Abstract
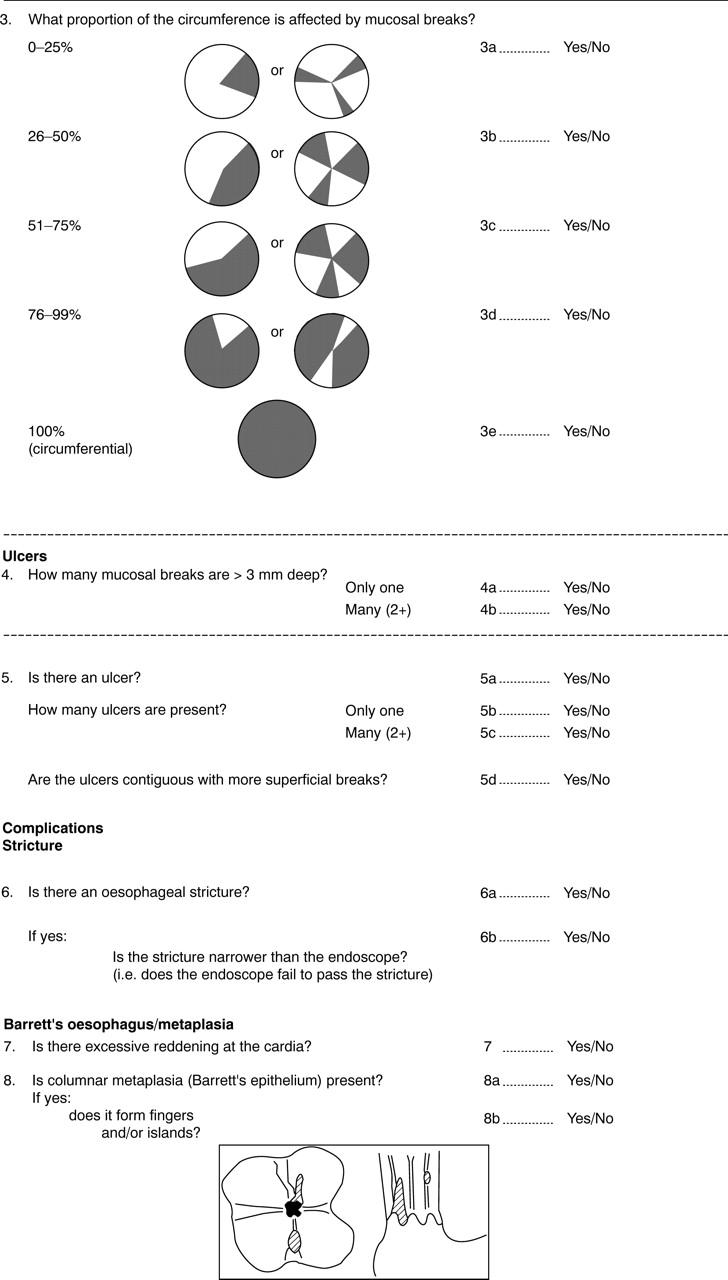
BACKGROUND—Endoscopic oesophageal changes are diagnostically helpful and identify patients exposed to the risk of disease chronicity. However, there is a serious lack of agreement about how to describe and classify the appearance of reflux oesophagitis AIMS—To examine the reliability of criteria that describe the circumferential extent of mucosal breaks and to evaluate the functional and clinical correlates of patients with reflux disease whose oesophagitis was graded according to the Los Angeles system. METHODS—Forty six endoscopists from different countries used a detailed worksheet to evaluate endoscopic video recordings from 22 patients with the full range of severity of reflux oesophagitis. In separate studies, Los Angeles system gradings were correlated with 24 hour oesophageal pH monitoring (178 patients), and with clinical trials of omeprazole treatment (277 patients). RESULTS—Evaluation of circumferential extent of oesophagitis by the criterion of whether mucosal breaks extended between the tops of mucosal folds, gave acceptable agreement (mean κ value 0.4) among observers. This approach is used in the Los Angeles system. An alternative approach of grouping the circumferential extent of mucosal breaks as occupying 0-25%, 26-50%, 51-75%, 76-99%, or 100% of the oesophageal circumference, gave unacceptably high interobserver variation (mean κ values 0-0.15) for all but the lowest category of extent (mean κ value 0.4). Severity of oesophageal acid exposure was significantly (p<0.001) related to the severity grade of oesophagitis. Preteatment oesophagitis grades A-C were related to heartburn severity (p<0.01), outcomes of omeprazole (10 mg daily) treatment (p<0.01), and the risk for symptom relapse off therapy over six months (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS—Results add further support to previous studies for the clinical utility of the Los Angeles system for endoscopic grading of oesophagitis. Keywords: oesophagitis; endoscopy; stricture; columnar lined mucosa; heartburn; omeprazole; acid reflux
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (146.1 KB).
