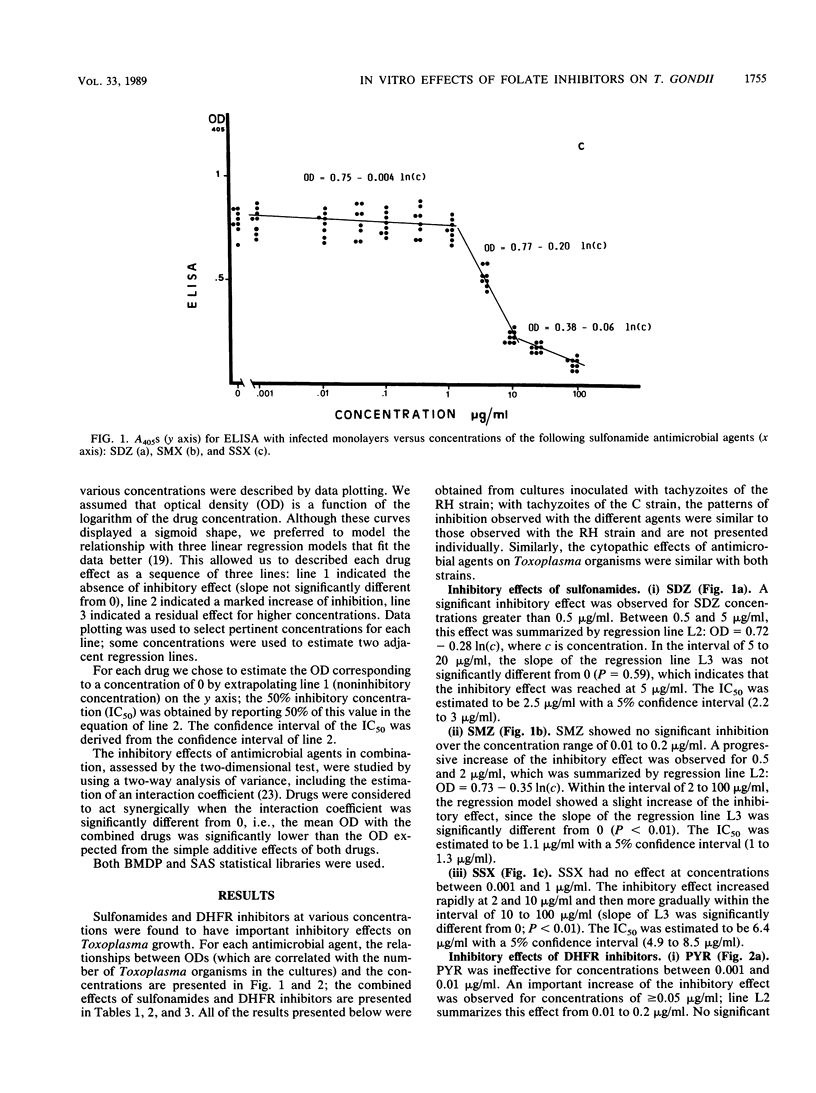
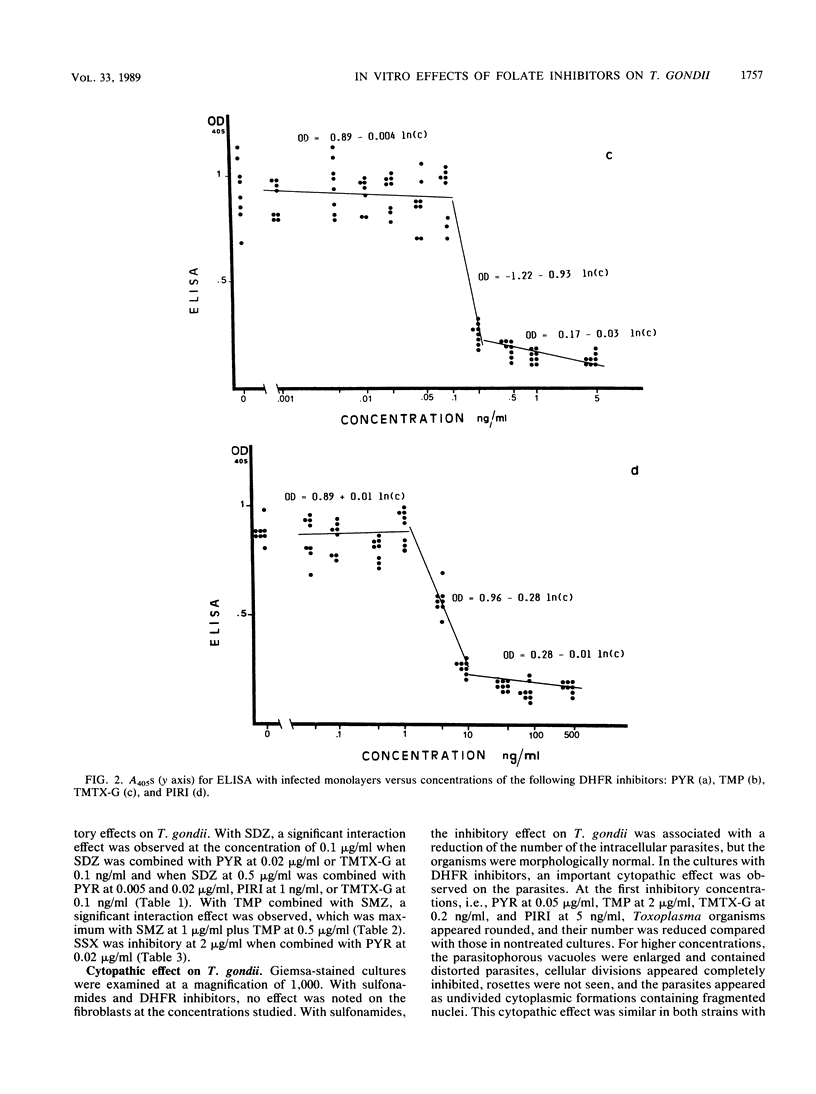
Abstract
Three sulfonamides and four dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors were tested alone and in combination to determine their in vitro effects on two strains of Toxoplasma gondii grown in MRC5 fibroblast tissue culture. Toxoplasma growth was quantitated by an enzyme immunoassay performed directly on the fixed cultures, and linear regression models were used to quantify the relationship between the optical density values generated by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and the concentrations of the antimicrobial agents in the culture medium. The cytopathic effects of antimicrobial agents on T. gondii were examined in Giemsa-stained cultures. Sulfonamides and dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors exhibited similar patterns of inhibition, consisting of an important increase of the inhibitory effect within a narrow range of concentrations. Sulfadiazine, sulfamethoxazole, and sulfisoxazole were all found to have important inhibitory effects on T. gondii; the 50% inhibitory concentrations estimated from the regression models were 2.5 micrograms/ml for sulfadiazine, 1.1 micrograms/ml for sulfamethoxazole, and 6.4 micrograms/ml for sulfisoxazole. This inhibition of growth was associated with a reduction of the number of parasitized cells and intracellular parasites that were morphologically normal. With dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors, including pyrimethamine, trimethoprim, trimetrexate-glycuronate, and piritrexim, a strong inhibition of Toxoplasma growth was observed, which was associated with striking morphological changes of the parasites. The 50% inhibitory concentrations were 0.04 microgram/ml for pyrimethamine, 2.3 micrograms/ml for trimethoprim, 0.16 ng/ml for trimetrexate-glycuronate, and 6.9 ng/ml for piritrexim. When sulfonamides and dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors were used in combination, a synergistic effect was observed with sulfadiazine combined with pyrimethamine, trimetrexate-glycuronate, and piritrexim; sulfisoxazole combined with pyrimethamine; and trimethoprim combined with sulfamethoxazole. These results were analyzed in comparison with human pharmacokinetics data.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad R. A., Rogers H. J. Pharmacokinetics and protein binding interactions of dapsone and pyrimethamine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;10(5):519–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1980.tb01798.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen F., Elsborg L., Husted S., Thomsen O. Pharmacokinetics of sulfadiazine and trimethoprim in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Nov 9;14(1):57–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00560259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araujo F. G., Guptill D. R., Remington J. S. In vivo activity of piritrexim [corrected] against Toxoplasma gondii. