 1992 May;37(5):239–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orth R. W., Weisman M. H., Cohen A. H., Talner L. B., Nachtsheim D., Zvaifler N. J. Lupus cystitis: primary bladder manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Mar;98(3):323–326. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-3-323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez-Mata M., Reyes P. A., Alarcon-Segovia D., Garza R. Esophageal motility in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Dig Dis. 1974 Feb;19(2):132–136. doi: 10.1007/BF01072623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuffler M. D., Rohrmann C. A., Chaffee R. G., Brand D. L., Delaney J. H., Young J. H. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. A report of 27 cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1981 May;60(3):173–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soudah H. C., Hasler W. L., Owyang C. Effect of octreotide on intestinal motility and bacterial overgrowth in scleroderma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Nov 21;325(21):1461–1467. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199111213252102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafford-Brady F. J., Kahn H. J., Ross T. M., Russell M. L. Advanced scleroderma bowel: complications and management. J Rheumatol. 1988;15(5):869–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanghellini V., Camilleri M., Malagelada J. R. Chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: clinical and intestinal manometric findings. Gut. 1987 Jan;28(1):5–12. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitali C., Bombardieri S., Moutsopoulos H. M., Balestrieri G., Bencivelli W., Bernstein R. M., Bjerrum K. B., Braga S., Coll J., de Vita S. Preliminary criteria for the classification of Sjögren's syndrome. Results of a prospective concerted action supported by the European Community. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Mar;36(3):340–347. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman M. H., McDanald E. C., Wilson C. B. Studies of the pathogenesis of interstitial cystitis, obstructive uropathy, and intestinal malabsorption in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1981 Apr;70(4):875–881. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90547-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A., Mogavero H. S., Jr, Synkowski D. R., Provost T. T. Diagnostic tests and clinical subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus: update 1983. Ann Allergy. 1983 Aug;51(2 Pt 1):135–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zizic T. M., Classen J. N., Stevens M. B. Acute abdominal complications of systemic lupus erythematosus and polyarteritis nodosa. Am J Med. 1982 Oct;73(4):525–531. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]