Abstract
Background—Life stress contributes to symptom onset and exacerbation in the majority of patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and functional dyspepsia (FD); research evidence is conflicting, however, as to the strength of these effects. Aims—To test prospectively the relation of chronic life stress threat to subsequent symptom intensity over time. Patients—One hundred and seventeen consecutive outpatients satisfying the modified Rome criteria for IBS (66% with one or more concurrent FD syndromes) participated. Methods—The life stress and symptom intensity measures were determined from interview data collected independently at entry, and at six and 16 months; these measures assessed the potency of chronic life stress threat during the prior six months or more, and the severity and frequency of IBS and FD symptoms during the following two weeks. Results—Chronic life stress threat was a powerful predictor of subsequent symptom intensity, explaining 97% of the variance on this measure over 16 months. No patient exposed to even one chronic highly threatening stressor improved clinically (by 50%) over the 16 months; all patients who improved did so in the absence of such a stressor. Conclusion—The level of chronic life stress threat predicts the clinical outcome in most patients with IBS/FD.
Keywords: irritable bowel syndrome; chronic life stress threat; symptom intensity
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (120.7 KB).
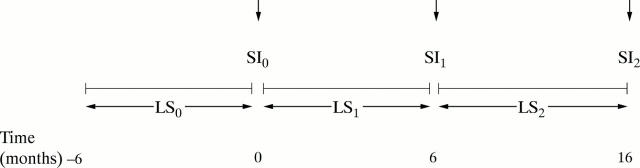
Figure 1 .
Schematic illustration of the longitudinal study design. LS, average chronic threat intensity during the six months or more prior to entry (LS0), at six months (LS1), and 16 months (LS2); SI, average symptom intensity during the following two weeks (SI0, SI1, SI2).
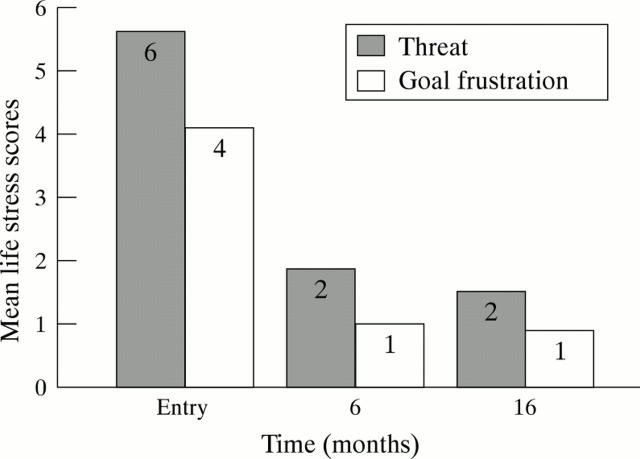
Figure 2 .
Mean chronic life stress scores for threat and goal frustration at entry, six months, and 16 months.
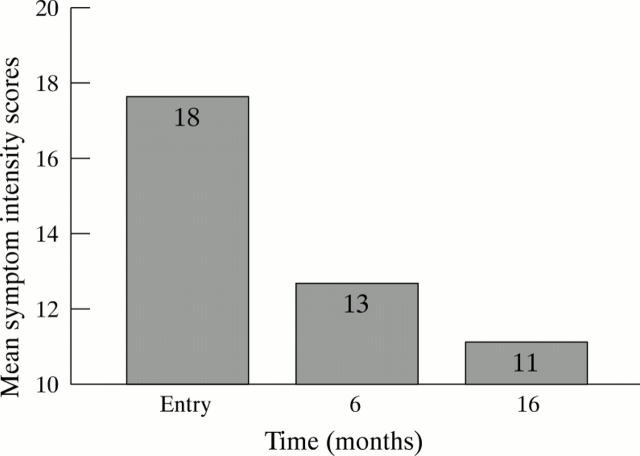
Figure 3 .
