Abstract
Background—Helicobacter pylori urease is a major target for immune responses among various bacterial components in H pylori infected patients. Aims—To analyse the relation between systemic and local humoral immune responses to H pylori urease and grades of chronic gastritis. Patients—Seventy five patients with chronic gastritis associated with H pylori infection were classified into three groups (grade I, superficial gastritis; II, atrophic gastritis, quiescent; or III, atrophic gastritis, active). Methods—Anti-H pylori urease specific antibodies in the serum, gastric juice, and biopsy specimens were determined by ELISA or western blotting analysis. The sites for H pylori urease and its specific antibody producing B lymphocytes were confirmed by immunohistochemical analysis. Results—In the sera of patients with grade I gastritis, weak IgG but relatively strong IgA responses to H pylori urease were observed; dominant strong IgG responses were detected in grade II gastritis. In grade III gastritis, significant IgG and IgA responses were obtained. A similar pattern of IgA and IgG responses was detected in gastric juice and tissue. H pylori urease specific, antibody producing B cells were not found in the gastric mucosa of patients with grade I gastritis despite the presence of such B cells in the duodenal bulb. Specific B cells were observed in the gastric mucosa of patients with grade II and III gastritis with atrophy. Conclusions—Purified H pylori urease, together with localisation of its specific antibody producing B cells, are useful for serological testing and histopathological analysis for determining the stage of chronic gastritis and studying the pathogenesis of H pylori infection.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; urease; chronic gastritis; B lymphocytes; antibody production; local immunity
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (243.6 KB).
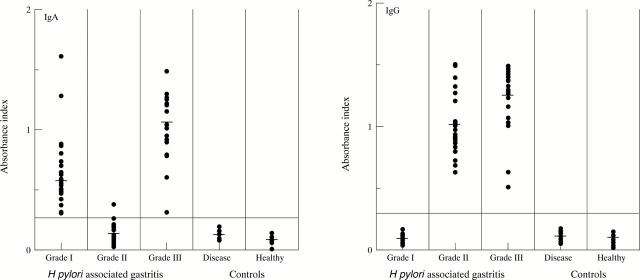
Figure 1 .
H pylori urease specific IgG and IgA responses in sera. Horizontal bars represent median values. Horizontal lines indicate cut off levels used in the assay.
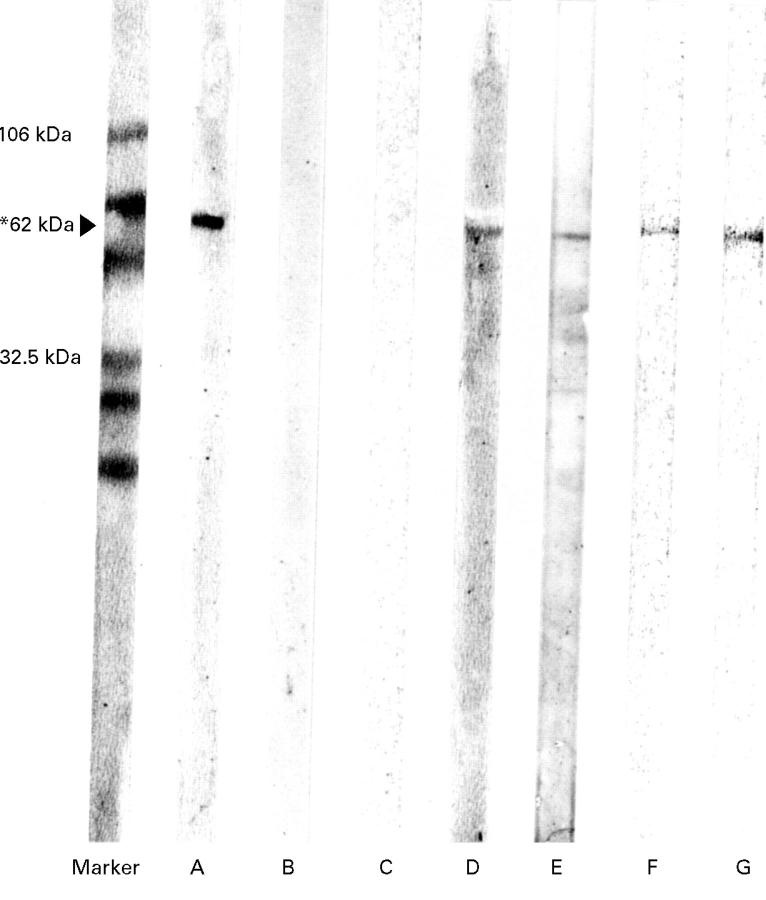
Figure 2 .
