Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (64.1 KB).
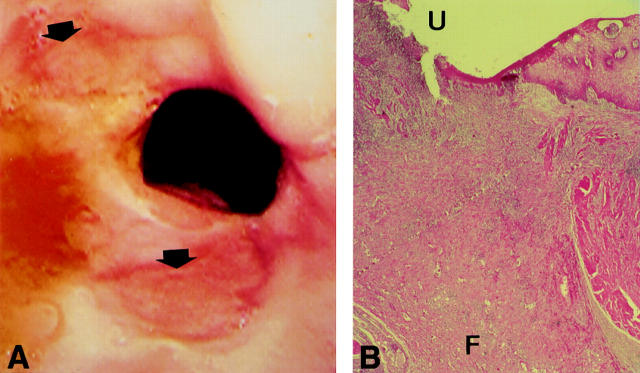
Figure 1 .
(A) Endoscopic image showing two large ulcerations of the distal oesophagus, above the oesophogastric anastomosis (arrows). (B) Microscopic view of surgical specimen (original magnification × 5; haematoxylin and eosin); the ulcer (U) extends to the adventitia with noticeable fibrosis (F).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehr P. H., McDonald G. B. Esophageal infections: risk factors, presentation, diagnosis, and treatment. Gastroenterology. 1994 Feb;106(2):509–532. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90613-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonacini M., Young T., Laine L. The causes of esophageal symptoms in human immunodeficiency virus infection. A prospective study of 110 patients. Arch Intern Med. 1991 Aug;151(8):1567–1572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly G. M., Hawkins D., Harcourt-Webster J. N., Parsons P. A., Husain O. A., Gazzard B. G. Oesophageal symptoms, their causes, treatment, and prognosis in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Gut. 1989 Aug;30(8):1033–1039. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.8.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson J. M., Greenspan J. S., Spritzler J., Ketter N., Fahey J. L., Jackson J. B., Fox L., Chernoff M., Wu A. W., MacPhail L. A. Thalidomide for the treatment of oral aphthous ulcers in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases AIDS Clinical Trials Group. N Engl J Med. 1997 May 22;336(21):1487–1493. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199705223362103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makonkawkeyoon S., Limson-Pobre R. N., Moreira A. L., Schauf V., Kaplan G. Thalidomide inhibits the replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5974–5978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naum S. M., Molloy P. J., Kania R. J., McGarr J., Van Thiel D. H. Use of thalidomide in treatment and maintenance of idiopathic esophageal ulcers in HIV+ individuals. Dig Dis Sci. 1995 May;40(5):1147–1148. doi: 10.1007/BF02064213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson D. L., Georghiou P. R., Allworth A. M., Kemp R. J. Thalidomide as treatment of refractory aphthous ulceration related to human immunodeficiency virus infection. Clin Infect Dis. 1995 Feb;20(2):250–254. doi: 10.1093/clinids/20.2.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabeneck L., Popovic M., Gartner S., McLean D. M., McLeod W. A., Read E., Wong K. K., Boyko W. J. Acute HIV infection presenting with painful swallowing and esophageal ulcers. JAMA. 1990 May 2;263(17):2318–2322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sire S., Fraisse P., Rey D., Jacquemin C., Kempf G., Partisani M., Lang J. M. Efficacité du thalidomide dans le traitement des ulcérations oesophagiennes au cours de l'infection par le virus de l'immunodéficience humaine. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1995 Jan;19(1):128–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. M., Hewan-Lowe K. Re: Etiology of human immunodeficiency virus-associated idiopathic esophageal ulcer. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994 Oct;89(10):1913–1914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. M., Schwartz D. A., Clark W. S. Esophageal ulceration in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Causes, response to therapy, and long-term outcome. Ann Intern Med. 1995 Jul 15;123(2):143–149. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-123-2-199507150-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]