Mean symptom intensity scores at entry, six months, and 16 months.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agréus L., Svärdsudd K., Nyrén O., Tibblin G. Irritable bowel syndrome and dyspepsia in the general population: overlap and lack of stability over time. Gastroenterology. 1995 Sep;109(3):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90373-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett E. J., Piesse C., Palmer K., Badcock C. A., Tennant C. C., Kellow J. E. Functional gastrointestinal disorders: psychological, social, and somatic features. Gut. 1998 Mar;42(3):414–420. doi: 10.1136/gut.42.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett E., Beaurepaire J., Langeluddecke P., Kellow J., Tennant C. Life stress and non-ulcer dyspepsia: a case-control study. J Psychosom Res. 1991;35(4-5):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(91)90052-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAUDHARY N. A., TRUELOVE S. C. The irritable colon syndrome. A study of the clinical features, predisposing causes, and prognosis in 130 cases. Q J Med. 1962 Jul;31:307–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassileth B. R., Drossman D. A. Psychosocial factors in gastrointestinal illness. Psychother Psychosom. 1993;59(3-4):131–143. doi: 10.1159/000288657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig T. K., Brown G. W. Goal frustration and life events in the aetiology of painful gastrointestinal disorder. J Psychosom Res. 1984;28(5):411–421. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(84)90073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dancey C. P., Whitehouse A., Painter J., Backhouse S. The relationship between hassles, uplifts and irritable bowel syndrome: a preliminary study. J Psychosom Res. 1995 Oct;39(7):827–832. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(95)00016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinan T. G., O'Keane V., O'Boyle C., Chua A., Keeling P. W. A comparison of the mental status, personality profiles and life events of patients with irritable bowel syndrome and peptic ulcer disease. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1991 Jul;84(1):26–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1991.tb01416.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drossman D. A., McKee D. C., Sandler R. S., Mitchell C. M., Cramer E. M., Lowman B. C., Burger A. L. Psychosocial factors in the irritable bowel syndrome. A multivariate study of patients and nonpatients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1988 Sep;95(3):701–708. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(88)80017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford M. J. The irritable bowel syndrome. J Psychosom Res. 1986;30(4):399–410. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(86)90079-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayson D. A. Latent trait analysis of the Eysenck Personality Questionnaire. J Psychiatr Res. 1986;20(3):217–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(86)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie E., Creed F., Dawson D., Tomenson B. A controlled trial of psychological treatment for the irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1991 Feb;100(2):450–457. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haug T. T., Wilhelmsen I., Berstad A., Ursin H. Life events and stress in patients with functional dyspepsia compared with patients with duodenal ulcer and healthy controls. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1995 Jun;30(6):524–530. doi: 10.3109/00365529509089784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui W. M., Shiu L. P., Lam S. K. The perception of life events and daily stress in nonulcer dyspepsia. Am J Gastroenterol. 1991 Mar;86(3):292–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Srivastava E. D., Sadlier M., Swann P., James J. Y., Rhodes J. Stress management for irritable bowel syndrome: a controlled trial. Digestion. 1991;50(1):36–42. doi: 10.1159/000200738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suls J., Wan C. K., Blanchard E. B. A multilevel data-analytic approach for evaluation of relationships between daily life stressors and symptomatology: patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Health Psychol. 1994 Mar;13(2):103–113. doi: 10.1037//0278-6133.13.2.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J., Piper D. W. A prospective study of social factors and major life event stress in patients with dyspepsia of unknown cause. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1987 Apr;22(3):268–272. doi: 10.3109/00365528709078590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J., Weaver A. L., Zinsmeister A. R., Melton L. J., 3rd Onset and disappearance of gastrointestinal symptoms and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Am J Epidemiol. 1992 Jul 15;136(2):165–177. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennant C., Smith A., Bebbington P., Hurry J. The contextual threat of life events: the concept and its reliability. Psychol Med. 1979 Aug;9(3):525–528. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700032086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller S. L., Misiewicz J. J. Prognosis in the irritable-bowel syndrome. A prospective study. Lancet. 1969 Oct 11;2(7624):754–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead W. E. Assessing the effects of stress on physical symptoms. Health Psychol. 1994 Mar;13(2):99–102. doi: 10.1037//0278-6133.13.2.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead W. E., Crowell M. D., Robinson J. C., Heller B. R., Schuster M. M. Effects of stressful life events on bowel symptoms: subjects with irritable bowel syndrome compared with subjects without bowel dysfunction. Gut. 1992 Jun;33(6):825–830. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.6.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]