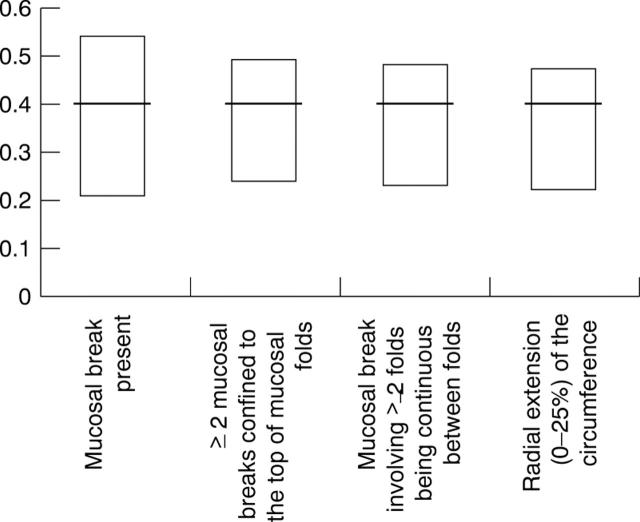
Figure 1 .
κ values for interobserver agreement on the presence and extent of mucosal breaks (median values and interquartile ranges).
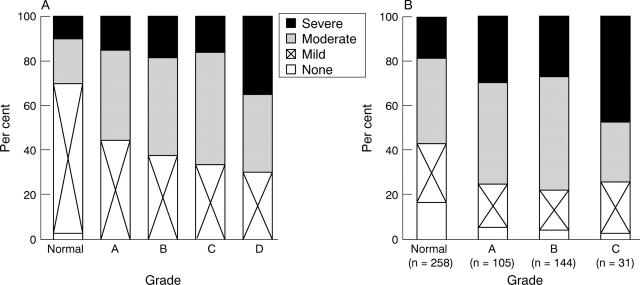
Figure 2 .
Symptom severity as related to endoscopic grading of mucosal breaks in study I (A) and study II (B). Symptoms were assessed with focus on the severity of heartburn.
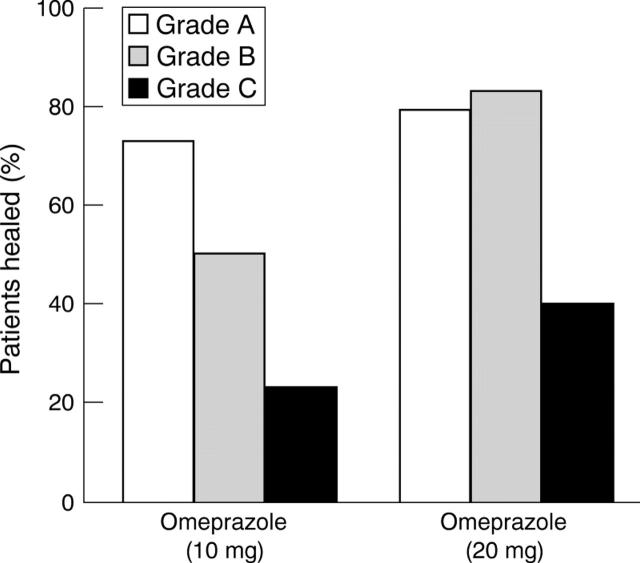
Figure 3 .
The relation between pretreatment endoscopic grading of mucosal breaks and healing of these mucosal breaks after four weeks of omeprazole 10 or 20 mg daily.
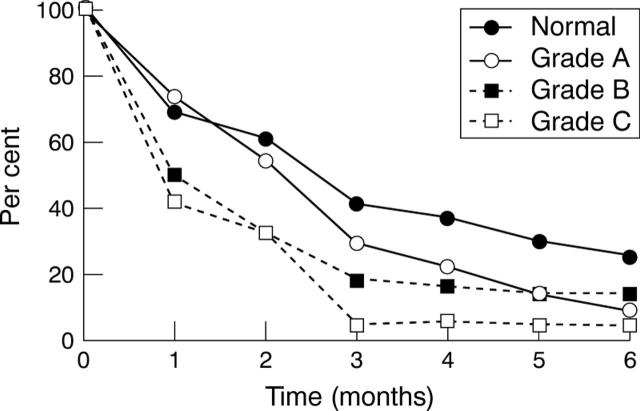
Figure 4 .
Percentage of patients in clinical remission during six months, follow up after initial treatment with omeprazole, which had healed the oesophagitis and controlled symptoms. The symptom relapse curves are given for each pretreatment endoscopic grade. Normal versus grade A, p=0.04; normal versus grade A + B + C, p=0.002; normal + grade A + B versus grade C, p=0.003.


