Abstract
BACKGROUND—Murine intraepithelial lymphocytes kill Giardia lambia; responses of human intestinal lymphocytes to this parasite are unknown. AIMS—To examine giardia induced proliferation, interferon γ production, migration, and cytotoxicity by lymphocytes from the human intestine and peripheral blood. METHODS—Giardia were added to intraepithelial lymphocytes, lamina propria lymphocytes, and peripheral blood lymphocytes, obtained from jejunal mucosa and blood of otherwise healthy patients undergoing gastric bypass surgery for morbid obesity. Proliferation was measured by 3H-thymidine incorporation; frequency of proliferation precursors, by limiting dilution analysis; interferon γ production, by ELISA; cytotoxicity, by 51Cr release of radiolabelled giardia and by release of serine esterases by effector lymphocytes that mediate cytotoxicity. RESULTS—The CD4+ T lymphocytes from intestine and blood proliferated in response to giardia. The stimulus by the parasite was mitogenic rather than antigenic due to the fact that the peak response was on day 3 rather than day 6, and the large number of precursors was in the range of that for mitogens. CD4+ T lymphocytes from both sites produced interferon γ in response to giardia. Lymphocytes did not migrate towards or kill the parasite. CONCLUSIONS—Giardia induced the same degree of proliferation and interferon γ production by CD4+ T lymphocytes in intestine and blood, but did not trigger cytotoxicity or migration.
Keywords: intraepithelial lymphocytes; lamina propria lymphocytes; parasite; chemotaxis; T cell mediated cytotoxicity; giardia
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (118.4 KB).
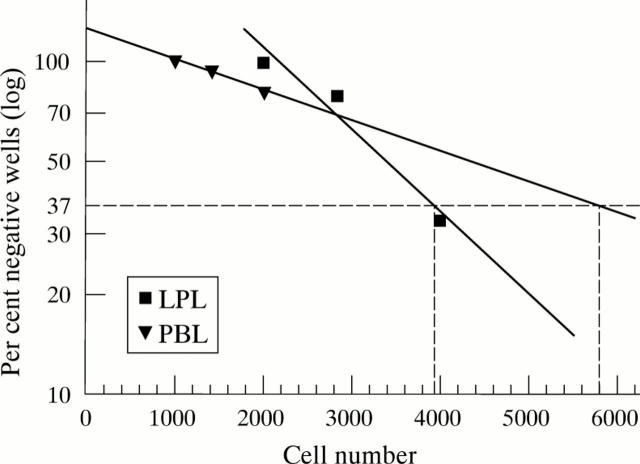
Figure 1 .
CD4+ T lymphocytes from LPL and PBL were combined with giardia (1 × 104) and irradiated autologous PBL (1 × 104) for 10 days. Linear regression analysis allowed an interpolation of the cell number (reciprocal of the precursor frequency) yielding 37% negative wells.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ament M. E., Rubin C. E. Relation of giardiasis to abnormal intestinal structure and function in gastrointestinal immunodeficiency syndromes. Gastroenterology. 1972 Feb;62(2):216–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardès T., Buzoni-Gatel D., Lepage A., Bernard F., Bout D. Toxoplasma gondii oral infection induces specific cytotoxic CD8 alpha/beta+ Thy-1+ gut intraepithelial lymphocytes, lytic for parasite-infected enterocytes. J Immunol. 1994 Nov 15;153(10):4596–4603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimier I. H., Bout D. T. Rat intestinal epithelial cell line IEC-6 is activated by recombinant interferon-gamma to inhibit replication of the coccidian Toxoplasma gondii. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Apr;23(4):981–983. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert E. C., Roberts A. I. Lymphokine-activated killing by human intestinal lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1993 Jan;146(1):107–116. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyworth M. F., Carlson J. R., Ermak T. H. Clearance of Giardia muris infection requires helper/inducer T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1743–1748. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyworth M. F., Owen R. L., Jones A. L. Comparison of leukocytes obtained from the intestinal lumen of Giardia-infected immunocompetent mice and nude mice. Gastroenterology. 1985 Dec;89(6):1360–1365. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90656-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar S. S., Ganguly N. K., Walia B. N., Mahajan R. C. Direct and antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity against Giardia lamblia by splenic and intestinal lymphoid cells in mice. Gut. 1986 Jan;27(1):73–77. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev B., Ward H., Keusch G. T., Pereira M. E. Lectin activation in Giardia lamblia by host protease: a novel host-parasite interaction. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):71–73. doi: 10.1126/science.3513312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lionetti P., Spencer J., Breese E. J., Murch S. H., Taylor J., MacDonald T. T. Activation of mucosal V beta 3+ T cells and tissue damage in human small intestine by the bacterial superantigen, Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Mar;23(3):664–668. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London S. D., Cebra J. J., Rubin D. H. Intraepithelial lymphocytes contain virus-specific, MHC-restricted cytotoxic cell precursors after gut mucosal immunization with reovirus serotype 1/Lang. Reg Immunol. 1989 Mar-Apr;2(2):98–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald T. T., Hutchings P., Choy M. Y., Murch S., Cooke A. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma production measured at the single cell level in normal and inflamed human intestine. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Aug;81(2):301–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03334.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald T. T., Spencer J. Evidence that activated mucosal T cells play a role in the pathogenesis of enteropathy in human small intestine. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1341–1349. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Stafford J. Interferon-gamma directly affects barrier function of cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):724–727. doi: 10.1172/JCI113938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Gillin F. D., Smith P. D. Excretory-secretory products of Giardia lamblia. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):2004–2010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhuber G., Vogelsang H., Stolte M., Muthenthaler S., Kummer J. A., Kummer A. J., Radaszkiewicz T. Evidence that intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes are activated cytotoxic T cells in celiac disease but not in giardiasis. Am J Pathol. 1996 May;148(5):1351–1357. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przemioslo R. T., Lundin K. E., Sollid L. M., Nelufer J., Ciclitira P. J. Histological changes in small bowel mucosa induced by gliadin sensitive T lymphocytes can be blocked by anti-interferon gamma antibody. Gut. 1995 Jun;36(6):874–879. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.6.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts-Thomson I. C., Mitchell G. F. Giardiasis in mice. I. Prolonged infections in certain mouse strains and hypothymic (nude) mice. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jul;75(1):42–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. I., Bilenker M., Ebert E. C. Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes have a promiscuous interleukin-8 receptor. Gut. 1997 Mar;40(3):333–338. doi: 10.1136/gut.40.3.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. I., Nadler S. C., Ebert E. C. Mesenchymal cells stimulate human intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Gastroenterology. 1997 Jul;113(1):144–150. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(97)70089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. I., O'Connell S. M., Biancone L., Brolin R. E., Ebert E. C. Spontaneous cytotoxicity of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes: clues to the mechanism. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Dec;94(3):527–532. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb08229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. I., O'Connell S. M., Ebert E. C. Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes bind to colon cancer cells by HML-1 and CD11a. Cancer Res. 1993 Apr 1;53(7):1608–1611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha T. K., Ghosh T. K. Invasion of small intestinal mucosa by Giardia lamblia in man. Gastroenterology. 1977 Mar;72(3):402–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuerer-Maly C. C., Eckmann L., Kagnoff M. F., Falco M. T., Maly F. E. Colonic epithelial cell lines as a source of interleukin-8: stimulation by inflammatory cytokines and bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Immunology. 1994 Jan;81(1):85–91. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. D., Keister D. B., Elson C. O. Human host response to Giardia lamblia. II. Antibody-dependent killing in vitro. Cell Immunol. 1983 Dec;82(2):308–315. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama H., Trenn G., Sitkovsky M. V. A novel cytotoxic T lymphocyte activation assay. Optimized conditions for antigen receptor triggered granule enzyme secretion. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Nov 23;104(1-2):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90502-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taswell C. Limiting dilution assays for the determination of immunocompetent cell frequencies. I. Data analysis. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1614–1619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]