H pylori urease heavy chain (62 kDa) specific IgG, IgA, and SC responses in the gastric juice of patients. Lanes A-C, grade II gastritis; lanes D-F, grade III gastritis with haemorrhagic erosions found endoscopically; lane G, duodenal ulcer (active stage). Lanes A,D, IgG; lanes B,E, IgA; lanes C,F,G, SC.
Figure 3 .
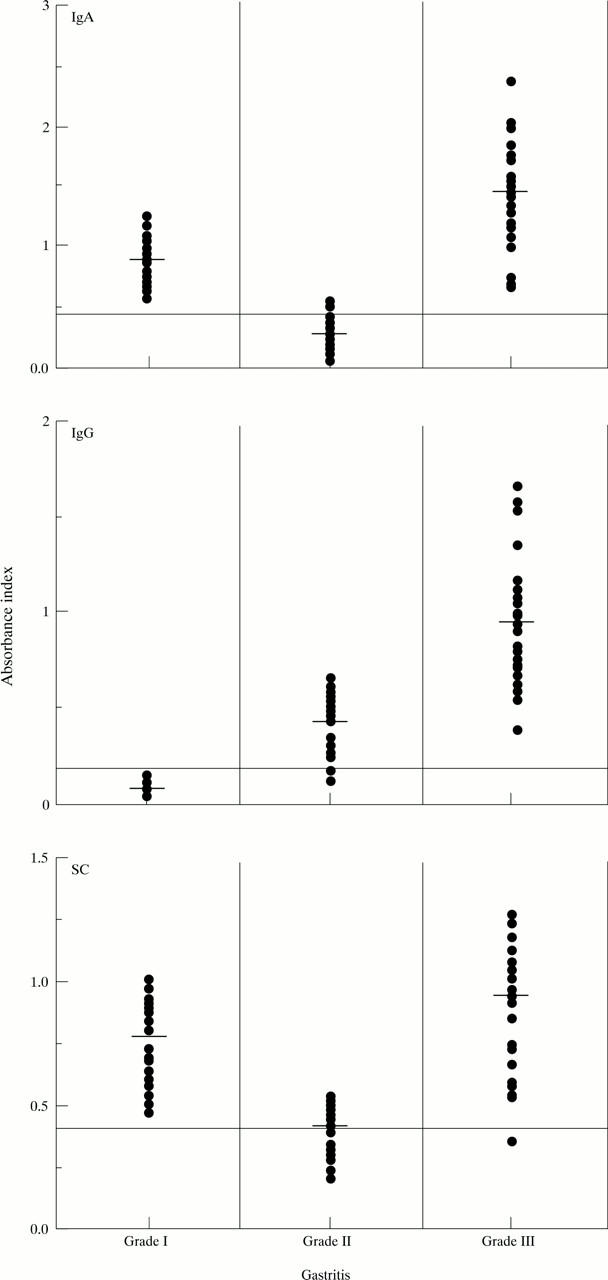
H pylori urease specific IgG, IgA, and SC responses in gastric tissue. Horizontal bars represent median values. Horizontal lines indicate cut off levels used in the assay.
Figure 4 .
