Abstract
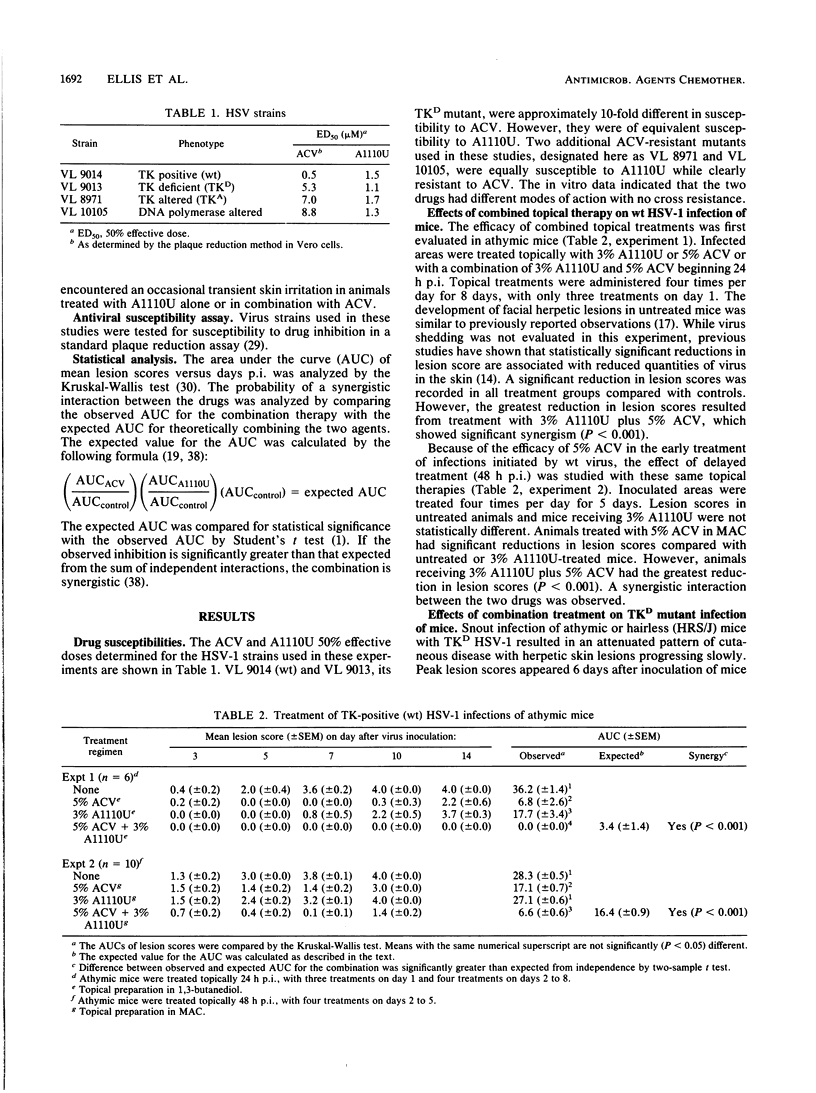
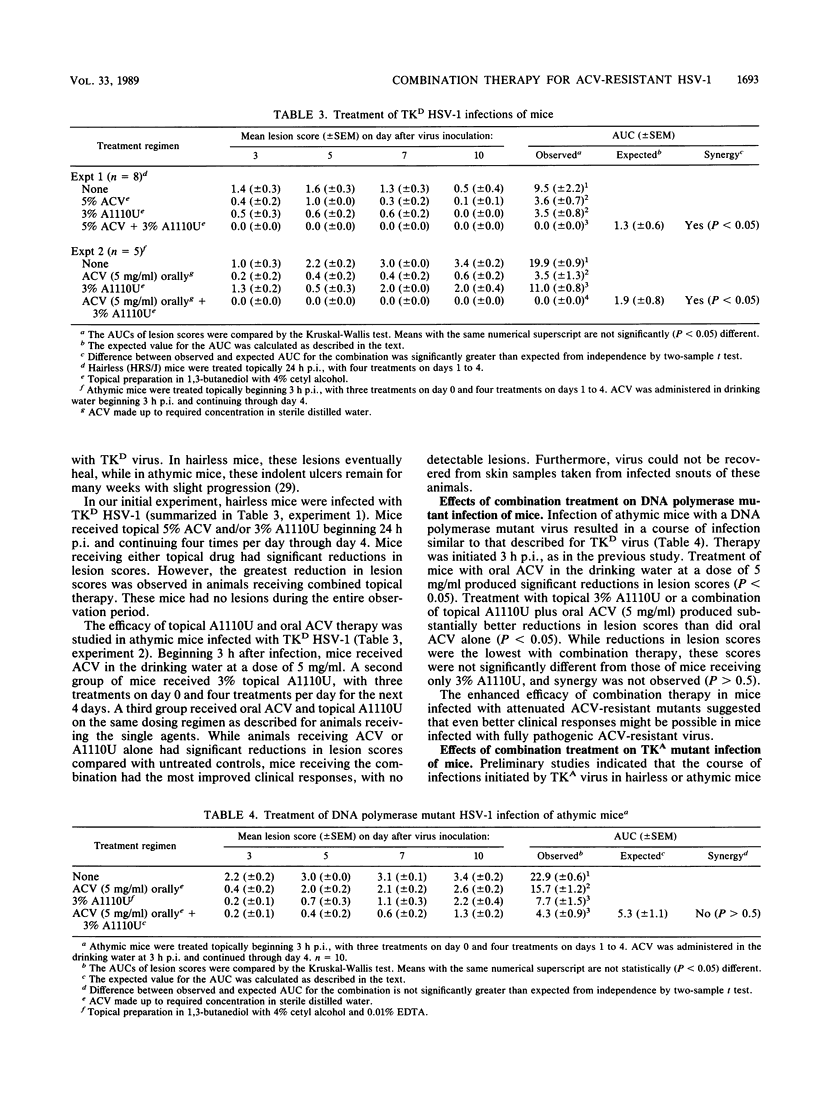
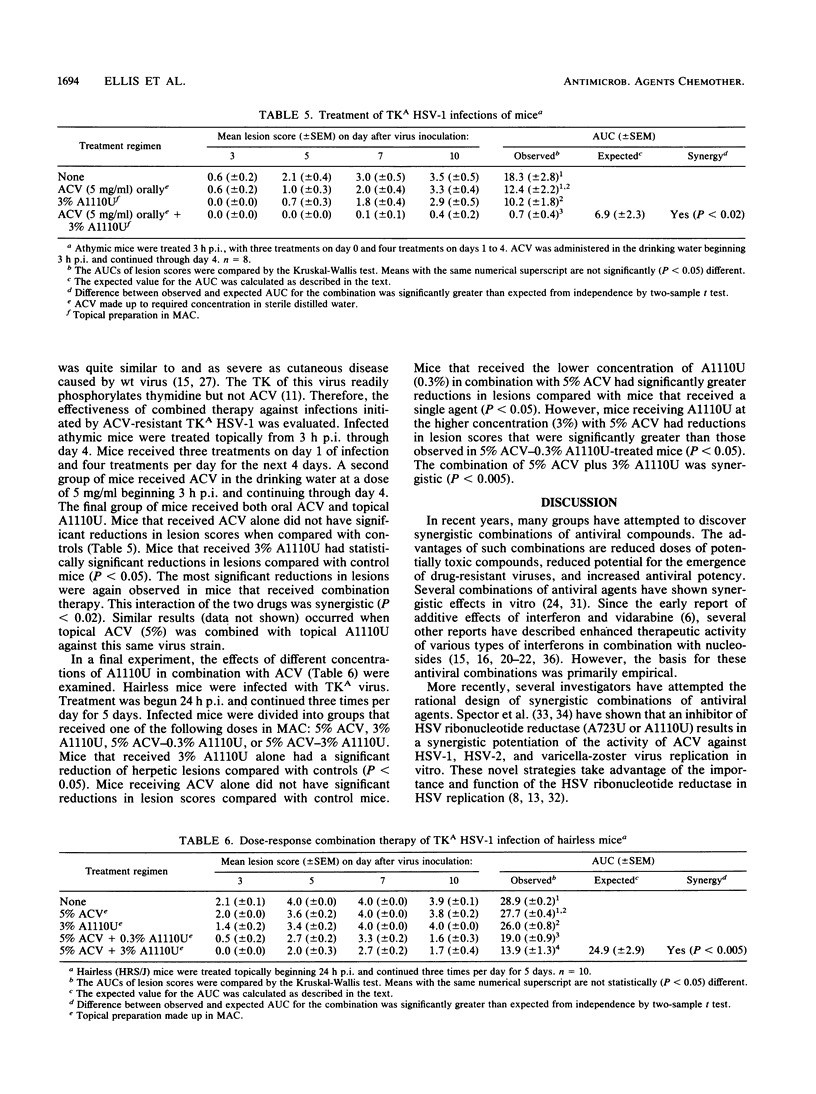
Clinical effects of the administration of a combination of acyclovir (ACV) and compound A1110U (a 2-acetylpyridine thiocarbonothiohydrazone inactivator of herpes simplex virus [HSV] ribonucleotide reductase) on the development of herpetic skin lesions were studied in athymic and hairless mice infected intracutaneously with different HSV type 1 (HSV-1) strains. ACV was administered topically (5%) or orally (5 mg/ml), while A1110U was applied topically (3%). In all but one experiment, the effect of combination therapy was greater than that calculated for the sum of the individual drug effects in limiting the development of herpetic skin lesions in mice. In several experiments, combination therapy totally eliminated all signs of infection. This synergistic chemotherapeutic efficacy was evident in infections caused by ACV-susceptible as well as several ACV-resistant HSV-1 strains. These results indicate that this combination therapy may provide a significant improvement in clinical responses over single-agent topical therapy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer D. J., St Vincent L., Kempe C. H., Young P. A., Downie A. W. Prophylaxis of smallpox with methisazone. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Aug;90(2):130–145. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B., Aeppli D. Adverse effects of high-dose intravenous acyclovir in ambulatory patients with acute herpes zoster. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):362–365. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryson Y. J., Dillon M., Lovett M., Acuna G., Taylor S., Cherry J. D., Johnson B. L., Wiesmeier E., Growdon W., Creagh-Kirk T. Treatment of first episodes of genital herpes simplex virus infection with oral acyclovir. A randomized double-blind controlled trial in normal subjects. N Engl J Med. 1983 Apr 21;308(16):916–921. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198304213081602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryson Y. J., Kronenberg L. H. Combined antiviral effects of interferon, adenine, arabinoside, hypoxanthine arabinoside, and adenine arabinoside-5'-monophosphate in human fibroblast cultures. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):299–306. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns W. H., Saral R., Santos G. W., Laskin O. L., Lietman P. S., McLaren C., Barry D. W. Isolation and characterisation of resistant Herpes simplex virus after acyclovir therapy. Lancet. 1982 Feb 20;1(8269):421–423. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91620-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. M., McDougall I., Marsden H. S., Preston V. G., Ryan D. M., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Ribonucleotide reductase encoded by herpes simplex virus is a determinant of the pathogenicity of the virus in mice and a valid antiviral target. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2607–2612. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook M. L., Stevens J. G. Pathogenesis of herpetic neuritis and ganglionitis in mice: evidence for intra-axonal transport of infection. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):272–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.272-288.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumpacker C. S., Schnipper L. E., Marlowe S. I., Kowalsky P. N., Hershey B. J., Levin M. J. Resistance to antiviral drugs of herpes simplex virus isolated from a patient treated with acyclovir. N Engl J Med. 1982 Feb 11;306(6):343–346. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198202113060606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby G., Field H. J., Salisbury S. A. Altered substrate specificity of herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase confers acyclovir-resistance. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):81–83. doi: 10.1038/289081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsky D. I., Crumpacker C. S. Drugs five years later: acyclovir. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Dec;107(6):859–874. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-6-859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutia B. M. Ribonucleotide reductase induced by herpes simplex virus has a virus-specified constituent. J Gen Virol. 1983 Mar;64(Pt 3):513–521. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-3-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis M. N., Waters R., Hill E. L., Lobe D. C., Selleseth D. W., Barry D. W. Orofacial infection of athymic mice with defined mixtures of acyclovir-susceptible and acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus type 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):304–310. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppstein D. A., Marsh Y. V. Potent synergistic inhibition of herpes simplex virus-2 by 9-[(1, 3-dihydroxy-2-propoxy)methyl]guanine in combination with recombinant interferons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 16;120(1):66–73. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91414-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser-Smith E. B., Eppstein D. A., Marsh Y. V., Matthews T. R. Enhanced efficacy of the acyclic nucleoside 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine in combination with beta-interferon against herpes simplex virus type 2 in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):563–565. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., Coen D. M., St Clair M. H., Schaffer P. A. Acyclovir-resistant mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 express altered DNA polymerase or reduced acyclovir phosphorylating activities. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):936–941. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.936-941.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T., Levinson W. Inhibition of RNA slow viruses by thiosemicarbazones. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 16;51(4):875–880. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. J. Antagonistic interaction of rifampicin and trimethoprim. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Jul;4(4):315–327. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.4.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilfenhaus J., De Clercq E., Köhler R., Geursen R., Seiler F. Combined antiviral effects of acyclovir or bromovinyldeoxyuridine and human immunoglobulin in herpes simplex virus-infected mice. Antiviral Res. 1987 May;7(4):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(87)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janz C., Wigand R. Combined interaction of antiherpes substances and interferon beta on the multiplication of herpes simplex virus. Arch Virol. 1982;73(2):135–143. doi: 10.1007/BF01314722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M. J., Leary P. L. Inhibition of human herpesviruses by combination of acyclovir and human leukocyte interferon. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):995–999. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.995-999.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindel A., Adler M. W., Sutherland S., Fiddian A. P. Intravenous acyclovir treatment for primary genital herpes. Lancet. 1982 Mar 27;1(8274):697–700. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92618-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park N. H., Callahan J. G., Pavan-Langston D. Effect of combined acyclovir and vidarabine on infection with herpes simplex virus in vitro and in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):757–762. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. L., Krill C. E., Jr Acyclovir crystalluria. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;5(6):710–712. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198611000-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw M., King M., Best J. M., Banatvala J. E., Gibson J. R., Klaber M. R. Failure of acyclovir cream in treatment of recurrent herpes labialis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Jul 6;291(6487):7–9. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6487.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipman C., Jr, Smith S. H., Drach J. C., Klayman D. L. Antiviral activity of 2-acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones against herpes simplex virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):682–685. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipman C., Jr, Smith S. H., Drach J. C., Klayman D. L. Thiosemicarbazones of 2-acetylpyridine, 2-acetylquinoline, 1-acetylisoquinoline, and related compounds as inhibitors of herpes simplex virus in vitro and in a cutaneous herpes guinea pig model. Antiviral Res. 1986 Jul;6(4):197–222. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(86)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibrack C. D., Gutman L. T., Wilfert C. M., McLaren C., St Clair M. H., Keller P. M., Barry D. W. Pathogenicity of acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus type 1 from an immunodeficient child. J Infect Dis. 1982 Nov;146(5):673–682. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.5.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. O., Galloway K. S., Ogilvie K. K., Cheriyan U. O. Synergism among BIOLF-62, phosphonoformate, and other antiherpetic compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Dec;22(6):1026–1030. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.6.1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T., Averett D. R., Nelson D. J., Lambe C. U., Morrison R. W., Jr, St Clair M. H., Furman P. A. Potentiation of antiherpetic activity of acyclovir by ribonucleotide reductase inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4254–4257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T., Harrington J. A., Morrison R. W., Jr, Lambe C. U., Nelson D. J., Averett D. R., Biron K., Furman P. A. 2-Acetylpyridine 5-[(dimethylamino)thiocarbonyl]-thiocarbonohydrazone (A1110U), a potent inactivator of ribonucleotide reductases of herpes simplex and varicella-zoster viruses and a potentiator of acyclovir. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):1051–1055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.1051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruance S. L., Crumpacker C. S., Schnipper L. E., Kern E. R., Marlowe S., Arndt K. A., Overall J. C., Jr Early, patient-initiated treatment of herpes labialis with topical 10% acyclovir. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):553–555. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanwick T. L., Schinazi R. F., Campbell D. E., Nahmias A. J. Combined antiviral effect of interferon and acyclovir on herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):672–674. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk S. R., Shipman C., Jr, Drach J. C. Selective inhibition of herpes simplex virus ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase by derivatives of 2-acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazone. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 May 1;35(9):1539–1545. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90122-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