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):828–830. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derouin F., Chastang C. Enzyme immunoassay to assess effect of antimicrobial agents on Toxoplasma gondii in tissue culture. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Mar;32(3):303–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.3.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derouin F., Nalpas J., Chastang C. Mesure in vitro de l'effet inhibiteur de macrolides, lincosamides et synergestines sur la croissance de Toxoplasma gondii. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1988 Dec;36(10):1204–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EYLES D. E. The present status of the chemotherapy of toxoplasmosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1953 May;2(3):429–444. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1953.2.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman P. L., Remington J. S. The effect of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole on Toxoplasma gondii in vitro and in vivo. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1979 May;28(3):445–455. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1979.28.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris C., Salgo M. P., Tanowitz H. B., Wittner M. In vitro assessment of antimicrobial agents against Toxoplasma gondii. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):14–22. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverkos H. W. Assessment of therapy for toxoplasma encephalitis. The TE Study Group. Am J Med. 1987 May;82(5):907–914. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90151-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Allegra C. J., Chabner B. A., Swan J. C., Drake J., Lunde M., Parrillo J. E., Masur H. Potent effect of trimetrexate, a lipid-soluble antifolate, on Toxoplasma gondii. J Infect Dis. 1987 May;155(5):1027–1032. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.5.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Allegra C. J., Swan J. C., Drake J. C., Parrillo J. E., Chabner B. A., Masur H. Potent antipneumocystis and antitoxoplasma activities of piritrexim, a lipid-soluble antifolate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):430–433. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause P. J., Owens N. J., Nightingale C. H., Klimek J. J., Lehmann W. B., Quintiliani R. Penetration of amoxicillin, cefaclor, erythromycin-sulfisoxazole, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole into the middle ear fluid of patients with chronic serous otitis media. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):815–821. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leport C., Raffi F., Matheron S., Katlama C., Regnier B., Saimot A. G., Marche C., Vedrenne C., Vilde J. L. Treatment of central nervous system toxoplasmosis with pyrimethamine/sulfadiazine combination in 35 patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Efficacy of long-term continuous therapy. Am J Med. 1988 Jan;84(1):94–100. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. T., Cashmore A. R., Baker M., Dreyer R. N., Ernstoff M., Marsh J. C., Bertino J. R., Whitfield L. R., Delap R., Grillo-Lopez A. Phase I studies with trimetrexate: clinical pharmacology, analytical methodology, and pharmacokinetics. Cancer Res. 1987 Jan 15;47(2):609–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack D. G., McLeod R. New micromethod to study the effect of antimicrobial agents on Toxoplasma gondii: comparison of sulfadoxine and sulfadiazine individually and in combination with pyrimethamine and study of clindamycin, metronidazole, and cyclosporin A. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):26–30. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midskov C. Rapid gas chromatographic determination of pyrimethamine in human plasma and urine. J Chromatogr. 1984 Mar 9;306:388–393. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)80904-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queener S. F., Bartlett M. S., Jay M. A., Durkin M. M., Smith J. W. Activity of lipid-soluble inhibitors of dihydrofolate reductase against Pneumocystis carinii in culture and in a rat model of infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1323–1327. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers P., Allegra C. J., Murphy R. F., Drake J. C., Masur H., Poplack D. G., Chabner B. A., Parrillo J. E., Lane H. C., Balis F. M. Bioavailability of oral trimetrexate in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Mar;32(3):324–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.3.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield H. G., Melton M. L. Effect of pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine on the fine structure and multiplication of Toxoplasma gondii in cell cultures. J Parasitol. 1975 Aug;61(4):704–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidekamm E., Plozza-Nottebrock H., Forgo I., Dubach U. C. Plasma concentrations in pyrimethamine and sulfadoxine and evaluation of pharmacokinetic data by computerized curve fitting. Bull World Health Organ. 1982;60(1):115–122. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Harris C., Berger M., Tanowitz H. B., Wittner M. Pyrimethamine concentrations in serum and cerebrospinal fluid during treatment of acute Toxoplasma encephalitis in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):580–583. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


