Abstract
An extracellular inhibitory substance produced by the marine Alteromonas strain P-31 (NCMB 2144) was isolated and purified. The inhibitor was a macromolecule with a molecular weight of 90,000 estimated by Sephadex G-100 chromatography and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The inhibitory activity was antagonized by proteinase K and beta-amylase and inactivated by heating at 80 degrees C for 30 min. The purified substance exhibited two typical absorption bands in the infrared spectrum at 1,650 and 1,075 cm-1, corresponding to peptide linkages and carbohydrate residues, respectively. These findings allowed us to characterize the antimicrobial compound as a thermolabile glycoprotein. The substance exhibited a broad inhibitory spectrum, being active against clinical and environmental isolates from related and nonrelated taxonomical bacterial groups as well as against the producer strain and other similar marine bacterial strains. The inhibitory glycoprotein did not display cytotoxicity toward mammalian and fish cell lines.
Full text
PDF

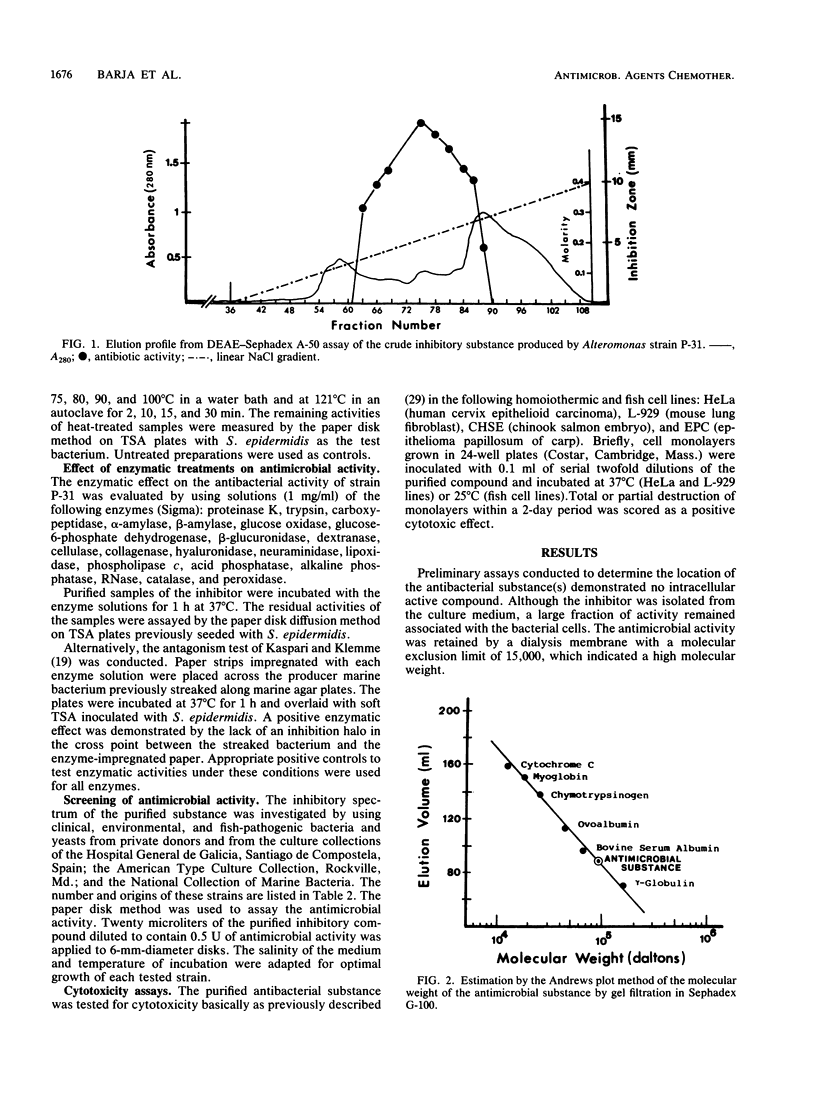
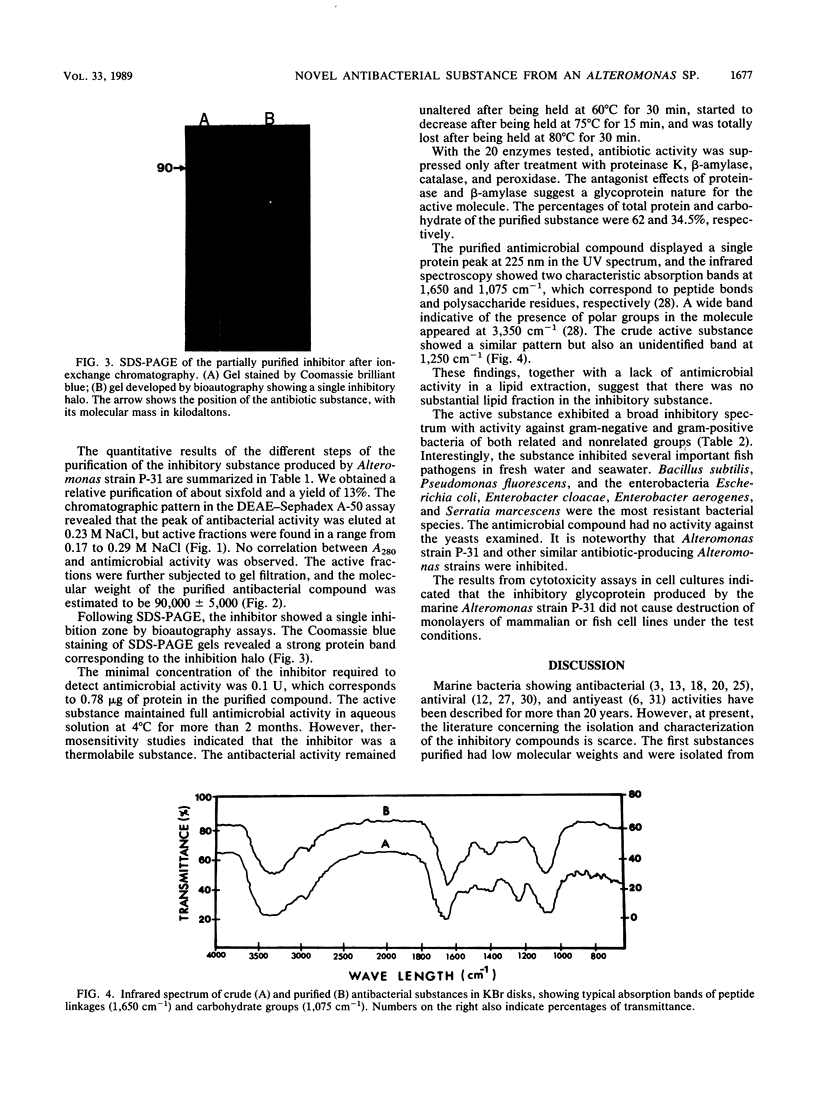


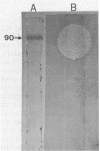
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck J. D., Meyers S. P., Kamp K. M. Marine Bacteria with Antiyeast Activity. Science. 1962 Dec 21;138(3547):1339–1340. doi: 10.1126/science.138.3547.1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder P. R., Pfister R. M., Leitz F. H. Production of a pyrrole antibiotic by a marine bacterium. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Jul;14(4):649–653. doi: 10.1128/am.14.4.649-653.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggett R. G. New anti-Pseudomonas agent isolated from a marine vibrio. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1972–1973. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1972-1973.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dopazo C. P., Lemos M. L., Lodeiros C., Bolinches J., Barja J. L., Toranzo A. E. Inhibitory activity of antibiotic-producing marine bacteria against fish pathogens. J Appl Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;65(2):97–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1988.tb01497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujioka R. S., Loh P. C., Lau L. S. Survival of human enteroviruses in the Hawaiian ocean environment: evidence for virus-inactivating microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jun;39(6):1105–1110. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.6.1105-1110.