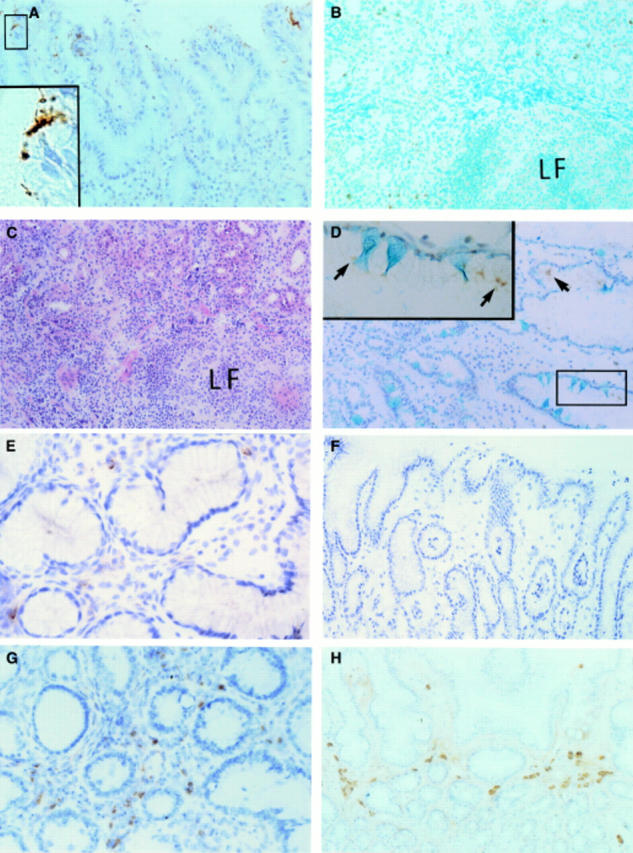
Immunohistochemical analysis of H pylori urease specific humoral responses. (A) Localisation of H pylori and H pylori urease in the stomach of a patient with grade III gastritis (enzyme immunohistochemistry with monoclonal H pylori urease specific antibody; Meyer's haematoxylin, original magnification ×160); a higher maginification (×800) of the boxed area indicated in the left upper corner is shown in the left lower corner. (B) Distribution of H pylori urease specific antibody producing B lymphocytes (plasma cells) in the same tissue (enzyme immunohistochemistry with purified H pylori urease and monoclonal H pylori urease specific antibody; methyl green, original magnification ×150); LF, lymphoid follicle. (C) Localisation of mononuclear cells in the same tissue (haematoxylin and eosin, original magnification ×150). (D) Localisation of H pylori and H pylori urease indicated by arrows in the stomach of a patient with grade II gastritis (enzyme immunohistochemistry with monoclonal H pylori urease specific antibody; Alcian blue, original magnification ×160); a higher magnification (×640) of the boxed area indicated in the right lower corner is shown in the left upper corner. (E) Distribution of H pylori urease specific B cells in the stomach from the same patient (enzyme immunohistochemistry with purified H pylori urease and monoclonal H pylori urease specific antibody; Meyer's haematoxylin, original magnification ×250). (F) Distribution of H pylori urease specific plasma cells in the stomach of a patient with grade I gastritis (enzyme immunohistochemistry with purified H pylori urease and monoclonal H pylori urease specific antibody; Meyer's haematoxylin, original magnification ×125). (G) Detection of H pylori urease specific B cells in the duodenal bulb from the same patient with grade I gastritis bearing duodenitis (enzyme immunohistochemistry with purified H pylori urease and monoclonal H pylori urease specific antibody; Meyer's haematoxylin, original magnification ×200). (H) Distribution of IgA producing B cells in the stomach of the same patient (enzyme immunohistochemistry with antihuman IgA antibody, original magnification ×132).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atherton J. C., Spiller R. C. The urea breath test for Helicobacter pylori. Gut. 1994 Jun;35(6):723–725. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.6.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum H., Davies H., Peakman M. Molecular mimicry in the MHC: hidden clues to autoimmunity? Immunol Today. 1996 Feb;17(2):64–70. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(96)80581-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berstad A. E., Brandtzaeg P., Stave R., Halstensen T. S. Epithelium related deposition of activated complement in Helicobacter pylori associated gastritis. Gut. 1997 Feb;40(2):196–203. doi: 10.1136/gut.40.2.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienenstock J., Befus A. D. Some thoughts on the biologic role of immunoglobulin A. Gastroenterology. 1983 Jan;84(1):178–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J. Gastric Campylobacter-like organisms, gastritis, and peptic ulcer disease. Gastroenterology. 1987 Aug;93(2):371–383. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)91028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X. G., Correa P., Offerhaus J., Rodriguez E., Janney F., Hoffmann E., Fox J., Hunter F., Diavolitsis S. Ultrastructure of the gastric mucosa harboring Campylobacter-like organisms. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Nov;86(5):575–582. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/86.5.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. L., Pallen M. J., Kleanthous H., Wren B. W., Tabaqchali S. Nucleotide sequence of two genes from Helicobacter pylori encoding for urease subunits. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 25;18(2):362–362. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.2.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covacci A., Censini S., Bugnoli M., Petracca R., Burroni D., Macchia G., Massone A., Papini E., Xiang Z., Figura N. Molecular characterization of the 128-kDa immunodominant antigen of Helicobacter pylori associated with cytotoxicity and duodenal ulcer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5791–5795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree J. E., Figura N., Taylor J. D., Bugnoli M., Armellini D., Tompkins D. S. Expression of 120 kilodalton protein and cytotoxicity in Helicobacter pylori. J Clin Pathol. 1992 Aug;45(8):733–734. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.8.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree J. E., Shallcross T. M., Heatley R. V., Wyatt J. I. Mucosal tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 in patients with Helicobacter pylori associated gastritis. Gut. 1991 Dec;32(12):1473–1477. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.12.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree J. E., Shallcross T. M., Wyatt J. I., Taylor J. D., Heatley R. V., Rathbone B. J., Losowsky M. S. Mucosal humoral immune response to Helicobacter pylori in patients with duodenitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1991 Sep;36(9):1266–1273. doi: 10.1007/BF01307520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czinn S., Carr H., Sheffler L., Aronoff S. Serum IgG antibody to the outer membrane proteins of Campylobacter pylori in children with gastroduodenal disease. J Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;159(3):586–589. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.3.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J. C., McNulty C. A., Uff J. S., Gear M. W., Wilkinson S. P. Campylobacter pylori urease: a new serological test. Lancet. 1988 Apr 30;1(8592):1002–1002. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91827-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon M. F. Helicobacter pylori and peptic ulceration: histopathological aspects. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1991 Mar-Apr;6(2):125–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1991.tb01451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. E., Roop R. M., 2nd, Sung C. C., Sharma S. A., Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Identification and purification of a cpn60 heat shock protein homolog from Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1946–1951. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1946-1951.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton K. A., Brooks C. L., Morgan D. R., Krakowka S. Essential role of urease in pathogenesis of gastritis induced by Helicobacter pylori in gnotobiotic piglets. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2470–2475. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2470-2475.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton K. A., Krakowka S. Effect of gastric pH on urease-dependent colonization of gnotobiotic piglets by Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun. 1994 Sep;62(9):3604–3607. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.9.3604-3607.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Engstrand L., Graham D. Y. Urease-associated heat shock protein of Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):2125–2127. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.2125-2127.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futagami S., Takahashi H., Norose Y., Nagata K., Kobayashi M., Nomura T. [Analysis of immune response to Helicobacter pylori--identification of the protein recognized by anti-Helicobacter pylori antibodies from sera of patients with gastroduodenal diseases]. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 1994 Dec;91(12):2202–2213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray S. F., Wyatt J. I., Rathbone B. J. Simplified techniques for identifying Campylobacter pyloridis. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Nov;39(11):1279–1279. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.11.1279-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaetzel C. S., Robinson J. K., Chintalacharuvu K. R., Vaerman J. P., Lamm M. E. The polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (secretory component) mediates transport of immune complexes across epithelial cells: a local defense function for IgA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8796–8800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karttunen R., Karttunen T., Ekre H. P., MacDonald T. T. Interferon gamma and interleukin 4 secreting cells in the gastric antrum in Helicobacter pylori positive and negative gastritis. Gut. 1995 Mar;36(3):341–345. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.3.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuning J., Lindeman J., Biemond I., Lamers C. B. Relation between IgG and IgA antibody titres against Helicobacter pylori in serum and severity of gastritis in asymptomatic subjects. J Clin Pathol. 1994 Mar;47(3):227–231. doi: 10.1136/jcp.47.3.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers E. J., Peña A. S., van Kamp G., Uyterlinde A. M., Pals G., Pels N. F., Kurz-Pohlmann E., Meuwissen S. G. Seroconversion for Helicobacter pylori. Lancet. 1993 Aug 7;342(8867):328–331. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91473-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leunk R. D., Ferguson M. A., Morgan D. R., Low D. E., Simor A. E. Antibody to cytotoxin in infection by Helicobacter pylori. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1181–1184. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1181-1184.