Abstract
BACKGROUND—Extrahepatic ethanol metabolism is postulated to take place via microbial oxidation in the colon, mediated by aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria. AIMS—To evaluate the role of microbial ethanol oxidation in the total elimination rate of ethanol in humans by reducing gut flora with ciprofloxacin. METHODS—Ethanol was administered intravenously at the beginning and end of a one week period to eight male volunteers. Between ethanol doses volunteers received 750 mg ciprofloxacin twice daily. RESULTS—A highly significant (p=0.001) reduction in the ethanol elimination rate (EER) was detected after ciprofloxacin medication. Mean (SEM) EER was 107.0 (5.3) and 96.9 (4.8) mg/kg/h before and after ciprofloxacin, respectively. Faecal Enterobacteriaceae and Enterococcus sp. were totally absent after medication, and faecal acetaldehyde production capacity was significantly (p<0.05) decreased from 0.91 (0.15) to 0.39 (0.08) nmol/min/mg protein. Mean faecal alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) activity was significantly (p<0.05) decreased after medication, but ciprofloxacin did not inhibit human hepatic ADH activity in vitro. CONCLUSIONS—Ciprofloxacin treatment decreased the ethanol elimination rate by 9.4%, with a concomitant decrease in intestinal aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria, faecal ADH activity, and acetaldehyde production. As ciprofloxacin has no effect on liver blood flow, hepatic ADH activity, or cytochrome CYP2E1 activity, these effects are probably caused by the reduction in intestinal flora.
Keywords: ciprofloxacin; ethanol; colonic bacteria; metabolism; alcohol dehydrogenase; acetaldehyde
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (128.1 KB).
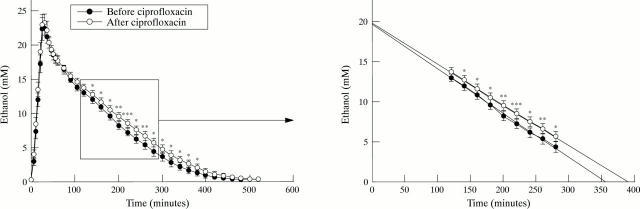
Figure 1 .
Blood ethanol concentrations (mean (SEM)) before and after ciprofloxacin treatment. *p<0.05, **p<0.001, ***p<0.0001.
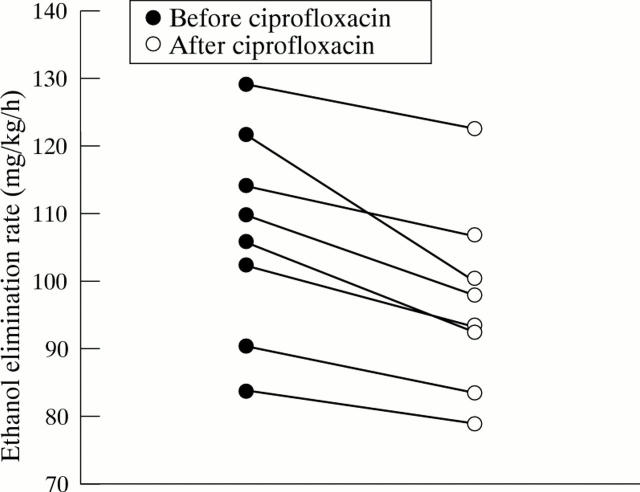
Figure 2 .
The effect of ciprofloxacin treatment (750 mg twice a day) for seven days on individual ethanol elimination rates in eight volunteers.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi Y., Moore L. E., Bradford B. U., Gao W., Thurman R. G. Antibiotics prevent liver injury in rats following long-term exposure to ethanol. Gastroenterology. 1995 Jan;108(1):218–224. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asai H., Imaoka S., Kuroki T., Monna T., Funae Y. Microsomal ethanol oxidizing system activity by human hepatic cytochrome P450s. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996 May;277(2):1004–1009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baraona E., Julkunen R., Tannenbaum L., Lieber C. S. Role of intestinal bacterial overgrowth in ethanol production and metabolism in rats. Gastroenterology. 1986 Jan;90(1):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90081-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjarnason I., Peters T. J., Wise R. J. The leaky gut of alcoholism: possible route of entry for toxic compounds. Lancet. 1984 Jan 28;1(8370):179–182. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92109-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode J. C., Bode C., Heidelbach R., Dürr H. K., Martini G. A. Jejunal microflora in patients with chronic alcohol abuse. Hepatogastroenterology. 1984 Feb;31(1):30–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar B., Edlund C., Malmborg A. S., Nord C. E. Ciprofloxacin concentrations and impact of the colon microflora in patients undergoing colorectal surgery. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Mar;34(3):481–483. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.3.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. H. Fermentation in the human large intestine: evidence and implications for health. Lancet. 1983 May 28;1(8335):1206–1209. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92478-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dan M., Verbin N., Gorea A., Nagar H., Berger S. A. Concentrations of ciprofloxacin in human liver, gallbladder, and bile after oral administration. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1987;32(2):217–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00542200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R., Markham A., Balfour J. A. Ciprofloxacin. An updated review of its pharmacology, therapeutic efficacy and tolerability. Drugs. 1996 Jun;51(6):1019–1074. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199651060-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estonius M., Svensson S., Hög J. O. Alcohol dehydrogenase in human tissues: localisation of transcripts coding for five classes of the enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1996 Nov 18;397(2-3):338–342. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(96)01204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser A. G. Pharmacokinetic interactions between alcohol and other drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997 Aug;33(2):79–90. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199733020-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui H., Brauner B., Bode J. C., Bode C. Plasma endotoxin concentrations in patients with alcoholic and non-alcoholic liver disease: reevaluation with an improved chromogenic assay. J Hepatol. 1991 Mar;12(2):162–169. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90933-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halsted C. H., Robles E. A., Mezey E. Distribution of ethanol in the human gastrointestinal tract. Am J Clin Nutr. 1973 Aug;26(8):831–834. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/26.8.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holford N. H. Clinical pharmacokinetics of ethanol. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1987 Nov;13(5):273–292. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198713050-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokelainen K., Matysiak-Budnik T., Mäkisalo H., Höckerstedt K., Salaspuro M. High intracolonic acetaldehyde values produced by a bacteriocolonic pathway for ethanol oxidation in piglets. Gut. 1996 Jul;39(1):100–104. doi: 10.1136/gut.39.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokelainen K., Nosova T., Koivisto T., Väkeväinen S., Jousimies-Somer H., Heine R., Salaspuro M. Inhibition of bacteriocolonic pathway for ethanol oxidation by ciprofloxacin in rats. Life Sci. 1997;61(18):1755–1762. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(97)00799-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokelainen K., Roine R. P., Vänänen H., Färkkilä M., Salaspuro M. In vitro acetaldehyde formation by human colonic bacteria. Gut. 1994 Sep;35(9):1271–1274. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.9.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokelainen K., Siitonen A., Jousimies-Somer H., Nosova T., Heine R., Salaspuro M. In vitro alcohol dehydrogenase-mediated acetaldehyde production by aerobic bacteria representing the normal colonic flora in man. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996 Sep;20(6):967–972. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1996.tb01932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamali F. No influence of ciprofloxacin on ethanol disposition. A pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic interaction study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1994;47(1):71–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00193482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koivisto T., Salaspuro M. Aldehyde dehydrogenases of the rat colon: comparison with other tissues of the alimentary tract and the liver. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996 May;20(3):551–555. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1996.tb01091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. D., Doizaki W., Levine A. S. Hypothesis: metabolic activity of the colonic bacteria influences organ injury from ethanol. Hepatology. 1982 Sep-Oct;2(5):598–600. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber C. S. Alcohol and the liver: 1994 update. Gastroenterology. 1994 Apr;106(4):1085–1105. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90772-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matysiak-Budnik T., Jokelainen K., Kärkkäinen P., Mäkisalo H., Ohisalo J., Salaspuro M. Hepatotoxicity and absorption of extrahepatic acetaldehyde in rats. J Pathol. 1996 Apr;178(4):469–474. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199604)178:4<469::AID-PATH510>3.0.CO;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLellan R. A., Drobitch R. K., Monshouwer M., Renton K. W. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics inhibit cytochrome P450-mediated microsomal drug metabolism in rat and human. Drug Metab Dispos. 1996 Oct;24(10):1134–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuki Y., Fujiwara I., Yamaguchi T. Pharmacokinetic interactions related to the chemical structures of fluoroquinolones. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1996 May;37 (Suppl A):41–55. doi: 10.1093/jac/37.suppl_a.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanji A. A., Khettry U., Sadrzadeh S. M., Yamanaka T. Severity of liver injury in experimental alcoholic liver disease. Correlation with plasma endotoxin, prostaglandin E2, leukotriene B4, and thromboxane B2. Am J Pathol. 1993 Feb;142(2):367–373. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neale A. D., Scopes R. K., Kelly J. M., Wettenhall R. E. The two alcohol dehydrogenases of Zymomonas mobilis. Purification by differential dye ligand chromatography, molecular characterisation and physiological roles. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jan 2;154(1):119–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09366.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nix D. E., DeVito J. M., Whitbread M. A., Schentag J. J. Effect of multiple dose oral ciprofloxacin on the pharmacokinetics of theophylline and indocyanine green. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Feb;19(2):263–269. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nosova T., Jokelainen K., Kaihovaara P., Jousimies-Somer H., Siitonen A., Heine R., Salaspuro M. Aldehyde dehydrogenase activity and acetate production by aerobic bacteria representing the normal flora of human large intestine. Alcohol Alcohol. 1996 Nov;31(6):555–564. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.alcalc.a008191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poxton I. R., Brown R., Sawyerr A., Ferguson A. Mucosa-associated bacterial flora of the human colon. J Med Microbiol. 1997 Jan;46(1):85–91. doi: 10.1099/00222615-46-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radandt J. M., Marchbanks C. R., Dudley M. N. Interactions of fluoroquinolones with other drugs: mechanisms, variability, clinical significance, and management. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;14(1):272–284. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.1.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao D. S., Parfitt A. M., Villanueva A. R., Dorman P. J., Kleerekoper M. Hypophosphatemic osteomalacia and adult Fanconi syndrome due to light-chain nephropathy. Another form of oncogenous osteomalacia. Am J Med. 1987 Feb;82(2):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohwedder R. W., Bergan T., Thorsteinsson S. B., Scholl H. Transintestinal elimination of ciprofloxacin. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Mar-Apr;13(2):127–133. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(90)90095-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salaspuro M. Bacteriocolonic pathway for ethanol oxidation: characteristics and implications. Ann Med. 1996 Jun;28(3):195–200. doi: 10.3109/07853899609033120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stowell A. R., Greenway R. M., Batt R. D. Acetaldehyde formation during deproteinization of human blood samples containing ethanol. Biochem Med. 1977 Dec;18(3):392–401. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(77)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utne H. E., Winkler K. Hepatic and extrahepatic elimination of ethanol in cirrhosis. With estimates of intrahepatic shunts and Km for ethanol elimination. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1980;15(3):297–304. doi: 10.3109/00365528009181473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin S. J., Liao C. S., Lee Y. C., Wu C. W., Jao S. W. Genetic polymorphism and activities of human colon alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenases: no gender and age differences. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1994 Oct;18(5):1256–1260. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1994.tb00115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]