Abstract
Background—Laminin receptors are involved in cell-extracellular matrix interactions in malignant cells that show invasion and metastasis. Hepatocellular carcinoma frequently shows early invasion into blood vessels, and intrahepatic and extrahepatic metastases. However, the role of laminin receptors in hepatocellular carcinoma is unknown. Aims—To examine the expression of mRNA for laminin receptors and their isoforms in hepatocellular carcinoma. Methods—The expression of several laminin receptors, including α1 integrin, α6 integrin and its isoforms α6A and α6B, β1 integrin and its isoforms β1A and β1B, and 32kD/67kDa laminin binding protein was examined in human hepatocellular carcinomas and non-cancerous liver tissues using the reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Results—α6 Integrin, β1 integrin, and laminin binding protein showed notably increased expression in hepatocellular carcinoma, compared with non-cancerous liver tissue, although the α1 integrin did not show a significant change. Furthermore, β1B integrin, a splicing variant of β1 integrin, was overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma while the β1A integrin isoform did not show significant changes between hepatocellular carcinoma and surrounding non-cancerous liver tissue. Conclusions—The differential upregulation of laminin receptors and their splicing isoforms was shown in hepatocellular carcinoma, suggesting that certain laminin receptors and their isoforms may be involved in the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Keywords: laminin receptor; integrin α6β1; hepatocellular carcinoma
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (202.0 KB).
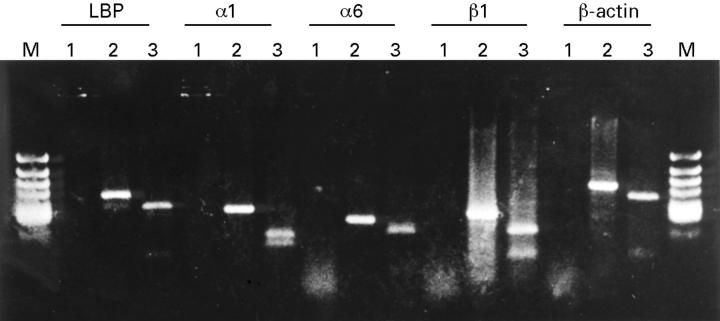
Figure 1 .
RT-PCR products of laminin binding protein (LBP), α1 integrin, α6 integrin, β1 integrin, and β-actin separated by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. Lane 1: RT-PCR without reverse transcriptase. Lane 2: RT-PCR with reverse transcriptase. Lane 3: the products of lane 2 digested with a specific restriction enzyme based on the sequence data.
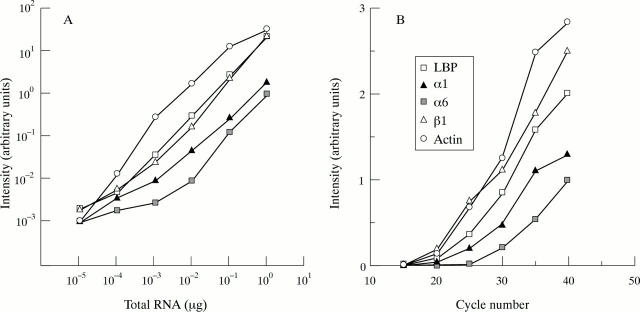
Figure 2 .
Densitometric semiquantification of the RT-PCR products showed association with the amount of RNA applied (A), and the number of PCR cycles (B).
