Abstract
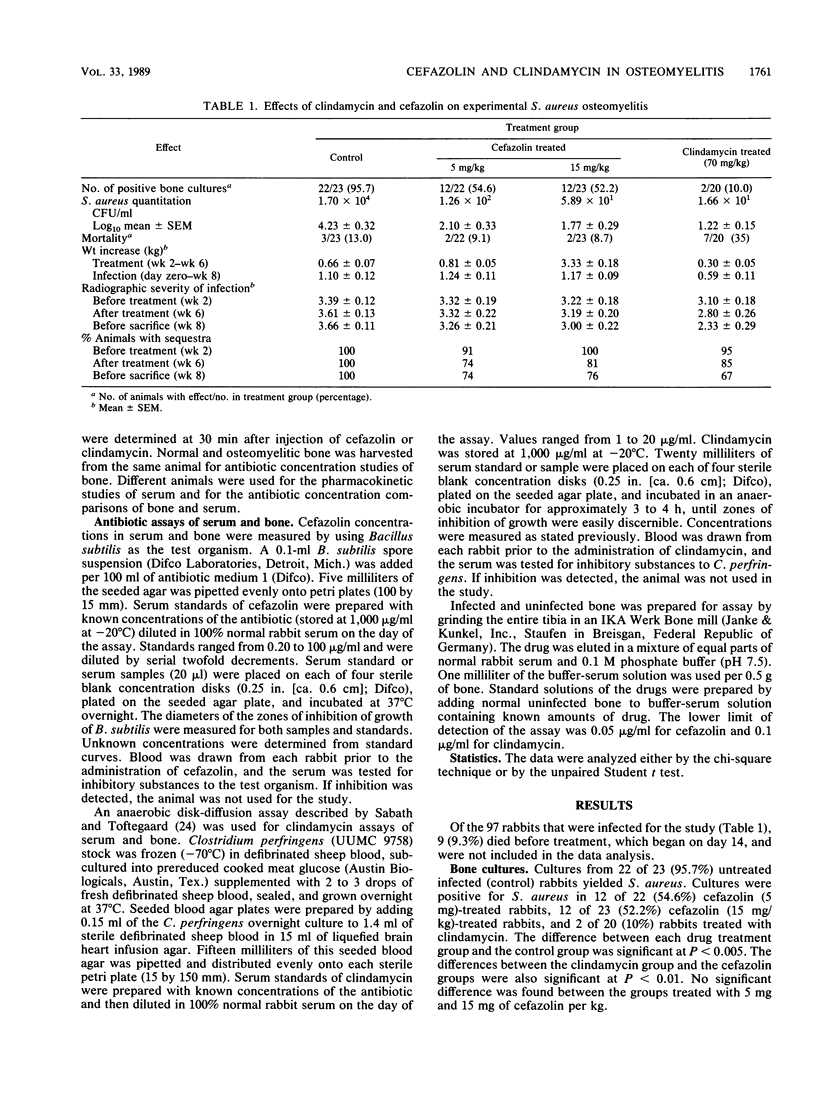
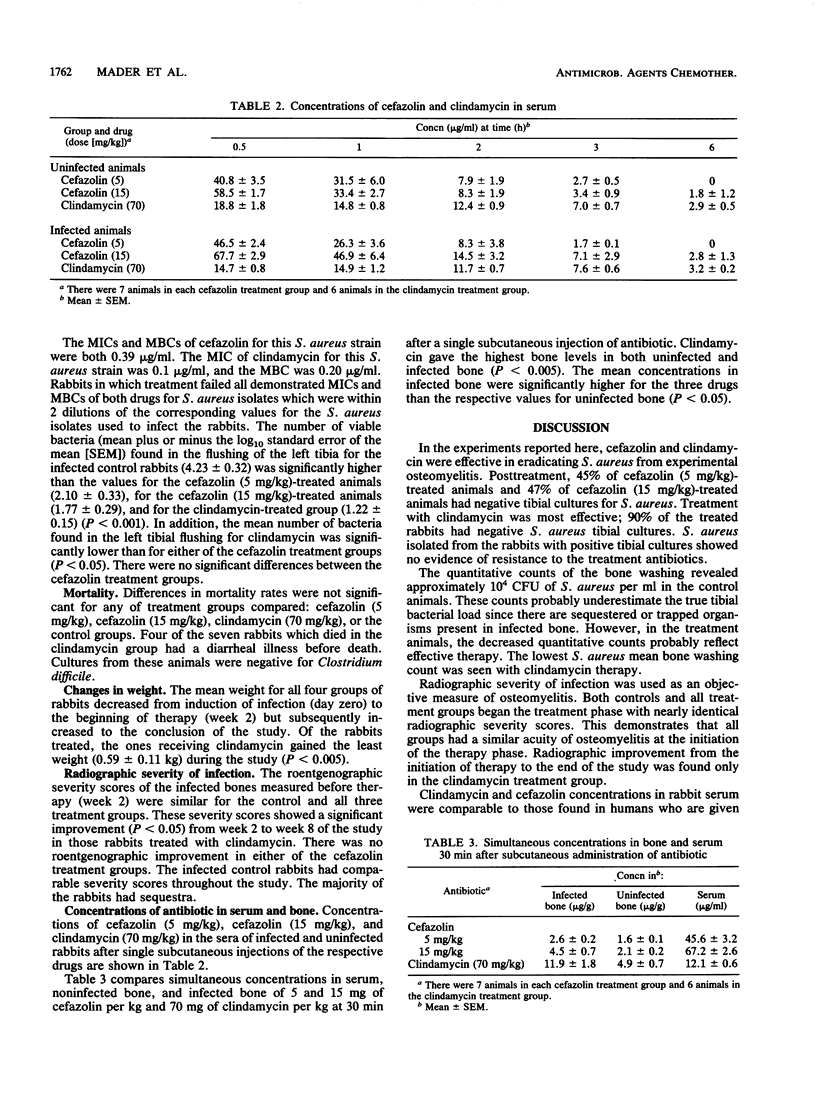
A rabbit model for Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis was used to compare treatment with clindamycin and cefazolin. Cefazolin (5 mg/kg), cefazolin (15 mg/kg), and clindamycin (70 mg/kg) were injected subcutaneously every 6 h for 28 days. After treatment, S. aureus was found in bone cultures from 22 of 23 control rabbits, 12 of 22 rabbits treated with cefazolin (5 mg/kg), 12 of 23 rabbits treated with cefazolin (15 mg/kg), and 2 of 20 rabbits treated with clindamycin. Drug concentrations in serum, uninfected bone, and infected bone were measured 30 min after cefazolin or clindamycin was injected into a group of rabbits which had been infected for 3 to 4 weeks. Clindamycin gave the highest concentration in infected and uninfected bone. The results of the study showed that clindamycin was superior to cefazolin in the eradication of S. aureus from infected bone in an experimental model.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crane L. R., Kapdi C. C., Wolfe J. N., Silberberg B. K., Lerner A. M. Xeroradiographic, bacteriologic, and pathologic studies in experimental staphylococcus osteomyelitis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Nov;156(2):303–314. doi: 10.3181/00379727-156-39926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornbusch K. Antibiotics in bone tissues. Methodological and practical aspects. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):177–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornbusch K., Carlström A., Hugo H., Lidström A. Antibacterial activity of clindamycin and lincomycin in human bone. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Mar;3(2):153–160. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.2.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigin R. D., Pickering L. K., Anderson D., Keeney R. E., Shackleford P. G. Clindamycin treatment of osteomyelitis and septic arthritis in children. Pediatrics. 1975 Feb;55(2):213–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes A. M., Dwyer N. S., Ball A. P., Amos R. S. Clindamycin in bone and joint infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Sep;3(5):501–507. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.5.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R. Mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the influence of culture medium on the stability of mucus production. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Nov;8(4):513–522. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-4-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Lowe B. R., Dzink J. L., Bartlett J. G. Antibiotic levels in infected and sterile subcutaneous abscesses in mice. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):487–494. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempner M. S., Styrt B. Clindamycin uptake by human neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1981 Nov;144(5):472–479. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.5.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFrock J. L., Molavi A., Prince R. A. Clindamycin. Med Clin North Am. 1982 Jan;66(1):103–120. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh D. A. Antibacterial activity and pharmacokinetics of clindamycin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Jun;7 (Suppl A):3–9. doi: 10.1093/jac/7.suppl_a.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mader J. T., Brown G. L., Guckian J. C., Wells C. H., Reinarz J. A. A mechanism for the amelioration by hyperbaric oxygen of experimental staphylococcal osteomyelitis in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):915–922. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mader J. T., Guckian J. C., Glass D. L., Reinarz J. A. Therapy with hyperbaric oxygen for experimental osteomyelitis due to Staphylococcus aureus in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1978 Sep;138(3):312–318. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.3.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mader J. T., Morrison L. T., Adams K. R. Comparative evaluation of A-56619, A-56620, and nafcillin in the treatment of experimental Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):259–263. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mader J. T., Wilson K. J. Comparative evaluation of cefamandole and cephalothin in the treatment of experimental Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis in rabbits. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983 Apr;65(4):507–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry-Carson K. J., Mayberry W. R., Tober-Meyer B. K., Costerton J. W., Lambe D. W., Jr An electron microscopic study of the effect of clindamycin on adherence of Staphylococcus aureus to bone surfaces. Microbios. 1986;45(182):21–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry-Carson K. J., Tober-Meyer B., Smith J. K., Lambe D. W., Jr, Costerton J. W. Bacterial adherence and glycocalyx formation in osteomyelitis experimentally induced with Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):825–833. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.825-833.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel J. C., Wright J. B., Ruseska I., Marrie T. J., Whitfield C., Costerton J. W. Antibiotic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonizing a urinary catheter in vitro. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;4(2):213–218. doi: 10.1007/BF02013600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W. Experimental osteomyelitis. I. A description of the model. J Infect Dis. 1970 Nov;122(5):410–418. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.5.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W., Shinners E., Niederriter K. Clindamycin treatment of experimental chronic osteomyelitis due to Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):956–959. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokesch R. C., Hand W. L. Antibiotic entry into human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Mar;21(3):373–380. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez W., Ross S., Khan W., McKay D., Moskowitz P. Clindamycin in the treatment of osteomyelitis in children: a report of 29 cases. Am J Dis Child. 1977 Oct;131(10):1088–1093. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1977.02120230034005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Toftegaard I. Rapid microassays for clindamycin and gentamicin when present together and the effect of pH and of each on the antibacterial activity of the other. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jul;6(1):54–59. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzmann S., Boring J. R. Antiphagocytic Effect of Slime from a Mucoid Strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):762–767. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.762-767.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summersgill J. T., Schupp L. G., Raff M. J. Comparative penetration of metronidazole, clindamycin, chloramphenicol, cefoxitin, ticarcillin, and moxalactam into bone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Apr;21(4):601–603. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.4.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


