Abstract
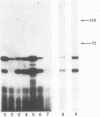
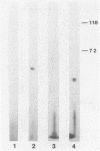
The effect of phosphorylated ribavirin on the vesicular stomatitis virus in vitro transcription reaction was examined. Analysis of the kinetics observed when the concentrations of nucleoside triphosphates were varied was performed with vesicular stomatitis virus wild-type standard virions. Double-reciprocal and Eadie-Hofstee plots showed competitive inhibition with all natural nucleoside triphosphates when both ribavirin diphosphate (RDP) and ribavirin triphosphate (RTP) were used. The Km values for ATP obtained for the wild-type polymerase were similar to those reported previously. To further characterize the observed inhibition kinetics, in vitro transcription products synthesized in the presence or absence of RDP and RTP were purified by CsCl centrifugation and were primer extended with oligonucleotides specific for either positive-sense leader or nucleocapsid mRNA transcripts. The ratios of leader to nucleocapsid mRNA were measured from primer-extended in vitro transcription products. It was found that the addition of RDP or RTP did not significantly change the in vitro ratio, suggesting that the polymerase is blocked before it enters the 3' end of the template.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen L. B., Boswell K. H., Khwaja T. A., Meyer R. B., Jr, Sidwell R. W., Witkowski J. T., Christensen L. F., Robins R. K. Synthesis and antiviral acticity of some phosphates of the broad-spectrum antiviral nucleoside, 1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide (ribavirin). J Med Chem. 1978 Aug;21(8):742–746. doi: 10.1021/jm00206a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellocq C., Raju R., Patterson J., Kolakofsky D. Translational requirement of La Crosse virus S-mRNA synthesis: in vitro studies. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):87–95. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.87-95.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De B. P., Banerjee A. K. Requirements and functions of vesicular stomatitis virus L and NS proteins in the transcription process in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):40–49. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90568-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson B., Helgstrand E., Johansson N. G., Larsson A., Misiorny A., Norén J. O., Philipson L., Stenberg K., Stening G., Stridh S. Inhibition of influenza virus ribonucleic acid polymerase by ribavirin triphosphate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jun;11(6):946–951. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.6.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Spector T. Acyclovir triphosphate is a suicide inactivator of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9575–9579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goswami B. B., Borek E., Sharma O. K., Fujitaki J., Smith R. A. The broad spectrum antiviral agent ribavirin inhibits capping of mRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):830–836. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91853-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green T. L., Emerson S. U. Effect of the beta-gamma phosphate bond of ATP on synthesis of leader RNA and mRNAs of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):255–257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.255-257.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverson L. E., Rose J. K. Localized attenuation and discontinuous synthesis during vesicular stomatitis virus transcription. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):477–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert M., Rittenhouse L., Perrault J., Summers D. F., Kolakofsky D. Plus and minus strand leader RNAs in negative strand virus-infected cells. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):735–747. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90127-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinoski F., Stollar V. Inhibitors of IMP dehydrogenase prevent sindbis virus replication and reduce GTP levels in Aedes albopictus cells. Virology. 1981 Apr 30;110(2):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell R. W., Huffman J. H., Khare G. P., Allen L. B., Witkowski J. T., Robins R. K. Broad-spectrum antiviral activity of Virazole: 1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):705–706. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T., Hajian G. Statistical methods to distinguish competitive, noncompetitive, and uncompetitive enzyme inhibitors. Anal Biochem. 1981 Aug;115(2):403–409. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M., Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Species of ribonucleic acid found in Chinese hamster ovary cells infected with plaque-forming and defective particles. J Virol. 1969 Aug;4(2):154–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.2.154-161.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeter D. G., Witkowski J. T., Khare G. P., Sidwell R. W., Bauer R. J., Robins R. K., Simon L. N. Mechanism of action of 1- -D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide (Virazole), a new broad-spectrum antiviral agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1174–1178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testa D., Banerjee A. K. Initiation of RNA synthesis in vitro by vesicular stomatitis virus. Role of ATP. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):2053–2058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toltzis P., O'Connell K., Patterson J. L. Effect of phosphorylated ribavirin on vesicular stomatitis virus transcription. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):492–497. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray S. K., Gilbert B. E., Knight V. Effect of ribavirin triphosphate on primer generation and elongation during influenza virus transcription in vitro. Antiviral Res. 1985 Feb;5(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(85)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray S. K., Gilbert B. E., Noall M. W., Knight V. Mode of action of ribavirin: effect of nucleotide pool alterations on influenza virus ribonucleoprotein synthesis. Antiviral Res. 1985 Feb;5(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(85)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]