Abstract
Background—An imbalance between the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) has been postulated as a pathogenic factor in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Aims—To study allelic frequencies of novel polymorphisms in the genes for IL-1β and IL-1ra in patients with IBD and to assess the relation between ex vivo cytokine production and allelic variants of the IL-1β and IL-1ra genes. Subjects—Two hundred and seventy healthy controls, 74 patients with ulcerative colitis (UC), 72 with Crohn's disease (CD), 40 with primary sclerosing cholangitis for the allelic frequencies, and 60 healthy individuals for the ex vivo stimulation test. Methods—Genotyping was performed by polymerase chain reaction and subsequent cleavage with specific endonucleases (Mwo1, MspAI1, Alu1, Taq1, BsoF1) for five novel restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) in the genes for IL-1ra and IL-1β. Results—No significant differences were found in the allelic frequencies or allele carriage rates of the markers in the IL-1β and IL-1ra genes between CD, UC, and healthy controls. No association between the genetic markers and cytokine production levels was observed. Patients with UC carried the combination of both the infrequent allele of the Taq1 RFLP and the Mwo1 RFLP significantly more frequently (35.2% in UC versus 71.1% in controls). Conclusions—UC is associated with carriage of both infrequent alleles of the Taq1 and Mwo1 RFLPs. However, it could not be confirmed whether the association reflects a pathogenic mechanism underlying UC.
Keywords: cytokine gene polymorphisms; interleukin 1 receptor antagonist; interleukin 1β; Crohn's disease; ulcerative colitis
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (151.7 KB).
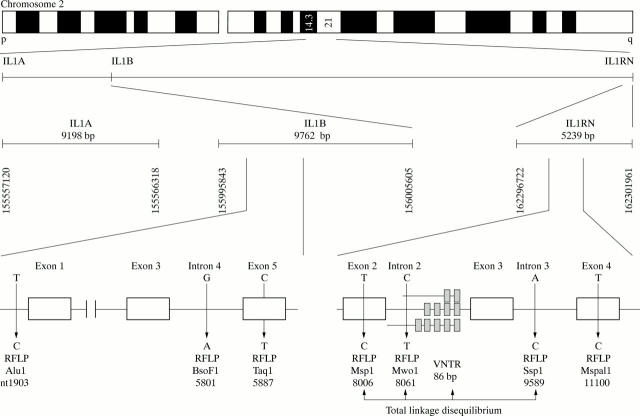
Figure 1 .
RFLPs in IL1RN. IL1A and IL1B are located close together on band q14.3 on chromosome 2 (first panel). IL1RN is located on q21 at a distance of about 7 cM from the IL1A/B locus (second panel). The third panel indicates the size of the IL1A, B, and IL1RN loci. The numbers indicate the nucleotide number of the NCBI-chromosome 2 map. The lower panel depicts the position of the RFLPs studied. The RFLPs joined by the arrows are in tight linkage disequilibrium.
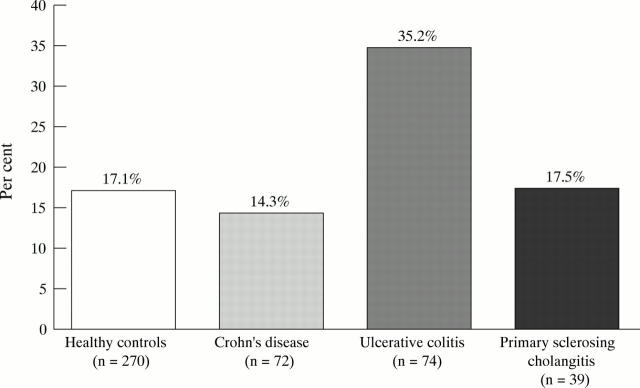
Figure 2 .
Percentage of persons carrying the combination of both the infrequent alleles of the Taq1 RFLP in IL1B and the Mwo1 RFLP in IL1RN.
Figure 3 .