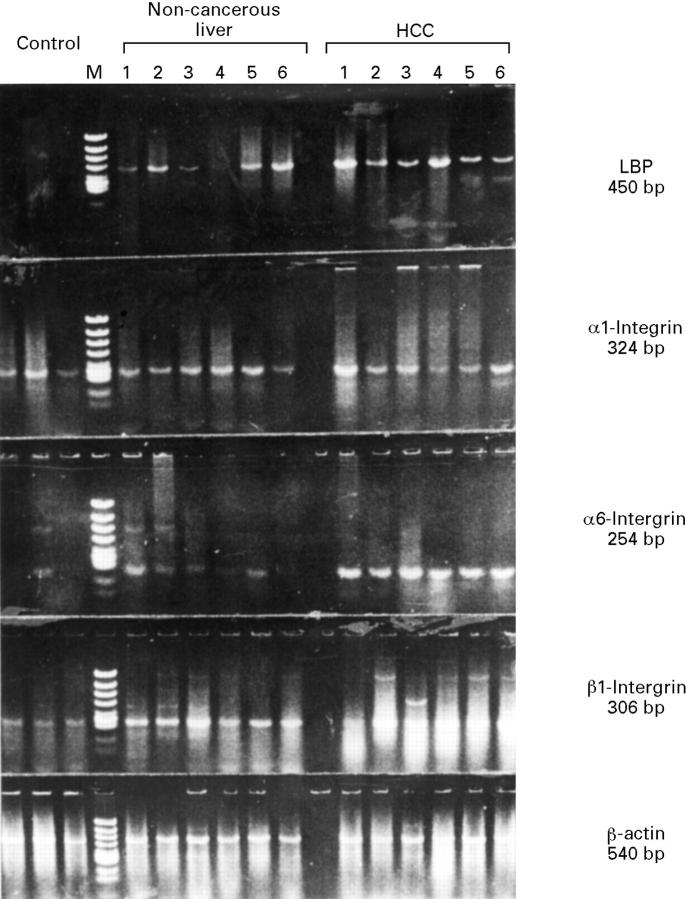
Figure 3 .
Gene expression of LBP, α1 integrin, α6 integrin, β1 integrin, and β-actin in six representative samples of human liver tissue detected by RT-PCR. Identical lane numbers indicate that the tissue was obtained from the same patient with chronic liver disease and HCC.
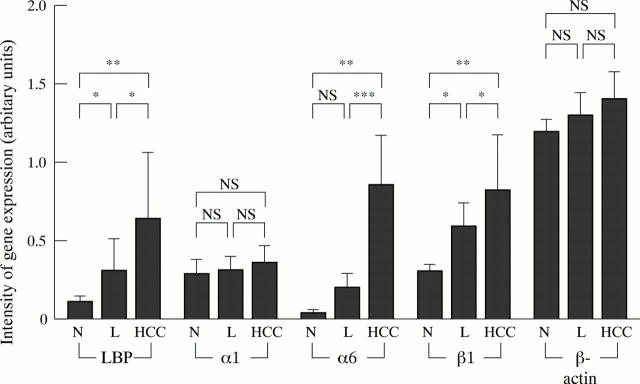
Figure 4 .
Semiquantitative analysis of LBP, α1 integrin, α6 integrin, β1 integrin, and β-actin gene expression in normal liver (N, n=3), chronically diseased, non-cancerous liver (L, n=16), and HCC tissue (n=16) detected by RT-PCR. Data are presented as mean (SD). *p<0.05; **p<0.01; *** p<0.001.
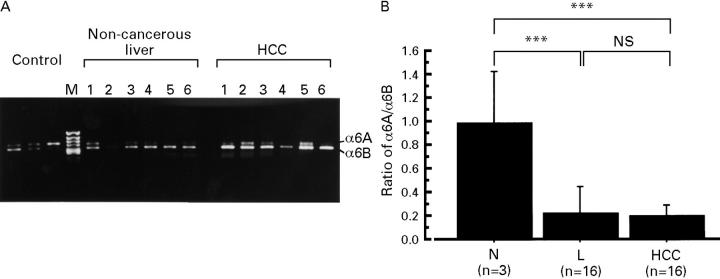
Figure 5 .
(A) Representative expression of the α6 integrin isoforms, α6A and α6B, by RT-PCR from six patients. (B) The α6B:α6A ratio detected by densitometry in normal liver (N, n=3), chronically diseased, non-cancerous liver (L, n=16), and HCC (n=16). Values are presented as mean (SD). ***p<0.001.
