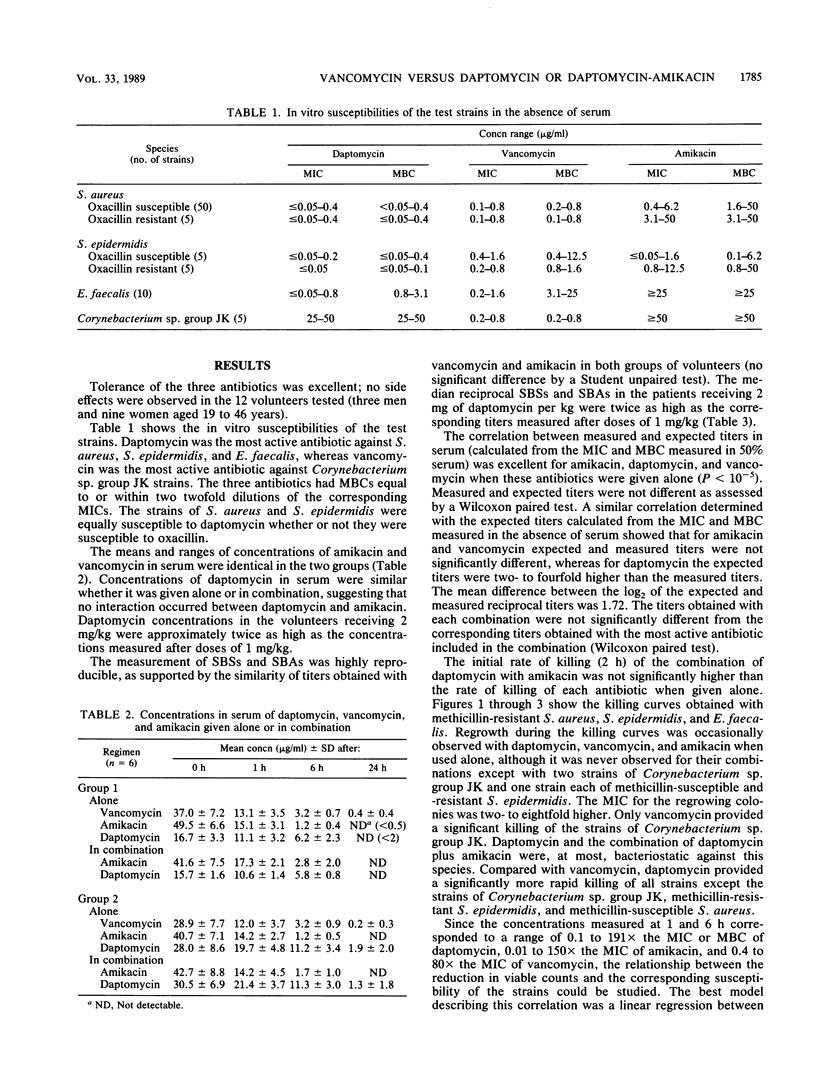
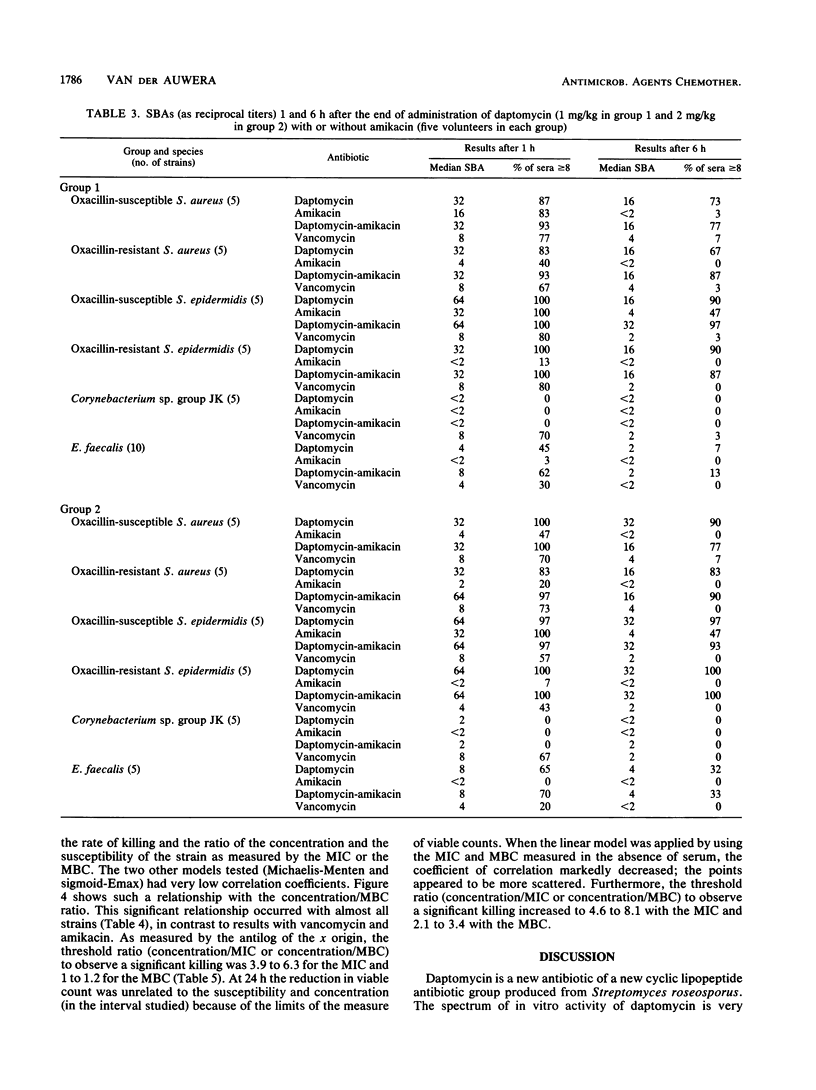
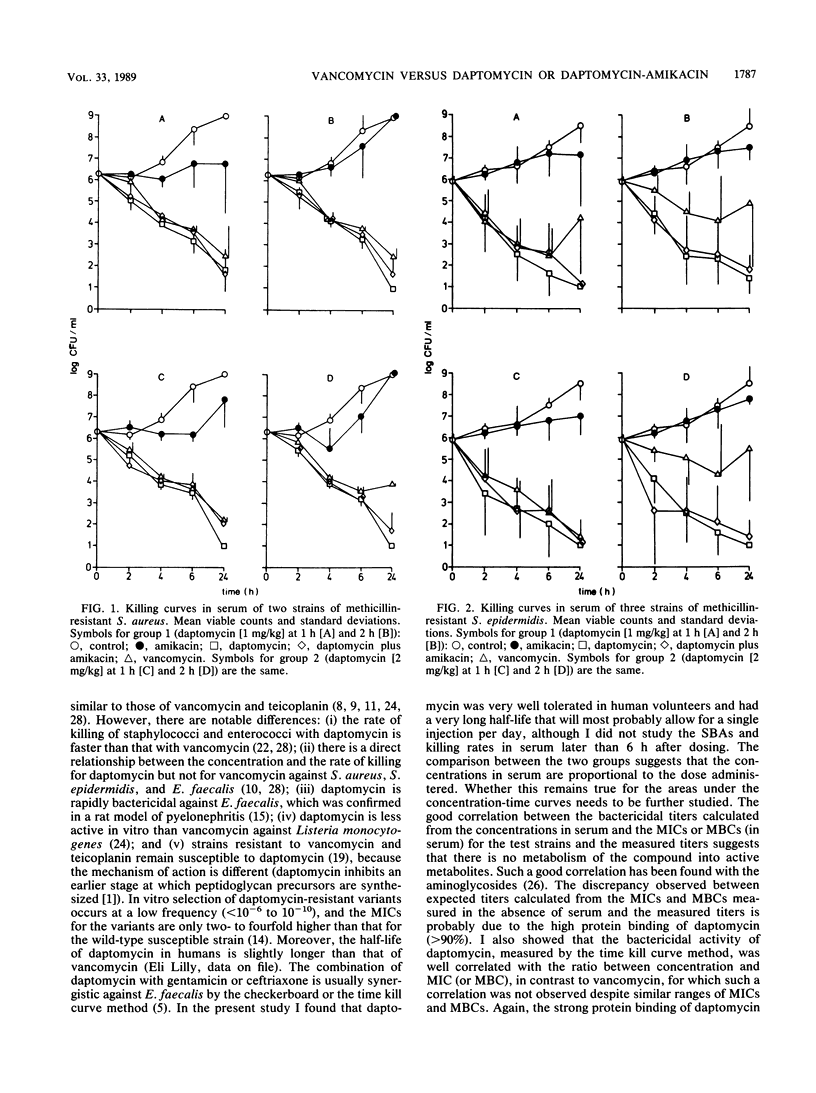
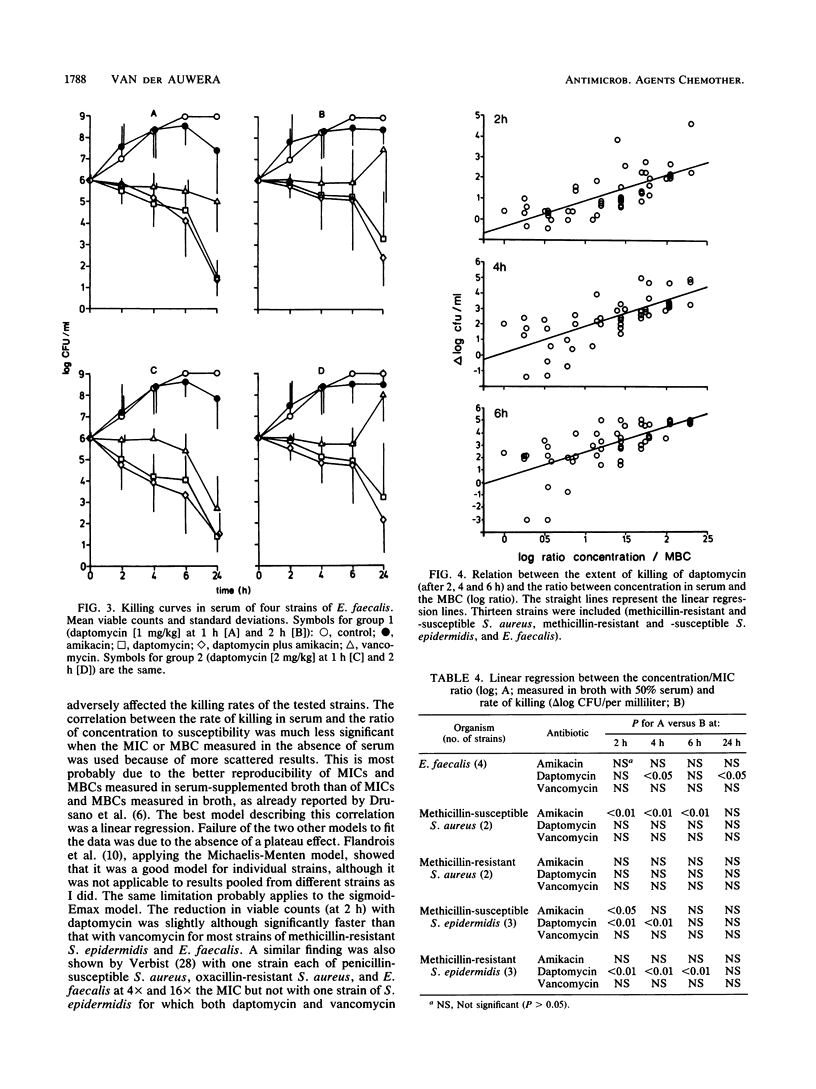
Abstract
Twelve volunteers, in two groups of six, received daptomycin at a dose of 1 or 2 mg/kg. In addition, they received in a randomly allocated order amikacin (500 mg), daptomycin-amikacin, and vancomycin (500 mg). Thirty-five clinical isolates, including Staphylococcus aureus, S. epidermidis, Corynebacterium sp. group JK, and Enterococcus faecalis, were tested in vitro for the measure of the serum bactericidal titers and killing rates. The mean peak concentrations of daptomycin in serum 1 h after the administration of 1 and 2 mg/kg were 11 and 20 micrograms/ml, respectively. At 24 h after the administration of 2 mg/kg, the mean level in serum was 1.9 micrograms/ml, which is higher than the MICs for susceptible pathogens. Daptomycin and amikacin provided identical concentrations in serum whether given alone or in combination. Among the six regimens tested, those including daptomycin provided the highest and the most prolonged serum bactericidal titers against S. aureus, S. epidermidis, and E. faecalis. The killing rates measured by the killing curves were correlated with the concentration/MIC and concentration/MBC ratios of daptomycin for all strains tested. Significant killing occurred once the concentration of daptomycin in the serum 4- to 6-fold the MIC or 1- to 1.2-fold the MBC. The combination of daptomycin and amikacin had no effect on either the serum bactericidal titers or the rates of killing. Only vancomycin provided significant killing of the strains of Corynebacterium sp. group JK.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen N. E., Hobbs J. N., Alborn W. E., Jr Inhibition of peptidoglycan biosynthesis in gram-positive bacteria by LY146032. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1093–1099. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. V., Brodie J. L., Benner E. J., Kirby W. M. Simplified, accurate method for antibiotic assay of clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):170–177. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.170-177.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blouin R. A., Bauer L. A., Miller D. D., Record K. E., Griffen W. O., Jr Vancomycin pharmacokinetics in normal and morbidly obese subjects. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Apr;21(4):575–580. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.4.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briceland L. L., Pasko M. T., Mylotte J. M. Serum bactericidal rate as measure of antibiotic interactions. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 May;31(5):679–685. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.5.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debbia E., Pesce A., Schito G. C. In vitro activity of LY146032 alone and in combination with other antibiotics against gram-positive bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Feb;32(2):279–281. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drusano G., Standiford H., Ryan P., McNamee W., Tatem B., Schimpff S. Correlation of predicted serum bactericidal activities and values measured in volunteers. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;5(1):88–92. doi: 10.1007/BF02013475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edberg S. C., Bottenbley C. J., Gam K. Use of sodium polyanethol sulfonate to selectively inhibit aminoglycoside and polymyxin antibiotics in a rapid blood level antibiotic assay. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):414–417. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Willey S., Reiszner E., Spitzer P. G., Caputo G., Moellering R. C., Jr In vitro and in vivo activity of LY 146032, a new cyclic lipopeptide antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Oct;30(4):532–535. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.4.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J., Helsel V. L. In vitro activity of LY146032 against staphylococci, streptococci, and enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):781–784. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flandrois J. P., Fardel G., Carret G. Early stages of in vitro killing curve of LY146032 and vancomycin for Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):454–457. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Barry A. L. Antimicrobial activity and spectrum of LY146032, a lipopeptide antibiotic, including susceptibility testing recommendations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):625–629. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby W. M. Vancomycin therapy of severe staphylococcal infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Dec;14 (Suppl 500):73–78. doi: 10.1093/jac/14.suppl_d.