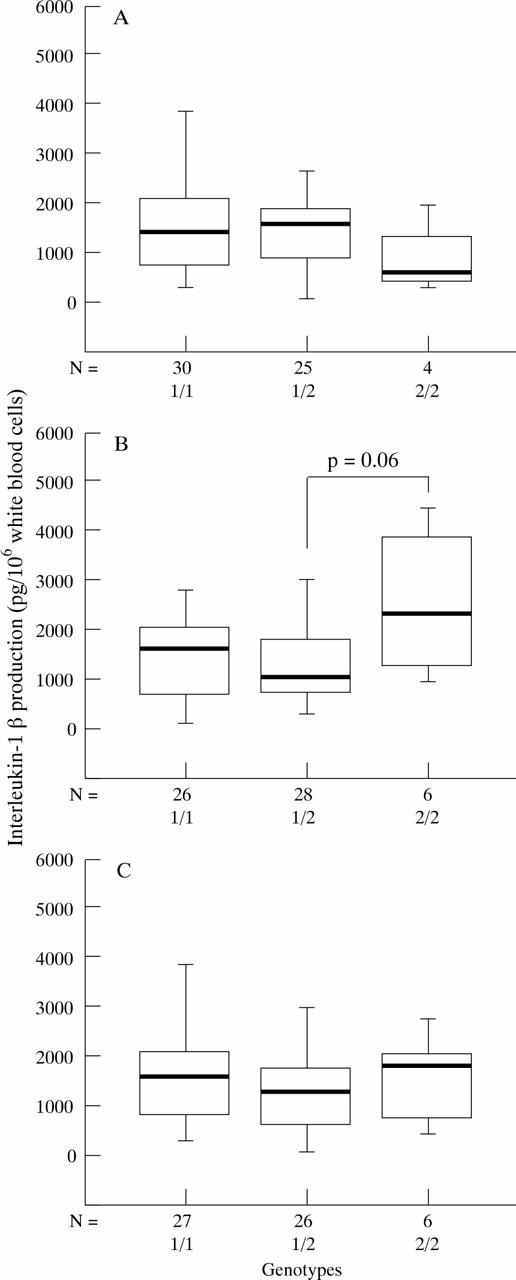
IL-1β production following ex vivo stimulation of whole blood with LPS in relation to genetic markers in IL1B. (A) Taq1; (B) BsoF1; (C) Alu1.
Figure 4 .
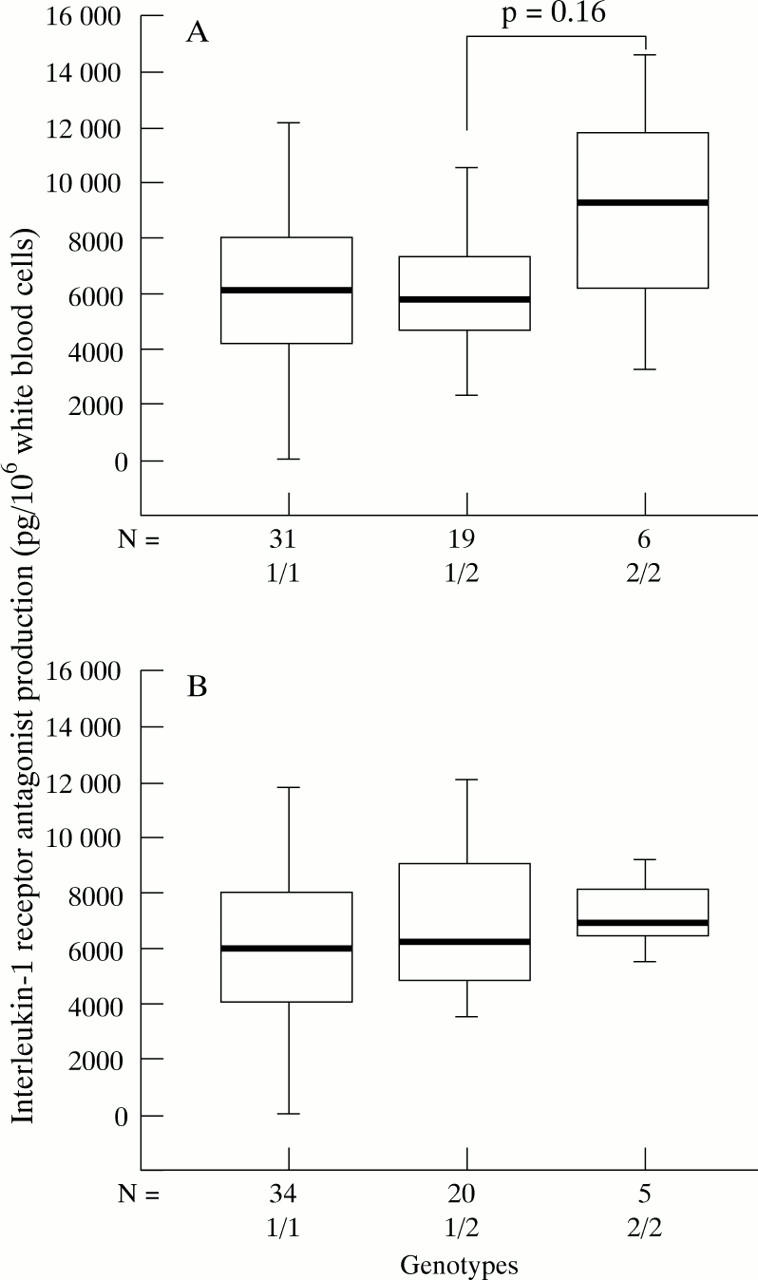
IL-1ra production following stimulation of whole blood with LPS in relation to genetic markers in IL1RN. (A) MspAI 1; (B) Mwo1.
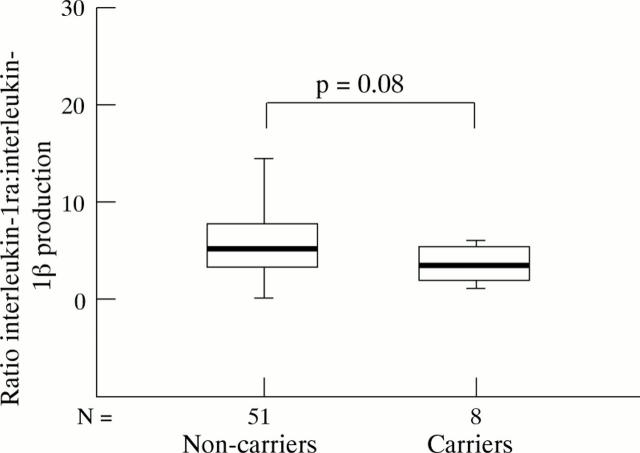
Figure 5 .
The ratio of IL-1ra and IL-1β production after LPS whole blood stimulation in healthy individuals carrying a combination of both infrequent alleles of the Taq1 and Mwo1 RFLPs (carriers) and in individuals that do not carry this combination (non-carriers).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bioque G., Crusius J. B., Koutroubakis I., Bouma G., Kostense P. J., Meuwissen S. G., Peña A. S. Allelic polymorphism in IL-1 beta and IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) genes in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1995 Nov;102(2):379–383. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb03793.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casini-Raggi V., Kam L., Chong Y. J., Fiocchi C., Pizarro T. T., Cominelli F. Mucosal imbalance of IL-1 and IL-1 receptor antagonist in inflammatory bowel disease. A novel mechanism of chronic intestinal inflammation. J Immunol. 1995 Mar 1;154(5):2434–2440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clay F. E., Tarlow J. K., Cork M. J., Cox A., Nicklin M. J., Duff G. W. Novel interleukin-1 receptor antagonist exon polymorphisms and their use in allele-specific mRNA assessment. Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;97(6):723–726. doi: 10.1007/BF02346180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cominelli F., Nast C. C., Clark B. D., Schindler R., Lierena R., Eysselein V. E., Thompson R. C., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin 1 (IL-1) gene expression, synthesis, and effect of specific IL-1 receptor blockade in rabbit immune complex colitis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):972–980. doi: 10.1172/JCI114799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danis V. A., Millington M., Hyland V. J., Grennan D. Cytokine production by normal human monocytes: inter-subject variation and relationship to an IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) gene polymorphism. Clin Exp Immunol. 1995 Feb;99(2):303–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb05549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groote D., Zangerle P. F., Gevaert Y., Fassotte M. F., Beguin Y., Noizat-Pirenne F., Pirenne J., Gathy R., Lopez M., Dehart I. Direct stimulation of cytokines (IL-1 beta, TNF-alpha, IL-6, IL-2, IFN-gamma and GM-CSF) in whole blood. I. Comparison with isolated PBMC stimulation. Cytokine. 1992 May;4(3):239–248. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(92)90062-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Thompson R. C. Blocking IL-1: interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in vivo and in vitro. Immunol Today. 1991 Nov;12(11):404–410. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90142-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Wolff S. M. The role of interleukin-1 in disease. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jan 14;328(2):106–113. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199301143280207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entzian P., Linnemann K., Schlaak M., Zabel P. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and circadian rhythms of hormones and cytokines. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996 Mar;153(3):1080–1086. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.153.3.8630548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furutani Y., Notake M., Fukui T., Ohue M., Nomura H., Yamada M., Nakamura S. Complete nucleotide sequence of the gene for human interleukin 1 alpha. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3167–3179. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granowitz E. V., Santos A. A., Poutsiaka D. D., Cannon J. G., Wilmore D. W., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. Production of interleukin-1-receptor antagonist during experimental endotoxaemia. Lancet. 1991 Dec 7;338(8780):1423–1424. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92725-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guasch J. F., Bertina R. M., Reitsma P. H. Five novel intragenic dimorphisms in the human interleukin-1 genes combine to high informativity. Cytokine. 1996 Aug;8(8):598–602. doi: 10.1006/cyto.1996.0080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker U. T., Gomolka M., Keller E., Eigler A., Folwaczny C., Fricke H., Albert E., Loeschke K., Endres S. Lack of association between an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene polymorphism and ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1997 May;40(5):623–627. doi: 10.1136/gut.40.5.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannum C. H., Wilcox C. J., Arend W. P., Joslin F. G., Dripps D. J., Heimdal P. L., Armes L. G., Sommer A., Eisenberg S. P., Thompson R. C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist activity of a human interleukin-1 inhibitor. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):336–340. doi: 10.1038/343336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heresbach D., Alizadeh M., Dabadie A., Le Berre N., Colombel J. F., Yaouanq J., Bretagne J. F., Semana G. Significance of interleukin-1beta and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist genetic polymorphism in inflammatory bowel diseases. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997 Jul;92(7):1164–1169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugot J. P., Laurent-Puig P., Gower-Rousseau C., Caillat-Zucman S., Beaugerie L., Dupas J. L., Van Gossum A., Bonäit-Pellie C., Cortot A., Thomas G. Linkage analyses of chromosome 6 loci, including HLA, in familial aggregations of Crohn disease. G.E.T.A.I.D. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Aug 15;52(2):207–213. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320520216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugot J. P., Laurent-Puig P., Gower-Rousseau C., Olson J. M., Lee J. C., Beaugerie L., Naom I., Dupas J. L., Van Gossum A., Orholm M. Mapping of a susceptibility locus for Crohn's disease on chromosome 16. Nature. 1996 Feb 29;379(6568):821–823. doi: 10.1038/379821a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafage M., Maroc N., Dubreuil P., de Waal Malefijt R., Pébusque M. J., Carcassonne Y., Mannoni P. The human interleukin-1 alpha gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 2 at band q13. Blood. 