Abstract
BACKGROUND—Endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration biopsy (EUS-FNA) is a recent innovation in the evaluation of gastrointestinal and pulmonary malignancies. AIMS—To review the experience with EUS-FNA of a large single centre. METHODS—333 consecutive patients underwent EUS-FNA. Follow up data were available on 327 lesions in 317 patients, including 160 lymph nodes, 144 pancreatic lesions, 15 extraintestinal masses, and eight intramural tumours. RESULTS—A primary diagnosis of malignancy was obtained by EUS-FNA in 62% of patients with clinically suspicious lesions. The overall accuracy of EUS-FNA for the diagnosis of malignancy was 86%, with sensitivity of 84% and specificity of 96%. With respect to lesion types, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 85%, 100%, and 89% for lymph nodes; 82%, 100%, and 85% for pancreatic lesions; 88%, 100%, and 90% for perirectal masses; and 50%, 25%, and 38% for intramural lesions, respectively. Compared with size and sonographic criteria, EUS-FNA in the evaluation of lymph nodes provided superior accuracy and specificity, without compromising sensitivity. Inadequate specimens were obtained from only six patients, including 3/5 with stromal tumors. Only one complication occurred. CONCLUSIONS—EUS-FNA is safe and can readily obtain tissue specimens adequate for cytopathological diagnoses. Compared with size and sonographic criteria, it is a superior modality for the detection of nodal metastases. While providing accurate diagnosis of pancreatic and perirectal malignancies, results suggest the technique is less useful for intramural lesions.
Keywords: endoscopic ultrasound; endosonography; fine needle aspiration biopsy
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (166.3 KB).
Figure 1 .
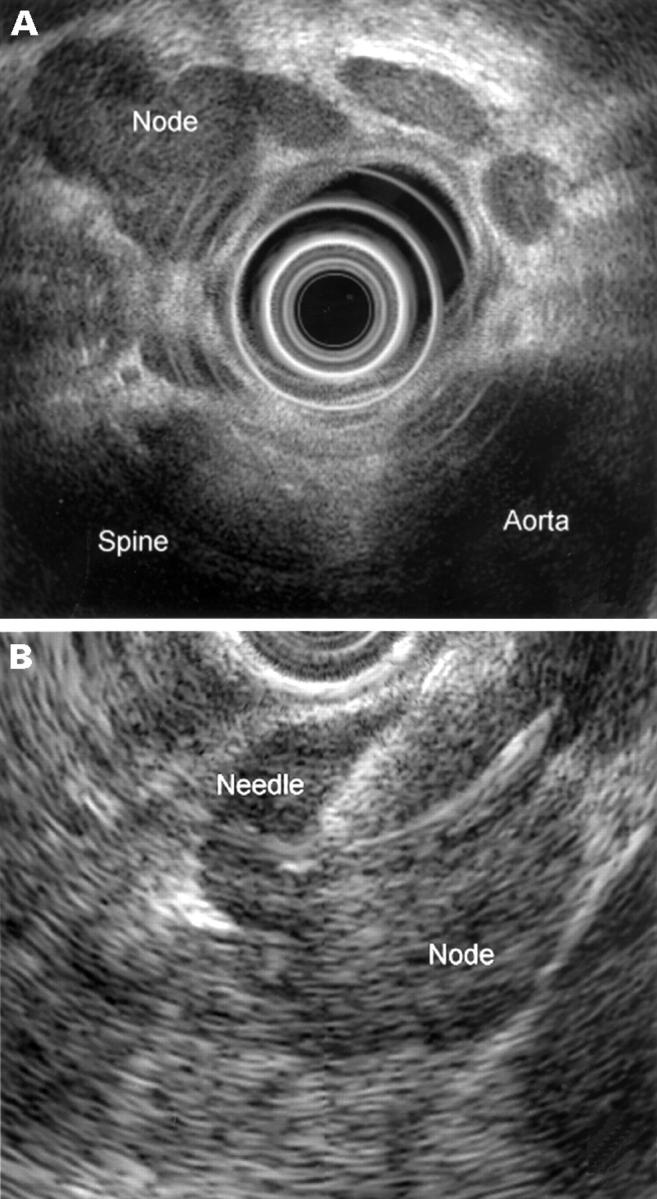
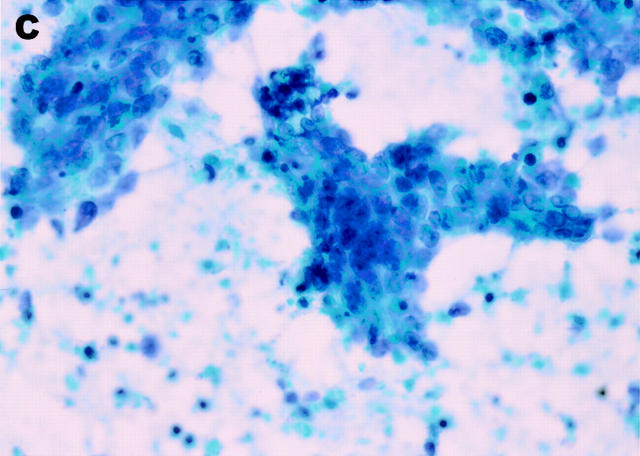
(A) Using a radial scanning echoendoscope, bulky hypoechoic lymph nodes are identified in the subcarinal region in a patient with NSCLC. (B) Real time, ultrasound directed needle aspiration biopsy of a subcarinal lymph node is performed. The echogenic needle is visualised within the target node. (C) The aspirate confirms sheets of malignant cells with large nuclei and prominent nucleoli. Necrotic debris is noted in the background. Papanicolou stain (original magnification ×200).
Figure 2 .
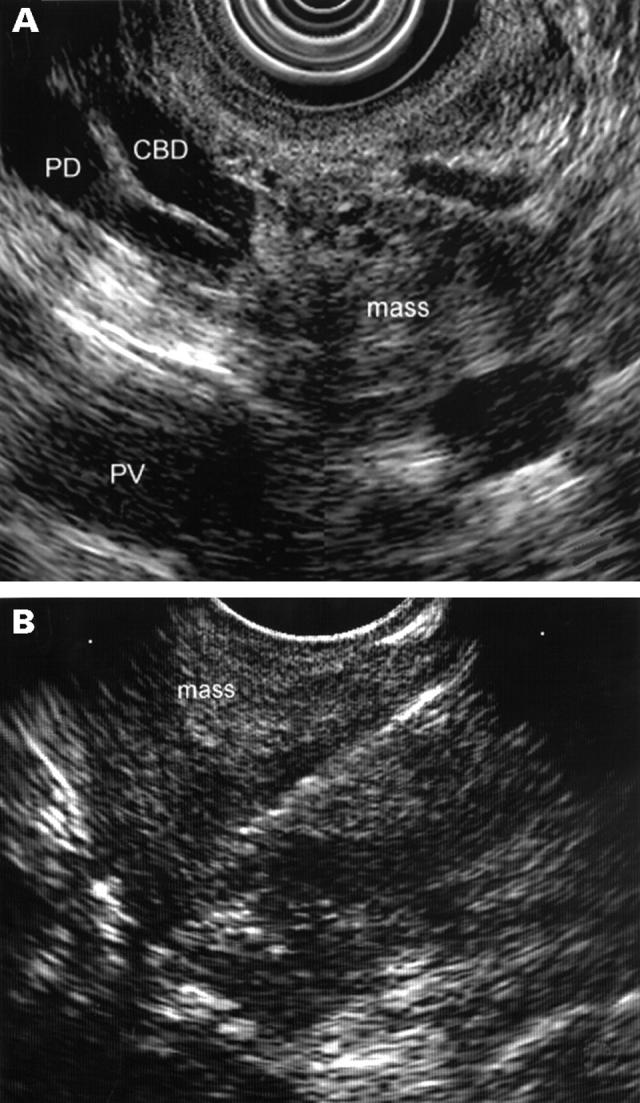
(A) A heterogenous hypoechoic mass is identified in the head of pancreas and is obstructing both the common bile duct (CBD) and main pancreatic duct (PD). The mass can also be seen to invade the portal vein (PV). (B) Using a linear scanning echoendoscope, the echogenic fine needle tip is directed into the pancreatic mass. Aspiration cytology confirmed adenocarcinoma.