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Moellering R. C., Jr, Greenblatt D. J. Single-dose kinetics of intravenous vancomycin. J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Apr;20(4 Pt 1):197–201. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1980.tb01696.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miniter P. M., Patterson T. F., Johnson M. A., Andriole V. T. Activity of LY146032 in vitro and in experimental enterococcal pyelonephritis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Aug;31(8):1199–1203. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.8.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D., Lietman P. S., Smith C. R. Clinical response to aminoglycoside therapy: importance of the ratio of peak concentration to minimal inhibitory concentration. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):93–99. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Steigbigel R. T., Davis H. T., Chapman S. W. Method of reliable determination of minimal lethal antibiotic concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):699–708. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller L. B., Stratton C. W. Serum dilution test for bactericidal activity. II. Standardization and correlation with antimicrobial assays and susceptibility tests. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136(2):196–204. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe R. S., Stapleton J. T., Gilligan P. H. Emergence of vancomycin resistance in coagulase-negative staphylococci. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 9;316(15):927–931. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704093161507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sculier J. P., Weerts D., Klastersky J. Causes of death in febrile granulocytopenic cancer patients receiving empiric antibiotic therapy. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1984 Jan;20(1):55–60. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(84)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton C. W., Liu C., Ratner H. B., Weeks L. S. Bactericidal activity of deptomycin (LY146032) compared with those of ciprofloxacin, vancomycin, and ampicillin against enterococci as determined by kill-kinetic studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1014–1016. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terragna A., Ferrea G., Loy A., Danese A., Bernareggi A., Cavenaghi L., Rosina R. Pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin in pediatric patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Aug;32(8):1223–1226. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.8.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Auwera P., Grenier P., Klastersky J. In-vitro activity of LY146032 against Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, Corynebacterium JK, and Bacillus spp., in comparison with various antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Aug;20(2):209–212. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Auwera P., Klastersky J. Bactericidal activity and killing rate of serum in volunteers receiving ciprofloxacin alone or in combination with vancomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):892–895. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Auwera P., Klastersky J. Bactericidal activity and killing rate of serum in volunteers receiving teicoplanin alone or in combination with oral or intravenous rifampin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1002–1005. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Auwera P., Klastersky J. Serum bactericidal activity and postantibiotic effect in serum of patients with urinary tract infection receiving high-dose amikacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1061–1068. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist L. In vitro activity of LY146032, a new lipopeptide antibiotic, against gram-positive cocci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):340–342. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist L., Tjandramaga B., Hendrickx B., Van Hecken A., Van Melle P., Verbesselt R., Verhaegen J., De Schepper P. J. In vitro activity and human pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):881–886. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viscoli C., Van der Auwera P., Meunier F. Gram-positive infections in granulocytopenic patients: an important issue? J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Apr;21 (Suppl 100):149–156. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_c.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Swartz M. N. Drug therapy. Serum bactericidal activity as a monitor of antibiotic therapy. N Engl J Med. 1985 Apr 11;312(15):968–975. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198504113121507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