1989 Jan;73(1):104–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennard A., Gorman P., Carrier M., Griffiths S., Scotney H., Sheer D., Solari R. Cloning and chromosome mapping of the human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene. Cytokine. 1992 Mar;4(2):83–89. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(92)90041-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligumsky M., Simon P. L., Karmeli F., Rachmilewitz D. Role of interleukin 1 in inflammatory bowel disease--enhanced production during active disease. Gut. 1990 Jun;31(6):686–689. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.6.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis E., Satsangi J., Roussomoustakaki M., Parkes M., Fanning G., Welsh K., Jewell D. Cytokine gene polymorphisms in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1996 Nov;39(5):705–710. doi: 10.1136/gut.39.5.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahida Y. R., Wu K., Jewell D. P. Enhanced production of interleukin 1-beta by mononuclear cells isolated from mucosa with active ulcerative colitis of Crohn's disease. Gut. 1989 Jun;30(6):835–838. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.6.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield J. C., Holden H., Tarlow J. K., Di Giovine F. S., McDowell T. L., Wilson A. G., Holdsworth C. D., Duff G. W. Novel genetic association between ulcerative colitis and the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Gastroenterology. 1994 Mar;106(3):637–642. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modi W. S., Masuda A., Yamada M., Oppenheim J. J., Matsushima K., O'Brien S. J. Chromosomal localization of the human interleukin 1 alpha (IL-1 alpha) gene. Genomics. 1988 May;2(4):310–314. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Saito H., Kasanuki J., Tamura Y., Yoshida S. Cytokine production in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1992 Jul;33(7):933–937. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.7.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerad J. L., Griffiths J. K., Van der Meer J. W., Endres S., Poutsiaka D. D., Keusch G. T., Bennish M., Salam M. A., Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G. Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta), IL-1 receptor antagonist, and TNF alpha production in whole blood. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Dec;52(6):687–692. doi: 10.1002/jlb.52.6.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmen J. D., Yang H. Y., Yamamoto K. K., Zhao H. Y., Ma Y., Bentley L. G., Huang Z., Gerwehr S., Pressman S., McElree C. Susceptibility locus for inflammatory bowel disease on chromosome 16 has a role in Crohn's disease, but not in ulcerative colitis. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Oct;5(10):1679–1683. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.10.1679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D., Jones C., Hart I., Bleskan J., Berger R., Geyer D., Eisenberg S. P., Smith M. F., Jr, Arend W. P. The human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL1RN) gene is located in the chromosome 2q14 region. Genomics. 1993 Jan;15(1):173–176. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevy S. E., Targan S. R., Yang H., Fernandez D., Rotter J. I., Toyoda H. Tumor necrosis factor microsatellites define a Crohn's disease-associated haplotype on chromosome 6. Gastroenterology. 1996 Apr;110(4):1053–1060. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8612993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pociot F., Mølvig J., Wogensen L., Worsaae H., Nerup J. A TaqI polymorphism in the human interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) gene correlates with IL-1 beta secretion in vitro. Eur J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;22(6):396–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1992.tb01480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachmilewitz D., Simon P. L., Schwartz L. W., Griswold D. E., Fondacaro J. D., Wasserman M. A. Inflammatory mediators of experimental colitis in rats. Gastroenterology. 1989 Aug;97(2):326–337. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussomoustakaki M., Satsangi J., Welsh K., Louis E., Fanning G., Targan S., Landers C., Jewell D. P. Genetic markers may predict disease behavior in patients with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1997 Jun;112(6):1845–1853. doi: 10.1053/gast.1997.v112.pm9178675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satsangi J., Parkes M., Louis E., Hashimoto L., Kato N., Welsh K., Terwilliger J. D., Lathrop G. M., Bell J. I., Jewell D. P. Two stage genome-wide search in inflammatory bowel disease provides evidence for susceptibility loci on chromosomes 3, 7 and 12. Nat Genet. 1996 Oct;14(2):199–202. doi: 10.1038/ng1096-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satsangi J., Welsh K. I., Bunce M., Julier C., Farrant J. M., Bell J. I., Jewell D. P. Contribution of genes of the major histocompatibility complex to susceptibility and disease phenotype in inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet. 1996 May 4;347(9010):1212–1217. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)90734-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sham P. C., Curtis D. Monte Carlo tests for associations between disease and alleles at highly polymorphic loci. Ann Hum Genet. 1995 Jan;59(Pt 1):97–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1995.tb01608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinkasserer A., Spurr N. K., Cox S., Jeggo P., Sim R. B. The human IL-1 receptor antagonist gene (IL1RN) maps to chromosome 2q14-q21, in the region of the IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta loci. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):654–657. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90137-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarlow J. K., Blakemore A. I., Lennard A., Solari R., Hughes H. N., Steinkasserer A., Duff G. W. Polymorphism in human IL-1 receptor antagonist gene intron 2 is caused by variable numbers of an 86-bp tandem repeat. Hum Genet. 1993 May;91(4):403–404. doi: 10.1007/BF00217368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb A. C., Collins K. L., Auron P. E., Eddy R. L., Nakai H., Byers M. G., Haley L. L., Henry W. M., Shows T. B. Interleukin-1 gene (IL1) assigned to long arm of human chromosome 2. Lymphokine Res. 1986 Spring;5(2):77–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]