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong D., Bennett J. R., Blum A. L., Dent J., De Dombal F. T., Galmiche J. P., Lundell L., Margulies M., Richter J. E., Spechler S. J. The endoscopic assessment of esophagitis: a progress report on observer agreement. Gastroenterology. 1996 Jul;111(1):85–92. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v111.pm8698230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D., Emde C., Inauen W., Blum A. L. Diagnostic assessment of gastroesophageal reflux disease: what is possible vs. what is practical? Hepatogastroenterology. 1992 Feb;39 (Suppl 1):3–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldi F., Ferrarini F., Longanesi A., Ragazzini M., Barbara L. Acid gastroesophageal reflux and symptom occurrence. Analysis of some factors influencing their association. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Dec;34(12):1890–1893. doi: 10.1007/BF01536707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum A. L., Adami B., Bouzo M. H., Brandstätter G., Fumagalli I., Galmiche J. P., Hebbeln H., Hentschel E., Hüttemann W., SChütz E. Effect of cisapride on relapse of esophagitis. A multinational, placebo-controlled trial in patients healed with an antisecretory drug. The Italian Eurocis Trialists. Dig Dis Sci. 1993 Mar;38(3):551–560. doi: 10.1007/BF01316514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan P., Silman A. Statistical methods for assessing observer variability in clinical measures. BMJ. 1992 Jun 6;304(6840):1491–1494. doi: 10.1136/bmj.304.6840.1491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bytzer P., Havelund T., Hansen J. M. Interobserver variation in the endoscopic diagnosis of reflux esophagitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1993 Feb;28(2):119–125. doi: 10.3109/00365529309096057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson R., Dent J., Bolling-Sternevald E., Johnsson F., Junghard O., Lauritsen K., Riley S., Lundell L. The usefulness of a structured questionnaire in the assessment of symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1998 Oct;33(10):1023–1029. doi: 10.1080/003655298750026697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson R., Dent J., Watts R., Riley S., Sheikh R., Hatlebakk J., Haug K., de Groot G., van Oudvorst A., Dalväg A. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in primary care: an international study of different treatment strategies with omeprazole. International GORD Study Group. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998 Feb;10(2):119–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J., Bremner C. G., Collen M. J., Haggitt R. C., Spechler S. J. Barrett's oesophagus. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1991 Jan-Feb;6(1):1–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1991.tb01137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J., Yeomans N. D., Mackinnon M., Reed W., Narielvala F. M., Hetzel D. J., Solcia E., Shearman D. J. Omeprazole v ranitidine for prevention of relapse in reflux oesophagitis. A controlled double blind trial of their efficacy and safety. Gut. 1994 May;35(5):590–598. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.5.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghillebert G., Demeyere A. M., Janssens J., Vantrappen G. How well can quantitative 24-hour intraesophageal pH monitoring distinguish various degrees of reflux disease? Dig Dis Sci. 1995 Jun;40(6):1317–1324. doi: 10.1007/BF02065545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatlebakk J. G., Berstad A. Endoscopic grading of reflux oesophagitis: what observations correlate with gastro-oesophageal reflux? Scand J Gastroenterol. 1997 Aug;32(8):760–765. doi: 10.3109/00365529708996531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetzel D. J., Dent J., Reed W. D., Narielvala F. M., Mackinnon M., McCarthy J. H., Mitchell B., Beveridge B. R., Laurence B. H., Gibson G. G. Healing and relapse of severe peptic esophagitis after treatment with omeprazole. Gastroenterology. 1988 Oct;95(4):903–912. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson F., Weywadt L., Solhaug J. H., Hernqvist H., Bengtsson L. One-week omeprazole treatment in the diagnosis of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1998 Jan;33(1):15–20. doi: 10.1080/00365529850166149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelz H. R., Birchler R., Bretholz A., Bron B., Capitaine Y., Delmore G., Fehr H. F., Fumagalli I., Gehrig J., Gonvers J. J. Healing and relapse of reflux esophagitis during treatment with ranitidine. Gastroenterology. 1986 Nov;91(5):1198–1205. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(86)80017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundell L. Acid suppression in the long-term treatment of peptic stricture and Barrett's oesophagus. Digestion. 1992;51 (Suppl 1):49–58. doi: 10.1159/000200916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundell L. Long-term treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease with omeprazole. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1994;201:74–78. doi: 10.3109/00365529409105368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace F., Santalucia F., Bianchi Porro G. Natural history of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease without oesophagitis. Gut. 1991 Aug;32(8):845–848. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.8.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandmark S., Carlsson R., Fausa O., Lundell L. Omeprazole or ranitidine in the treatment of reflux esophagitis. Results of a double-blind, randomized, Scandinavian multicenter study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1988 Jun;23(5):625–632. doi: 10.3109/00365528809093923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindlbeck N. E., Klauser A. G., Berghammer G., Londong W., Müller-Lissner S. A. Three year follow up of patients with gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Gut. 1992 Aug;33(8):1016–1019. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.8.1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J. Epidemiology and natural history of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Digestion. 1992;51 (Suppl 1):24–29. doi: 10.1159/000200911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tytgat G. N., Anker Hansen O. J., Carling L., de Groot G. H., Geldof H., Glise H., Efskind P., Elsborg L., Karvonen A. L., Ohlin B. Effect of cisapride on relapse of reflux oesophagitis, healed with an antisecretory drug. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1992;27(3):175–183. doi: 10.3109/00365529208999945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tytgat G. N., Nio C. Y., Schotborgh R. H. Reflux esophagitis. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1990;175:1–12. doi: 10.3109/00365529009093121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]