Abstract
Background—bcl-2 and bax belong to the bcl-2-related gene family, which marks a new class of genes that influence apoptosis. The bcl-2 oncogene acts as a broad antiapoptotic factor and extends both normal and tumour cell survival. In contrast, the bax gene is a promoter of apoptosis. Aims—To analyse the expression of bcl-2 and bax in pancreatic cancer and correlate the results with clinical parameters. Patients—Pancreatic cancer tissue samples were obtained from 28 female and 32 male patients (median age 63, range 43-79 years) having surgery for pancreatic cancer. Normal pancreatic tissues obtained from 18 previously healthy organ donors served as controls. Methods—The levels of bcl-2 and bax mRNA expression were analysed by northern blot and the exact site of mRNA transcription was determined by in situ hybridisation. The presence of the corresponding proteins was determined by immunohistochemistry. Results—Northern blot analysis indicated that, in comparison with the normal pancreas, bcl-2 mRNA was overexpressed in 30% and bax mRNA in 61% of the pancreatic cancer samples. Concomitant overexpression of bcl-2 and bax was present in 26% of the cancer samples. Pancreatic adenocarcinomas exhibited 3.7-fold and 5.4-fold increases (p<0.001) in bcl-2 and bax mRNA levels respectively. In situ hybridisation showed that both bcl-2 and bax mRNA were expressed in the cancer cells. Immunohistochemical analysis showed positive Bcl-2 and Bax immunostaining in 28 and 83% of the cancer samples respectively. In multivariate analysis (Cox regression model), bax expression was found to be a strong indicator of survival (p<0.001). Patients whose tumours exhibited Bax immunostaining lived significantly longer (12 months) than those whose tumours were Bax negative (five months) (p<0.039). In contrast, no relation was found between Bcl-2 and survival time. Conclusions—The data indicate that genes that are involved in the regulation of apoptosis are upregulated in human pancreatic cancer cells. Prolonged survival times in patients in whom apoptosis promoting factors are upregulated indicate that apoptotic pathways are of biological significance in pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: pancreatic cancer; apoptosis; immunohistochemistry; northern blot analysis; in situ hybridisation
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (229.2 KB).
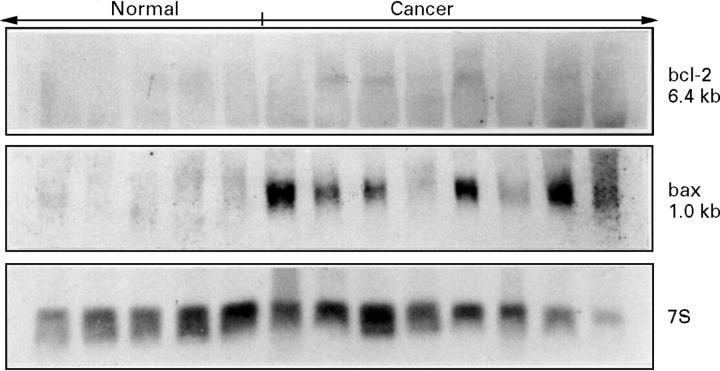
Figure 1 .
Northern blot analysis of bcl-2 and bax in the normal pancreas (Normal, n=5) and in pancreatic cancer (Cancer, n=8).
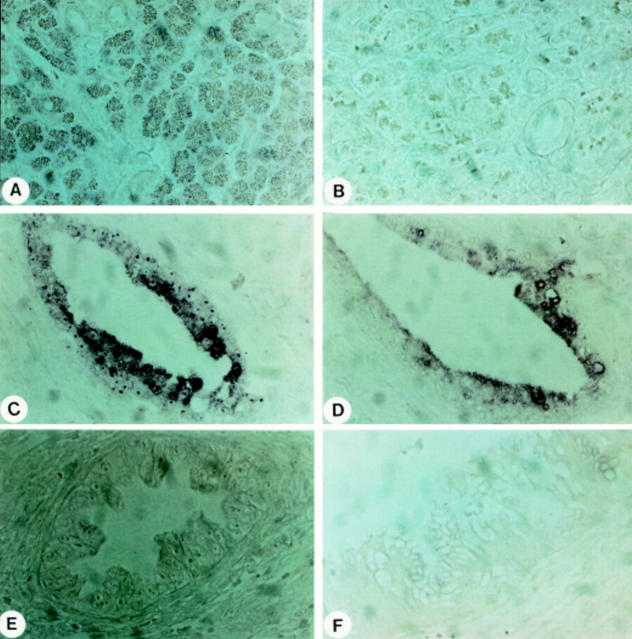
Figure 2 .
