Abstract
BACKGROUND/AIMS—Endoscopic ultrasonography is expected to be useful for invasion depth staging of early gastric cancer. A prospective blind study of the staging characteristics of endoscopy and endoscopic ultrasonography for early gastric cancer was performed. METHODS—Findings of endoscopy and endoscopic ultrasonography using a 20 MHz thin ultrasound probe were independently reviewed and the results of 52 early gastric cancer lesions analysed. RESULTS—The overall accuracy rates in invasion depth staging of early gastric cancer were 63% for endoscopy and 71% for endoscopic ultrasonography. No statistically significant differences were observed in overall accuracy. Endoscopic ultrasonography tended to overstage, and lesions that were classified as mucosal cancer by endoscopic ultrasonography were very likely (95%) to be limited to the mucosa on histological examination. All 16 lesions staged as mucosal cancer independently but coincidentally by both methods were histologically limited to the mucosa. CONCLUSIONS—Endoscopic ultrasonography is expected to compensate for the understaging of lesions with submucosal invasion that are endoscopically staged as mucosal cancer.
Keywords: early gastric cancer; endoscopic ultrasonography; endoscopy
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (146.4 KB).
Figure 1 .
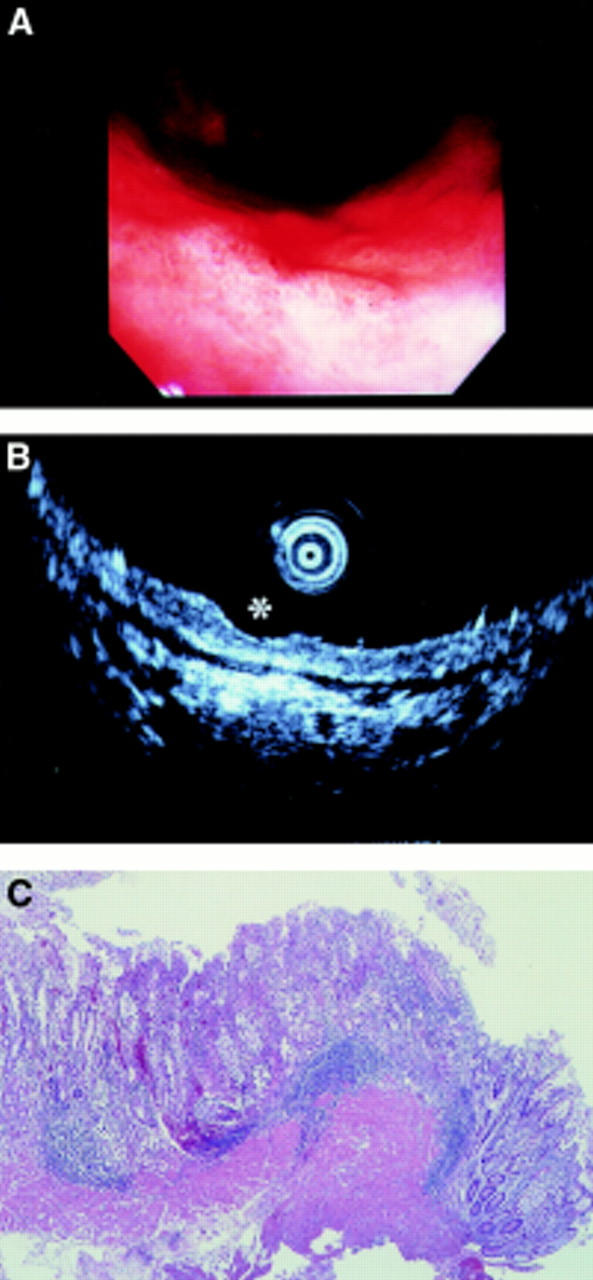
A superficial depressed type early gastric cancer located in the lower gastric body. Endoscopy (A) and endoscopic ultrasonography (B, asterisk) reviewers independently but coincidentally staged this as mucosal. Histological examination (C) of its endoscopically resected strip biopsy specimen also proved that it was mucosal cancer. In this case, both methods staged correctly.
