Abstract
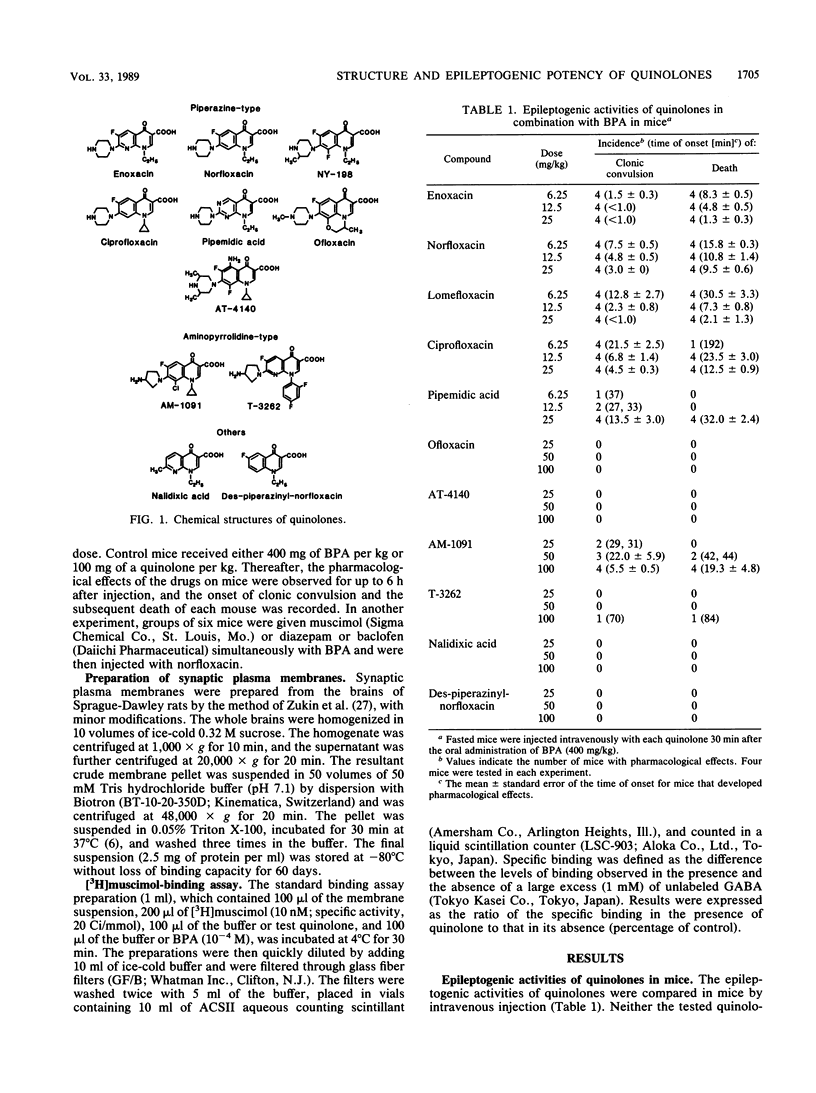
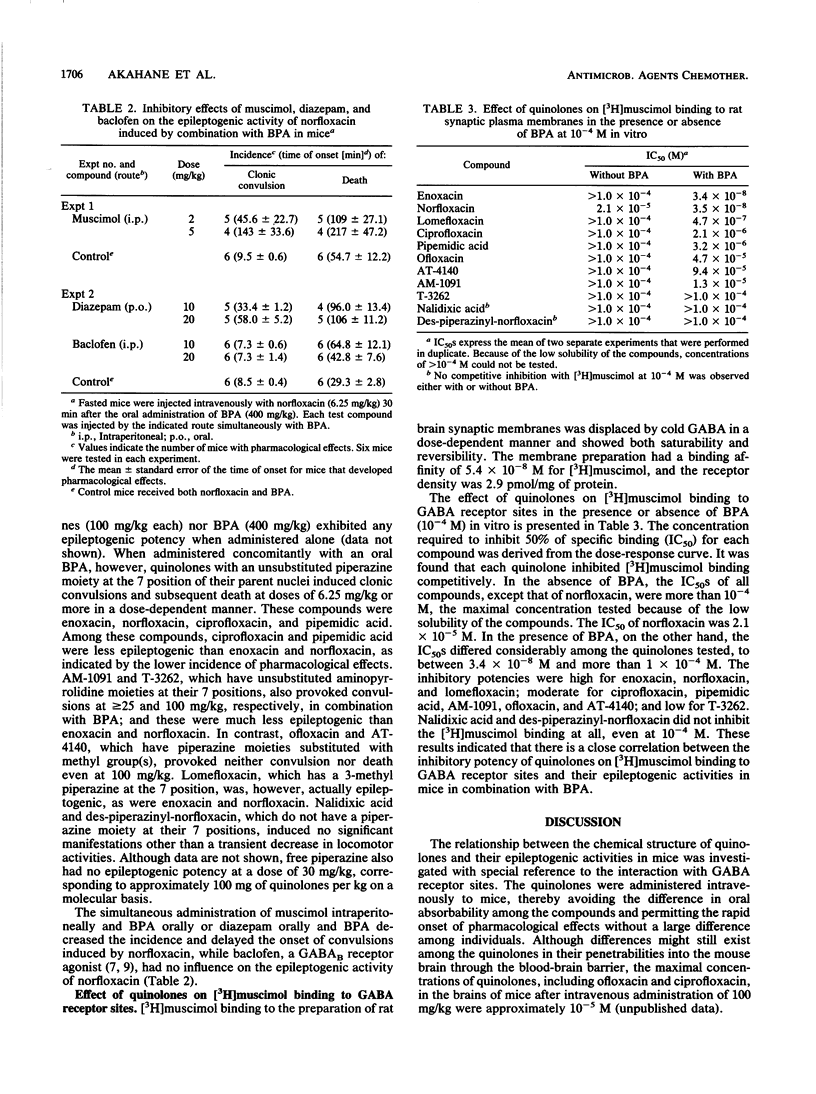
The relationship between the chemical structure and epileptogenic activity of quinolones was investigated. When the quinolones were administered intravenously to mice concomitantly with oral biphenylacetic acid, a major metabolite of the nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug fenbufen, enoxacin, norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and pipemidic acid, which have an unsubstituted piperazine moiety at the 7 position of their parent nuclei, provoked clonic convulsions and subsequent death at doses of 6.25 mg/kg or more in a dose-dependent manner. AM-1091 and T-3262, which have an unsubstituted aminopyrrolidine moiety at their 7 positions, were less epileptogenic than the compounds listed above were. In contrast, ofloxacin, AT-4140, and nalidixic acid, which have piperazine substituted with methyl group(s) or no piperazine moiety at their 7 positions, never induced convulsions, even at doses of 100 mg/kg. Lomefloxacin, which has a 3-methyl piperazine, however, provoked convulsions at doses of 6.25 mg/kg or more. In the presence of biphenylacetic acid, all the test quinolones except nalidixic acid competitively inhibited [3H]muscimol binding to receptor sites for gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in vitro. Nalidixic acid did not inhibit the binding at all, even at the highest concentration tested, i.e., 10(-4) M. The 50% inhibition doses for [3H]muscimol binding varied within 4 orders of magnitude or more, between 10(-8) to more than 10(-4) M for various compounds, and there was a close correlation between the epileptogenic activities of quinolones and their inhibitory potencies for [3H]muscimol binding to GABA receptor sites. These results indicate that the epileptogenic activity of quinolones possibly relates to the GABA-like structures of substituents at their 7 positions, which act as antagonists of GABA receptors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anastasio G. D., Menscer D., Little J. M., Jr Norfloxacin and seizures. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Jul 15;109(2):169–170. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-2-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. R., Johnston G. A. Conformational analysis of muscimol, a GABA agonist. J Theor Biol. 1979 Aug 7;79(3):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(79)90345-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arcieri G., Griffith E., Gruenwaldt G., Heyd A., O'Brien B., Becker N., August R. Ciprofloxacin: an update on clinical experience. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):381–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball P. Ciprofloxacin: an overview of adverse experiences. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Nov;18 (Suppl 500):187–193. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.sd.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey P. G. Overview of drug interactions with the quinolones. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Sep;22 (Suppl 100):97–107. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.supplement_c.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. Influences ions, enzymes, and detergents on gamma-aminobutyric acid-receptor binding in synaptic membranes of rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 May;13(3):442–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falch E., Hedegaard A., Nielsen L., Jensen B. R., Hjeds H., Krogsgaard-Larsen P. Comparative stereostructure-activity studies on GABAA and GABAB receptor sites and GABA uptake using rat brain membrane preparations. J Neurochem. 1986 Sep;47(3):898–903. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb00695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halkin H. Adverse effects of the fluoroquinolones. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jan-Feb;10 (Suppl 1):S258–S261. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.supplement_1.s258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. R., Bowery N. G. 3H-baclofen and 3H-GABA bind to bicuculline-insensitive GABA B sites in rat brain. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):149–152. doi: 10.1038/290149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito A., Hirai K., Inoue M., Koga H., Suzue S., Irikura T., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro antibacterial activity of AM-715, a new nalidixic acid analog. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):103–108. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouno K., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activity of AT-2266. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):78–84. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucet J. C., Tilly H., Lerebours G., Gres J. J., Piguet H. Neurological toxicity related to pefloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jun;21(6):811–812. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.6.811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk J. P., Campoli-Richards D. M. Ofloxacin. A review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1987 Apr;33(4):346–391. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198733040-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W. GABA-benzodiazepine-barbiturate receptor interactions. J Neurochem. 1981 Jul;37(1):1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb05284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Matsuura Y., Inoue M., Une T., Osada Y., Ogawa H., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo activity of DL-8280, a new oxazine derivative. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):548–553. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schousboe A., Thorbek P., Hertz L., Krogsgaard-Larsen P. Effects of GABA analogues of restricted conformation on GABA transport in astrocytes and brain cortex slices and on GABA receptor binding. J Neurochem. 1979 Jul;33(1):181–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb11720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segev S., Rehavi M., Rubinstein E. Quinolones, theophylline, and diclofenac interactions with the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Nov;32(11):1624–1626. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.11.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson K. J., Brodie M. J. Convulsions related to enoxacin. Lancet. 1985 Jul 20;2(8447):161–161. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavich I. L., Gleffe R. F., Haas E. J. Grand mal epileptic seizures during ciprofloxacin therapy. JAMA. 1989 Jan 27;261(4):558–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Sato H., Kume Y., Tamai I., Okezaki E., Nagata O., Kato H. Inhibitory effects of quinolone antibacterial agents on gamma-aminobutyric acid binding to receptor sites in rat brain membranes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Feb;32(2):190–194. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.2.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Edwards L. J. In vitro activity of Bay 09867, a new quinoline derivative, compared with those of other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Apr;23(4):559–564. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.4.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin S. R., Young A. B., Snyder S. H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid binding to receptor sites in the rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4802–4807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