In situ hybridisation of bcl-2 (A, C) and bax (B, D) in the normal pancreas (A, B) and in pancreatic cancer (C-F). Panels C and D are consecutive pancreatic cancer tissue sections showing cancer cells with concomitant bcl-2 (C) and bax (D) mRNA expression. However, not all cancer cells exhibit bax or bcl-2 mRNA expression. Hybridisation of pancreatic cancer sections with the bcl-2 (E) and bax (F) sense probes failed to give a signal. Original magnification × 400.
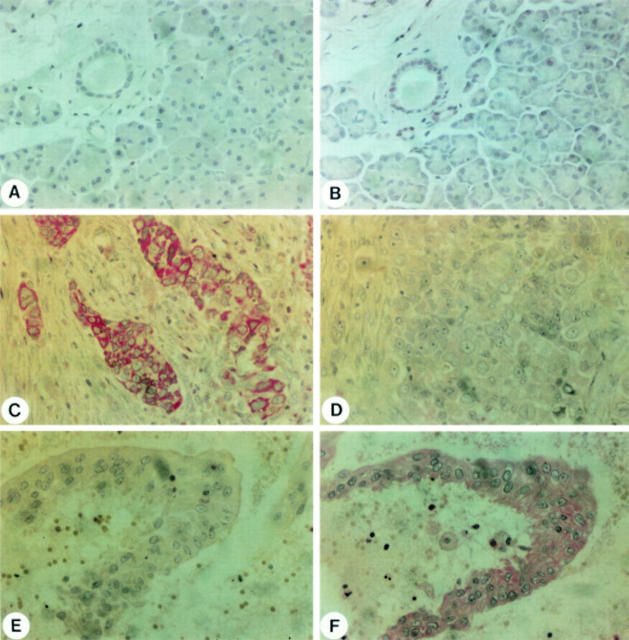
Figure 3 .
Immunohistochemical analysis of Bcl-2 (A, C, E) and Bax (B, D, F) in the normal pancreas (A, B) and in pancreatic cancer (C-F). Panels C and D and E and F are consecutive pancreatic cancer tissue sections. Panels C and D show pancreatic cancer cells that exhibit Bcl-2 (C) immunoreactivity but no Bax (D) immunostaining. Panels E and F show pancreatic cancer cells that do not exhibit Bcl-2 (E) immunoreactivity but do exhibit Bax (F) immunostaining. Original magnification × 400.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bargou R. C., Daniel P. T., Mapara M. Y., Bommert K., Wagener C., Kallinich B., Royer H. D., Dörken B. Expression of the bcl-2 gene family in normal and malignant breast tissue: low bax-alpha expression in tumor cells correlates with resistance towards apoptosis. Int J Cancer. 1995 Mar 16;60(6):854–859. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910600622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosari S., Moneghini L., Graziani D., Lee A. K., Murray J. J., Coggi G., Viale G. bcl-2 oncoprotein in colorectal hyperplastic polyps, adenomas, and adenocarcinomas. Hum Pathol. 1995 May;26(5):534–540. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90250-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchler M., Friess H., Schultheiss K. H., Gebhardt C., Kübel R., Muhrer K. H., Winkelmann M., Wagener T., Klapdor R., Kaul M. A randomized controlled trial of adjuvant immunotherapy (murine monoclonal antibody 494/32) in resectable pancreatic cancer. Cancer. 1991 Oct 1;68(7):1507–1512. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19911001)68:7<1507::aid-cncr2820680707>3.0.co;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos L., Rouault J. P., Sabido O., Oriol P., Roubi N., Vasselon C., Archimbaud E., Magaud J. P., Guyotat D. High expression of bcl-2 protein in acute myeloid leukemia cells is associated with poor response to chemotherapy. Blood. 1993 Jun 1;81(11):3091–3096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattoretti G., Becker M. H., Key G., Duchrow M., Schlüter C., Galle J., Gerdes J. Monoclonal antibodies against recombinant parts of the Ki-67 antigen (MIB 1 and MIB 3) detect proliferating cells in microwave-processed formalin-fixed paraffin sections. J Pathol. 1992 Dec;168(4):357–363. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox K. H., DeLeon D. V., Angerer L. M., Angerer R. C. Detection of mrnas in sea urchin embryos by in situ hybridization using asymmetric RNA probes. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):485–502. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friess H., Berberat P., Schilling M., Kunz J., Korc M., Büchler M. W. Pancreatic cancer: the potential clinical relevance of alterations in growth factors and their receptors. J Mol Med (Berl) 1996 Jan;74(1):35–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00202070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friess H., Büchler M., Krüger M., Beger H. G. Treatment of duct carcinoma of the pancreas with the LH-RH analogue buserelin. Pancreas. 1992;7(5):516–521. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199209000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friess H., Yamanaka Y., Büchler M., Berger H. G., Kobrin M. S., Baldwin R. L., Korc M. Enhanced expression of the type II transforming growth factor beta receptor in human pancreatic cancer cells without alteration of type III receptor expression. Cancer Res. 1993 Jun 15;53(12):2704–2707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friess H., Yamanaka Y., Büchler M., Ebert M., Beger H. G., Gold L. I., Korc M. Enhanced expression of transforming growth factor beta isoforms in pancreatic cancer correlates with decreased survival. Gastroenterology. 