Figure 2 .
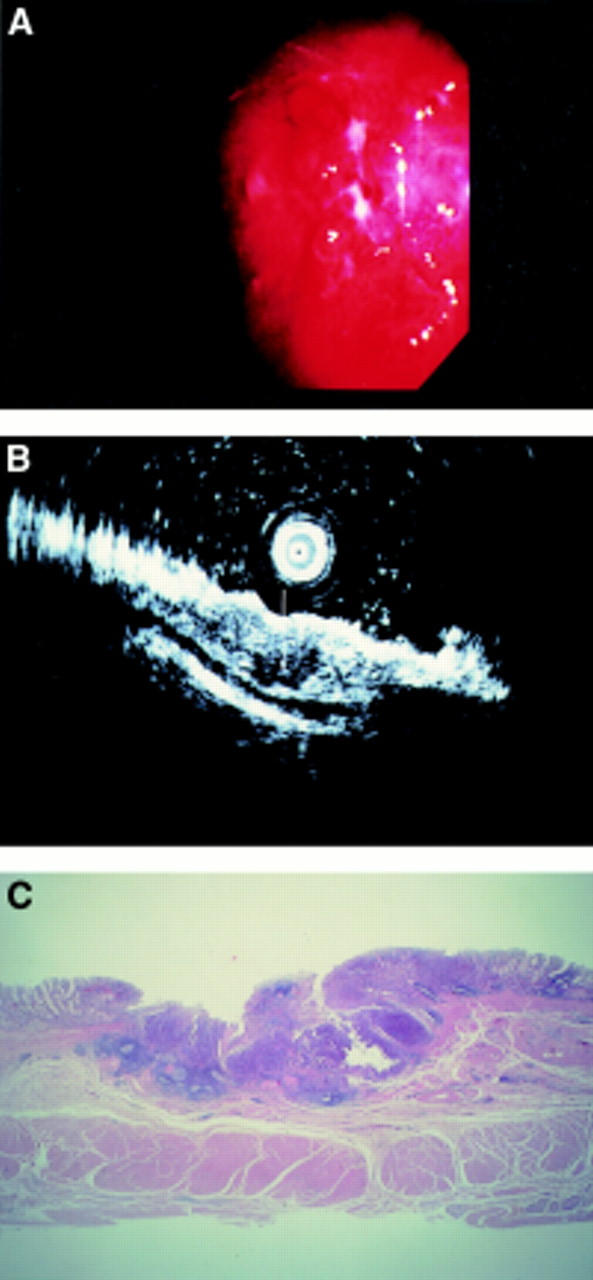
A superficial depressed type early gastric cancer located in the middle gastric body. This case was understaged by endoscopy. The endoscopy reviewer observed that the surface of the depression was not so rough, and staged it as endoscopy-mucosal (A). In contrast, the endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) reviewer observed hypoechoic tumorous invasion and irregular narrowing of the third layer (B, white arrow). He staged it as depth EUS-submucosal. Histological findings of a surgically resected specimen corresponded well to the EUS image analysis (C).
Figure 3 .