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mai U. E., Perez-Perez G. I., Wahl L. M., Wahl S. M., Blaser M. J., Smith P. D. Soluble surface proteins from Helicobacter pylori activate monocytes/macrophages by lipopolysaccharide-independent mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):894–900. doi: 10.1172/JCI115095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Warren J. R., Francis G. J., Langton S. R., Goodwin C. S., Blincow E. D. Rapid urease test in the management of Campylobacter pyloridis-associated gastritis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987 Mar;82(3):200–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukura N., Onda M., Tokunaga A., Matsuda N., Yamashita K. Mucosal IgA antibody against Helicobacter pylori in chronic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia detected by the Tes-Tape method in resection specimens after gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Cancer. 1995 Mar 15;75(6 Suppl):1472–1477. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19950315)75:6+<1472::aid-cncr2820751515>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazanec M. B., Nedrud J. G., Kaetzel C. S., Lamm M. E. A three-tiered view of the role of IgA in mucosal defense. Immunol Today. 1993 Sep;14(9):430–435. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90245-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Mizuta T., Tonokatu Y., Fukuda Y., Okamura H., Hayashi T., Shimoyama T., Tamura T. Monoclonal antibodies against the native urease of Helicobacter pylori: synergistic inhibition of urease activity by monoclonal antibody combinations. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4826–4831. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4826-4831.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negrini R., Lisato L., Cavazzini L., Maini P., Gullini S., Basso O., Lanza G., Jr, Garofalo M., Nenci I. Monoclonal antibodies for specific immunoperoxidase detection of Campylobacter pylori. Gastroenterology. 1989 Feb;96(2 Pt 1):414–420. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91565-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. G. Identification of the outer membrane proteins of Campylobacter pyloridis and antigenic cross-reactivity between C. pyloridis and C. jejuni. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jan;133(1):163–170. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-1-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Friedman G. D., Orentreich N., Vogelman H. Risk for gastric cancer in people with CagA positive or CagA negative Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut. 1997 Mar;40(3):297–301. doi: 10.1136/gut.40.3.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P., Mendall M. A., Khulusi S., Molineaux N., Levy J., Maxwell J. D., Northfield T. C. Salivary antibodies to Helicobacter pylori: screening dyspeptic patients before endoscopy. Lancet. 1994 Aug 20;344(8921):511–512. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91899-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peña A. S., Endtz H. P., Offerhaus G. J., Hoogenboom-Verdegaal A., van Duijn W., de Vargas N., den Hartog G., Kreuning J., van der Reyden J., Mouton R. P. Value of serology (ELISA and immunoblotting) for the diagnosis of Campylobacter pylori infection. Digestion. 1989;44(3):131–141. doi: 10.1159/000199902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. B. The Sydney System: histological division. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1991 May-Jun;6(3):209–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1991.tb01468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Pérez G. I., Brown W. R., Cover T. L., Dunn B. E., Cao P., Blaser M. J. Correlation between serological and mucosal inflammatory responses to Helicobacter pylori. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1994 May;1(3):325–329. doi: 10.1128/cdli.1.3.325-329.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veenendaal R. A., Götz J. M., Schroijen V., Kurban F., Bernards A. T., Veselic M., Peña A. S., Lamers C. B. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection by specific gastric mucosal IgA and IgG pylori antibodies. J Clin Pathol. 1995 Nov;48(11):990–993. doi: 10.1136/jcp.48.11.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead R., Truelove S. C., Gear M. W. The histological diagnosis of chronic gastritis in fibreoptic gastroscope biopsy specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Jan;25(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. I., Rathbone B. J., Heatley R. V. Local immune response to gastric Campylobacter in non-ulcer dyspepsia. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Aug;39(8):863–870. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.8.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]