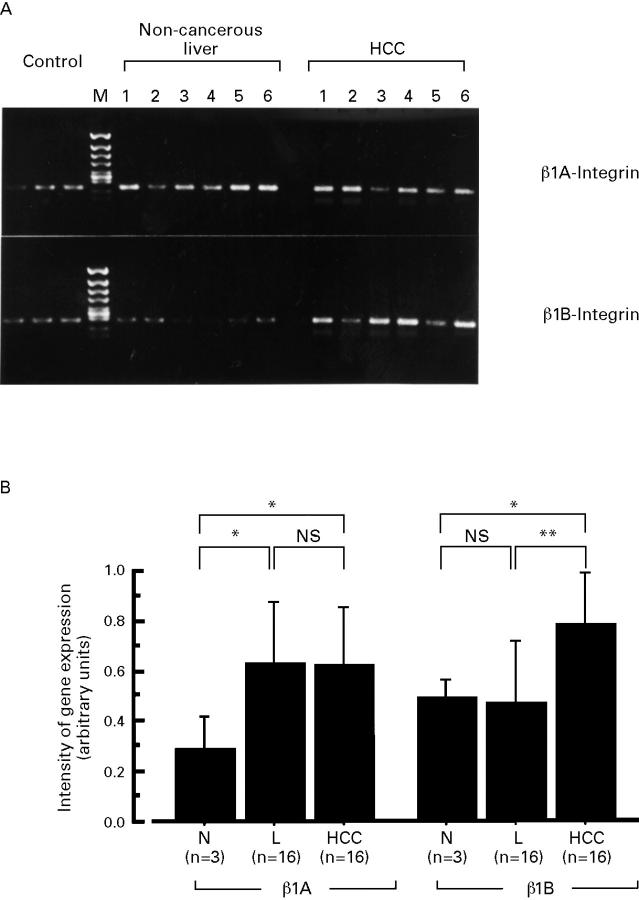
Figure 6 .
(A) Representative expression of the β1 integrin isoforms, β1A and β1B, by RT-PCR from six patients. (B) Semiquantification of β1A and β1B integrin in normal liver (N, n=3), chronically diseased non-cancerous liver (L, n=16), and HCC (n=16). Data are presented as mean (SD). *p<0.05; **p<0.01.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altruda F., Cervella P., Tarone G., Botta C., Balzac F., Stefanuto G., Silengo L. A human integrin beta 1 subunit with a unique cytoplasmic domain generated by alternative mRNA processing. Gene. 1990 Nov 15;95(2):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90369-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argraves W. S., Suzuki S., Arai H., Thompson K., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Amino acid sequence of the human fibronectin receptor. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1183–1190. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzac F., Belkin A. M., Koteliansky V. E., Balabanov Y. V., Altruda F., Silengo L., Tarone G. Expression and functional analysis of a cytoplasmic domain variant of the beta 1 integrin subunit. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):171–178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzac F., Retta S. F., Albini A., Melchiorri A., Koteliansky V. E., Geuna M., Silengo L., Tarone G. Expression of beta 1B integrin isoform in CHO cells results in a dominant negative effect on cell adhesion and motility. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(2):557–565. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begum N. A., Mori M., Matsumata T., Takenaka K., Sugimachi K., Barnard G. F. Differential display and integrin alpha 6 messenger RNA overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1995 Nov;22(5):1447–1455. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840220518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briesewitz R., Epstein M. R., Marcantonio E. E. Expression of native and truncated forms of the human integrin alpha 1 subunit. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2989–2996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgeson R. E., Chiquet M., Deutzmann R., Ekblom P., Engel J., Kleinman H., Martin G. R., Meneguzzi G., Paulsson M., Sanes J. A new nomenclature for the laminins. Matrix Biol. 1994 Apr;14(3):209–211. doi: 10.1016/0945-053x(94)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couvelard A., Scoazec J. Y., Feldmann G. Expression of cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion proteins by sinusoidal endothelial cells in the normal and cirrhotic human liver. Am J Pathol. 1993 Sep;143(3):738–752. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDMONDSON H. A., STEINER P. E. Primary carcinoma of the liver: a study of 100 cases among 48,900 necropsies. Cancer. 1954 May;7(3):462–503. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195405)7:3<462::aid-cncr2820070308>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrichs K., Ruiz P., Franke F., Gille I., Terpe H. J., Imhof B. A. High expression level of alpha 6 integrin in human breast carcinoma is correlated with reduced survival. Cancer Res. 1995 Feb 15;55(4):901–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigioni W. F., D'Errico A., Mancini A. M., Biagini G., Gozzetti G., Mazziotti A., Garbisa S. Hepatocellular carcinoma: expression of basement membrane glycoproteins. An immunohistochemical approach. J Pathol. 1987 Aug;152(4):325–332. doi: 10.1002/path.1711520411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigioni W. F., Garbisa S., D'Errico A., Baccarini P., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Liotta L. A., Mancini A. M. Evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma aggressiveness by a panel of extracellular matrix antigens. Am J Pathol. 1991 Mar;138(3):647–654. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogervorst F., Admiraal L. G., Niessen C., Kuikman I., Janssen H., Daams H., Sonnenberg A. Biochemical characterization and tissue distribution of the A and B variants of the integrin alpha 6 subunit. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):179–191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto Y., Robey F. A., Graf J., Sasaki M., Kleinman H. K., Yamada Y., Martin G. R. YIGSR, a synthetic laminin pentapeptide, inhibits experimental metastasis formation. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1132–1134. doi: 10.1126/science.2961059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanemoto T., Reich R., Royce L., Greatorex D., Adler S. H., Shiraishi N., Martin G. R., Yamada Y., Kleinman H. K. Identification of an amino acid sequence from the laminin A chain that stimulates metastasis and collagenase IV production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2279–2283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. S., Zhang K., Kramer R. Alpha 6 integrin is up-regulated in step increments accompanying neoplastic transformation and tumorigenic conversion of human fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1993 Jul 1;53(13):2950–2953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Rao C. N., Wewer U. M. Biochemical interactions of tumor cells with the basement membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1037–1057. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mafune K., Ravikumar T. S., Wong J. M., Yow H., Chen L. B., Steele G. D., Jr Expression of a Mr 32,000 laminin-binding protein messenger RNA in human colon carcinoma correlates with disease progression. Cancer Res. 1990 Jul 1;50(13):3888–3891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecham R. P. Receptors for laminin on mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1991 Aug;5(11):2538–2546. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.11.1651264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Patton B. L., Lentz S. I., Gilbert D. J., Snider W. D., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Sanes J. R. The laminin alpha chains: expression, developmental transitions, and chromosomal locations of alpha1-5, identification of heterotrimeric laminins 8-11, and cloning of a novel alpha3 isoform. J Cell Biol. 1997 May 5;137(3):685–701. doi: 10.1083/jcb.137.3.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima-Iijima S., Hamada H., Reddy P., Kakunaga T. Molecular structure of the human cytoplasmic beta-actin gene: interspecies homology of sequences in the introns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6133–6137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda K. Early recognition of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1986 Jul-Aug;6(4):729–738. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos D. M., Cheng Y. F., Kramer R. H. Role of laminin-binding integrin in the invasion of basement membrane matrices by fibrosarcoma cells. Invasion Metastasis. 1991;11(3):125–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto N., Iwahana M., Tanaka N. G., Osada Y. Inhibition of angiogenesis and tumor growth by a synthetic laminin peptide, CDPGYIGSR-NH2. Cancer Res. 1991 Feb 1;51(3):903–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw L. M., Mercurio A. M. Regulation of cellular interactions with laminin by integrin cytoplasmic domains: the A and B structural variants of the alpha 6 beta 1 integrin differentially modulate the adhesive strength, morphology, and migration of macrophages. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Jun;5(6):679–690. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.6.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw L. M., Turner C. E., Mercurio A. M. The alpha 6A beta 1 and alpha 6B beta 1 integrin variants signal differences in the tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin and other proteins. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 6;270(40):23648–23652. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.40.23648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura R. N., Cooper H. M., Collo G., Quaranta V. Cell type-specific integrin variants with alternative alpha chain cytoplasmic domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10183–10187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura R. N., Rozzo C., Starr L., Chambers J., Reichardt L. F., Cooper H. M., Quaranta V. Epithelial integrin alpha 6 beta 4: complete primary structure of alpha 6 and variant forms of beta 4. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1593–1604. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Robey P. G., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., Martin G. R. Laminin--a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9933–9937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpes R., van den Oord J. J., Desmet V. J. Distribution of the VLA family of integrins in normal and pathological human liver tissue. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jul;101(1):200–206. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90478-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpes R., van den Oord J. J., Desmet V. J. Integrins as differential cell lineage markers of primary liver tumors. Am J Pathol. 1993 May;142(5):1483–1492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewer U. M., Liotta L. A., Jaye M., Ricca G. A., Drohan W. N., Claysmith A. P., Rao C. N., Wirth P., Coligan J. E., Albrechtsen R. Altered levels of laminin receptor mRNA in various human carcinoma cells that have different abilities to bind laminin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7137–7141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Nelkin B. D., Celano P., Yen R. W., Falco J. P., Hamilton S. R., Baylin S. B. High expression of the DNA methyltransferase gene characterizes human neoplastic cells and progression stages of colon cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3470–3474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]