1993 Dec;105(6):1846–1856. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91084-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graber H. U., Müller C. F., Vandevelde M., Zurbriggen A. Restricted infection with canine distemper virus leads to down-regulation of myelin gene transcription in cultured oligodendrocytes. Acta Neuropathol. 1995;90(3):312–318. doi: 10.1007/BF00296516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gress T. M., Müller-Pillasch F., Lerch M. M., Friess H., Büchler M., Adler G. Expression and in-situ localization of genes coding for extracellular matrix proteins and extracellular matrix degrading proteases in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 1995 Aug 9;62(4):407–413. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910620409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo X., Friess H., Graber H. U., Kashiwagi M., Zimmermann A., Korc M., Büchler M. W. KAI1 expression is up-regulated in early pancreatic cancer and decreased in the presence of metastases. Cancer Res. 1996 Nov 1;56(21):4876–4880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellemans P., van Dam P. A., Weyler J., van Oosterom A. T., Buytaert P., Van Marck E. Prognostic value of bcl-2 expression in invasive breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1995 Aug;72(2):354–360. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korc M., Chandrasekar B., Yamanaka Y., Friess H., Buchier M., Beger H. G. Overexpression of the epidermal growth factor receptor in human pancreatic cancer is associated with concomitant increases in the levels of epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor alpha. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1352–1360. doi: 10.1172/JCI116001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 initiates a new category of oncogenes: regulators of cell death. Blood. 1992 Aug 15;80(4):879–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S. J., Shutter J. R., Veis D. J., Merry D. E., Oltvai Z. N. Bcl-2/Bax: a rheostat that regulates an anti-oxidant pathway and cell death. Semin Cancer Biol. 1993 Dec;4(6):327–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajewski S., Blomqvist C., Franssila K., Krajewska M., Wasenius V. M., Niskanen E., Nordling S., Reed J. C. Reduced expression of proapoptotic gene BAX is associated with poor response rates to combination chemotherapy and shorter survival in women with metastatic breast adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1995 Oct 1;55(19):4471–4478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauwers G. Y., Scott G. V., Karpeh M. S. Immunohistochemical evaluation of bcl-2 protein expression in gastric adenocarcinomas. Cancer. 1995 May 1;75(9):2209–2213. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19950501)75:9<2209::aid-cncr2820750904>3.0.co;2-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leek R. D., Kaklamanis L., Pezzella F., Gatter K. C., Harris A. L. bcl-2 in normal human breast and carcinoma, association with oestrogen receptor-positive, epidermal growth factor receptor-negative tumours and in situ cancer. Br J Cancer. 1994 Jan;69(1):135–139. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemoine N. R., Lobresco M., Leung H., Barton C., Hughes C. M., Prigent S. A., Gullick W. J., Klöppel G. The erbB-3 gene in human pancreatic cancer. J Pathol. 1992 Nov;168(3):269–273. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Deane N., Platt F. M., Nunez G., Jaeger U., McKearn J. P., Korsmeyer S. J. bcl-2-immunoglobulin transgenic mice demonstrate extended B cell survival and follicular lymphoproliferation. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Troncoso P., Brisbay S. M., Logothetis C., Chung L. W., Hsieh J. T., Tu S. M., Campbell M. L. Expression of the protooncogene bcl-2 in the prostate and its association with emergence of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 15;52(24):6940–6944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit K., Wong G., Filippa D. A., Tao Y., Chaganti R. S. Cytogenetic analysis of 434 consecutively ascertained specimens of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: clinical correlations. Blood. 