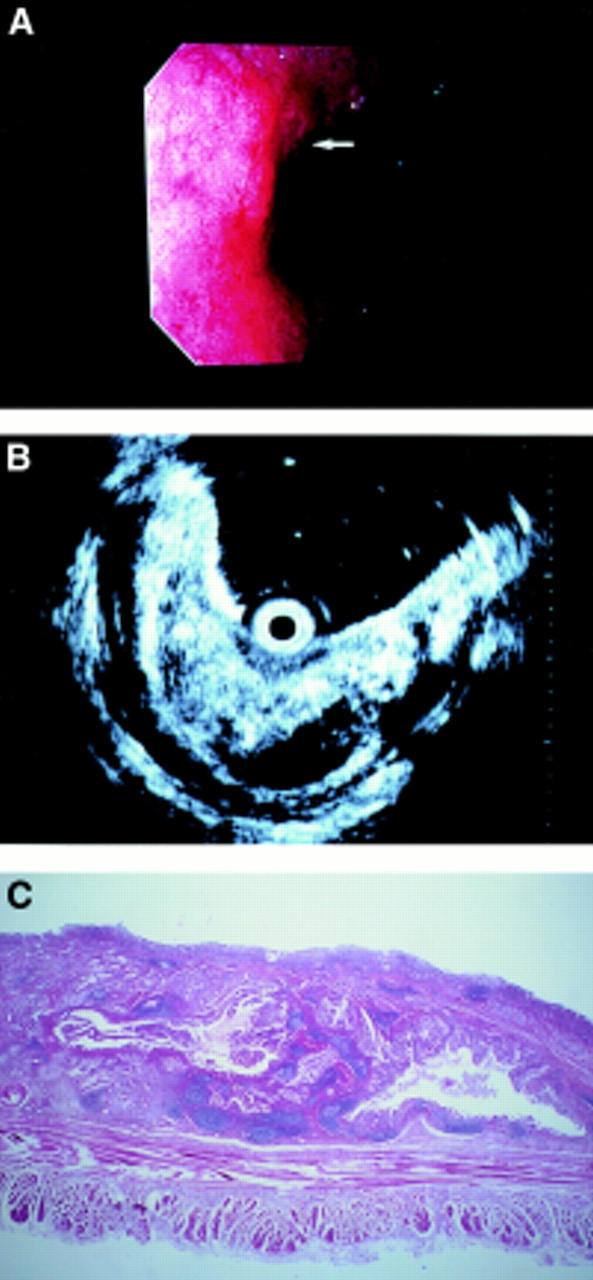
A superficial depressed type early gastric cancer located in the cardia. This was also understaged by endoscopy. As the lesser curvature of the cardia is a difficult location for a forward viewing type endoscope, it is likely that the endoscopy reviewer could not detect any apparent submucosal invasion (A, white arrow). In contrast, the endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) picture provided a clear image of rough swelling and irregular cystic changes of the third layer (B). Histological examination (C) confirmed its submucosal invasion, which corresponded well to the EUS findings.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aibe T., Fuji T., Okita K., Takemoto T. A fundamental study of normal layer structure of the gastrointestinal wall visualized by endoscopic ultrasonography. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1986;123:6–15. doi: 10.3109/00365528609091857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akahoshi K., Misawa T., Fujishima H., Chijiiwa Y., Maruoka A., Ohkubo A., Nawata H. Preoperative evaluation of gastric cancer by endoscopic ultrasound. Gut. 1991 May;32(5):479–482. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.5.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonenkamp J. J., Songun I., Hermans J., Sasako M., Welvaart K., Plukker J. T., van Elk P., Obertop H., Gouma D. J., Taat C. W. Randomised comparison of morbidity after D1 and D2 dissection for gastric cancer in 996 Dutch patients. Lancet. 1995 Mar 25;345(8952):745–748. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)90637-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colin-Jones D. G., Rösch T., Dittler H. J. Staging of gastric cancer by endoscopy. Endoscopy. 1993 Jan;25(1):34–38. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMagno E. P., Buxton J. L., Regan P. T., Hattery R. R., Wilson D. A., Suarez J. R., Green P. S. Ultrasonic endoscope. Lancet. 1980 Mar 22;1(8169):629–631. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimagno E. P., Regan P. T., Clain J. E., James E. M., Buxton J. L. Human endoscopic ultrasonography. Gastroenterology. 1982 Oct;83(4):824–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittler H. J., Siewert J. R. Role of endoscopic ultrasonography in gastric carcinoma. Endoscopy. 1993 Feb;25(2):162–166. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm H., Binmoeller K. F., Hamper K., Koch J., Henne-Bruns D., Soehendra N. Endosonography for preoperative locoregional staging of esophageal and gastric cancer. Endoscopy. 1993 Mar;25(3):224–230. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikura T., Uefuji K., Tomimatsu S., Okusa Y., Yahara T., Tamakuma S. Surgical strategy for patients with gastric carcinoma with submucosal invasion. A multivariate analysis. Cancer. 1995 Sep 15;76(6):935–940. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19950915)76:6<935::aid-cncr2820760605>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmey M. B., Martin R. W., Haggitt R. C., Wang K. Y., Franklin D. W., Silverstein F. E. Histologic correlates of gastrointestinal ultrasound images. Gastroenterology. 1989 Feb;96(2 Pt 1):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91568-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightdale C. J. Endoscopic ultrasonography in the diagnosis, staging and follow-up of esophageal and gastric cancer. Endoscopy. 1992 May;24 (Suppl 1):297–303. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisborg P., Jatzko G., Horn M., Neumann H. J., Müller M., Stettner H., Denk H. Radical surgery (R2 resection) for gastric cancer. A multivariate analysis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1994 Nov;29(11):1024–1028. doi: 10.3109/00365529409094880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickl N. J., Bhutani M. S., Catalano M., Hoffman B., Hawes R., Chak A., Roubein L. D., Kimmey M., Johnson M., Affronti J. Clinical implications of endoscopic ultrasound: the American Endosonography Club Study. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996 Oct;44(4):371–377. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(96)70083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano T., Okuyama Y., Kobori O., Shimizu T., Morioka Y. Early gastric cancer. Endoscopic diagnosis of depth of invasion. Dig Dis Sci. 1990 Nov;35(11):1340–1344. doi: 10.1007/BF01536738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlemper R. J., Itabashi M., Kato Y., Lewin K. J., Riddell R. H., Shimoda T., Sipponen P., Stolte M., Watanabe H., Takahashi H. Differences in diagnostic criteria for gastric carcinoma between Japanese and western pathologists. Lancet. 1997 Jun 14;349(9067):1725–1729. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)12249-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada M., Murakami A., Karita M., Yanai H., Okita K. Endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer. Endoscopy. 1993 Sep;25(7):445–450. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto T., Yanai H., Tada M., Aibe T., Fujimura H., Murata N., Karita M., Okita K. Application of ultrasonic probes prior to endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer. Endoscopy. 1992 May;24 (Suppl 1):329–333. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tio T. L., Schouwink M. H., Cikot R. J., Tytgat G. N. Preoperative TNM classification of gastric carcinoma by endosonography in comparison with the pathological TNM system: a prospective study of 72 cases. Hepatogastroenterology. 1989 Apr;36(2):51–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamao T., Shirao K., Ono H., Kondo H., Saito D., Yamaguchi H., Sasako M., Sano T., Ochiai A., Yoshida S. Risk factors for lymph node metastasis from intramucosal gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 1996 Feb 15;77(4):602–606. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960215)77:4<602::AID-CNCR3>3.0.CO;2-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanai H., Fujimura H., Suzumi M., Matsuura S., Awaya N., Noguchi T., Karita M., Tada M., Okita K., Aibe T. Delineation of the gastric muscularis mucosae and assessment of depth of invasion of early gastric cancer using a 20-megahertz endoscopic ultrasound probe. Gastrointest Endosc. 1993 Jul-Aug;39(4):505–512. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(93)70160-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanai H., Matsumoto Y., Harada T., Nishiaki M., Tokiyama H., Shigemitsu T., Tada M., Okita K. Endoscopic ultrasonography and endoscopy for staging depth of invasion in early gastric cancer: a pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997 Sep;46(3):212–216. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(97)70088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanai H., Tada M., Karita M., Okita K. Diagnostic utility of 20-megahertz linear endoscopic ultrasonography in early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996 Jul;44(1):29–33. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(96)70225-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanai H., Yoshida T., Harada T., Matsumoto Y., Nishiaki M., Shigemitsu T., Tada M., Okita K., Kawano T., Nagasaki S. Endoscopic ultrasonography of superficial esophageal cancers using a thin ultrasound probe system equipped with switchable radial and linear scanning modes. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996 Nov;44(5):578–582. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(96)70012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda K. Endoscopic ultrasonic probes and mucosectomy for early gastric carcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996 Feb;43(2 Pt 2):S29–S31. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(96)81511-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