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREIN A., MEYERS S. P. Growth characteristics and antibiotic production of actinomycetes isolated from littoral sediments and materials suspended in sea water. J Bacteriol. 1958 Nov;76(5):457–463. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.5.457-463.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier M. J., Flatau G. N. Antibacterial activity of marine violet-pigmented Alteromonas with special reference to the production of brominated compounds. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Nov;22(11):1612–1619. doi: 10.1139/m76-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier M. J. Modification of bacterial respiration by a macromolecular polyanionic antibiotic produced by a marine Alteromonas. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):361–366. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier M. J., Shewan J. M., Gibson D. M., Lee J. V. Taxonomic position and seasonal variations in marine neritic environment of some gram-negative antibiotic-producing bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Apr;87(2):211–218. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-2-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IMSHENETSKII A. A. [On microbiology in Cairo]. Mikrobiologiia. 1961 May-Jun;30:545–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemos M. L., Toranzo A. E., Barja J. L. Modified medium for the oxidation-fermentation test in the identification of marine bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1541–1543. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1541-1543.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld W. D., Zobell C. E. Antibiotic Production by Marine Microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1947 Sep;54(3):393–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.54.3.393-398.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toranzo A. E., Barja J. L., Hetrick F. M. Antiviral activity of antibiotic-producing marine bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Feb;28(2):231–238. doi: 10.1139/m82-031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wratten S. J., Wolfe M. S., Andersen R. J., Faulkner D. J. Antibiotic metabolites from a marine pseudomonad. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):411–414. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharius R. M., Zell T. E., Morrison J. H., Woodlock J. J. Glycoprotein staining following electrophoresis on acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jul;30(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]