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caletti G. C., Brocchi E., Ferrari A., Bonora G., Santini D., Mazzoleni G., Barbara L. Guillotine needle biopsy as a supplement to endosonography in the diagnosis of gastric submucosal tumors. Endoscopy. 1991 Sep;23(5):251–254. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano M. F., Sivak M. V., Jr, Rice T., Gragg L. A., Van Dam J. Endosonographic features predictive of lymph node metastasis. Gastrointest Endosc. 1994 Jul-Aug;40(4):442–446. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(94)70206-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Nguyen P., Erickson R. A., Durbin T. E., Katz K. D. The clinical utility of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration in the diagnosis and staging of pancreatic carcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997 May;45(5):387–393. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(97)70149-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Wiersema M. J. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy and interventional endoscopic ultrasonography. Emerging technologies. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 1997 Apr;7(2):221–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannini M., Seitz J. F., Monges G., Perrier H., Rabbia I. Fine-needle aspiration cytology guided by endoscopic ultrasonography: results in 141 patients. Endoscopy. 1995 Feb;27(2):171–177. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1005657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gress F. G., Hawes R. H., Savides T. J., Ikenberry S. O., Lehman G. A. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy using linear array and radial scanning endosonography. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997 Mar;45(3):243–250. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(97)70266-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gress F. G., Savides T. J., Sandler A., Kesler K., Conces D., Cummings O., Mathur P., Ikenberry S., Bilderback S., Hawes R. Endoscopic ultrasonography, fine-needle aspiration biopsy guided by endoscopic ultrasonography, and computed tomography in the preoperative staging of non-small-cell lung cancer: a comparison study. Ann Intern Med. 1997 Oct 15;127(8 Pt 1):604–612. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-127-8_part_1-199710150-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz A., Mildenberger P., Georg M., Braunstein S., Junginger T. Endoscopic ultrasonography in the diagnosis of regional lymph nodes in esophageal and gastric cancer--results of studies in vitro. Endoscopy. 1993 Mar;25(3):231–235. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt U., Feifel G. Endosonography in the diagnosis of lymph nodes. Endoscopy. 1993 Mar;25(3):243–245. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. J., Hawes R. H. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided puncture of the lymph nodes: first experience and clinical consequences. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 1995 Jul;5(3):587–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo D., Imaizumi M., Abe T., Naruke T., Suemasu K. Endoscopic ultrasound examination for mediastinal lymph node metastases of lung cancer. Chest. 1990 Sep;98(3):586–593. doi: 10.1378/chest.98.3.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. F., Meyenberger C., Bertschinger P., Schaer R., Marincek B. Pancreatic tumors: evaluation with endoscopic US, CT, and MR imaging. Radiology. 1994 Mar;190(3):745–751. doi: 10.1148/radiology.190.3.8115622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palazzo L., Roseau G., Gayet B., Vilgrain V., Belghiti J., Fékéte F., Paolaggi J. A. Endoscopic ultrasonography in the diagnosis and staging of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Results of a prospective study with comparison to ultrasonography and CT scan. Endoscopy. 1993 Feb;25(2):143–150. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rösch T. Staging of pancreatic cancer. Analysis of literature results. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 1995 Oct;5(4):735–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savides T. J., Gress F. G., Wheat L. J., Ikenberry S., Hawes R. H. Dysphagia due to mediastinal granulomas: diagnosis with endoscopic ultrasonography. Gastroenterology. 1995 Aug;109(2):366–373. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvestri G. A., Hoffman B. J., Bhutani M. S., Hawes R. H., Coppage L., Sanders-Cliette A., Reed C. E. Endoscopic ultrasound with fine-needle aspiration in the diagnosis and staging of lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 1996 May;61(5):1441–1446. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(95)00052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tio T. L., Cohen P., Coene P. P., Udding J., den Hartog Jager F. C., Tytgat G. N. Endosonography and computed tomography of esophageal carcinoma. Preoperative classification compared to the new (1987) TNM system. Gastroenterology. 1989 Jun;96(6):1478–1486. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90515-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiersema M. J., Vilmann P., Giovannini M., Chang K. J., Wiersema L. M. Endosonography-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy: diagnostic accuracy and complication assessment. Gastroenterology. 1997 Apr;112(4):1087–1095. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(97)70164-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler K., Sanft C., Zimmer T., Zeitz M., Felsenberg D., Stein H., Germer C., Deutschmann C., Riecken E. O. Comparison of computed tomography, endosonography, and intraoperative assessment in TN staging of gastric carcinoma. Gut. 1993 May;34(5):604–610. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.5.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]