1991 Apr 1;77(7):1508–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofner D., Riehemann K., Maier H., Riedmann B., Nehoda H., Tötsch M., Böcker W., Jasani B., Schmid K. W. Immunohistochemically detectable bcl-2 expression in colorectal carcinoma: correlation with tumour stage and patient survival. Br J Cancer. 1995 Oct;72(4):981–985. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oltvai Z. N., Milliman C. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):609–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90509-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker S. L., Tong T., Bolden S., Wingo P. A. Cancer statistics, 1997. CA Cancer J Clin. 1997 Jan-Feb;47(1):5–27. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.47.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella F., Turley H., Kuzu I., Tungekar M. F., Dunnill M. S., Pierce C. B., Harris A., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. bcl-2 protein in non-small-cell lung carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1993 Sep 2;329(10):690–694. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199309023291003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilotti S., Collini P., Rilke F., Cattoretti G., Del Bo R., Pierotti M. A. Bcl-2 protein expression in carcinomas originating from the follicular epithelium of the thyroid gland. J Pathol. 1994 Apr;172(4):337–342. doi: 10.1002/path.1711720408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C. Bcl-2 and the regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riesle E., Friess H., Zhao L., Wagner M., Uhl W., Baczako K., Gold L. I., Korc M., Büchler M. W. Increased expression of transforming growth factor beta s after acute oedematous pancreatitis in rats suggests a role in pancreatic repair. Gut. 1997 Jan;40(1):73–79. doi: 10.1136/gut.40.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedlak T. W., Oltvai Z. N., Yang E., Wang K., Boise L. H., Thompson C. B., Korsmeyer S. J. Multiple Bcl-2 family members demonstrate selective dimerizations with Bax. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 15;92(17):7834–7838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto M., Jaeger U., Hockett R. D., Graninger W., Bennett S., Goldman P., Korsmeyer S. J. Alternative promoters and exons, somatic mutation and deregulation of the Bcl-2-Ig fusion gene in lymphoma. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):123–131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02791.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Croce C. M. Analysis of the structure, transcripts, and protein products of bcl-2, the gene involved in human follicular lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5214–5218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie F. S., Dawson T., Bond J. A., Goretzki P., Game S., Prime S., Wynford-Thomas D. Correlated abnormalities of transforming growth factor-beta 1 response and p53 expression in thyroid epithelial cell transformation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1991 Apr;76(1-3):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(91)90255-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka Y., Friess H., Buchler M., Beger H. G., Uchida E., Onda M., Kobrin M. S., Korc M. Overexpression of acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors in human pancreatic cancer correlates with advanced tumor stage. Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 1;53(21):5289–5296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J., Mayer M. G., Arnesen M. A., Aeppli D. P., Oken M. M., Frizzera G. bcl-2 and other genomic alterations in the prognosis of large-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 20;320(16):1047–1054. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904203201605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]