Abstract
BACKGROUND—Data on meconium bile acid composition in newborn babies of patients with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) are relatively scant, and changes that occur on ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) administration have not been evaluated. AIMS—To investigate bile acid profiles in meconium of neonates from untreated and UDCA treated patients with ICP. Maternal serum bile acid composition was also analysed both at diagnosis and delivery to determine whether this influences the concentration and proportion of bile acids in the meconium. PATIENTS/METHODS—The population included eight healthy pregnant women and 16 patients with ICP, nine of which received UDCA (12.5-15.0 mg/kg body weight/day) for 15±4 days until parturition. Bile acids were assessed in the meconium by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and in maternal serum by high performance liquid chromatography. RESULTS—Total bile acid and cholic acid concentrations in the meconium were increased (p<0.01) in newborns from patients with ICP (13.5 (5.1) and 8.4 (4.1) µmol/g respectively; mean (SEM)) as compared with controls (2.0 (0.5) and 0.8 (0.3) µmol/g respectively), reflecting the total bile acid and cholic acid levels in the maternal serum (r = 0.85 and r = 0.84, p<0.01). After UDCA administration, total bile acid concentrations decreased in the mother (~3-fold, p<0.05) but not in the meconium. UDCA concentration in the meconium showed only a 2-fold increase after treatment, despite the much greater increase in the maternal serum (p<0.01). Lithocholic acid concentration in the meconium was not increased by UDCA treatment. CONCLUSIONS—UDCA administration does not influence the concentration and proportion of bile acids in the meconium, which in turn are altered by ICP. Moreover, this beneficial treatment for the mother does not increase meconium levels of potentially toxic metabolites of UDCA such as lithocholic acid. Keywords: bile acids; cholestasis; pregnancy; cholic acid; meconium; ursodeoxycholic acid therapy
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (104.1 KB).
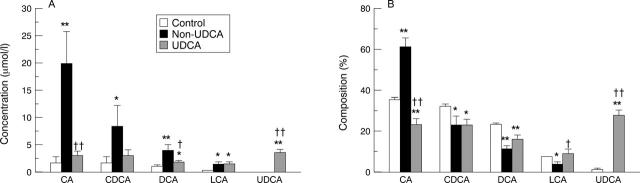
Figure 1 .
Concentration (A) and percentage composition (B) of the usual bile acids in serum of normal pregnant women (control; n = 8) and patients with cholestasis of pregnancy receiving classical palliative treatment (non-UDCA group; n = 7) or treated with ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) until labour (UDCA group; n = 9). Results are expressed as mean (SEM). **p<0.01 and *p<0.05, non-UDCA and UDCA v control;††p<0.01 and †p<0.05, non-UDCA v UDCA. CA, cholic acid; CDCA, chenodeoxycholic acid; DCA, deoxycholic acid; LCA, lithocholic acid.
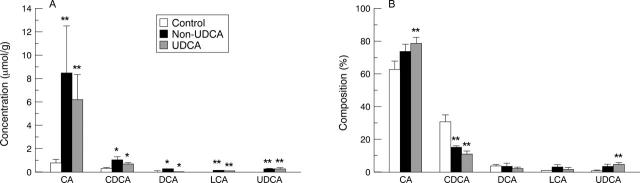
Figure 2 .
Concentration (A) and percentage composition (B) of the usual bile acids in meconium samples of newborns from normal pregnancies (control; n = 8) and from pregnancies complicated by intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy receiving classical palliative treatment (non-UDCA group; n = 7) or treated with ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) until labour (UDCA group; n = 9). Results are expressed as mean (SEM). **p<0.01 and *p<0.05, non-UDCA and UDCA v control. CA, cholic acid; CDCA, chenodeoxycholic acid; DCA, deoxycholic acid; LCA, lithocholic acid.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almé B., Bremmelgaard A., Sjövall J., Thomassen P. Analysis of metabolic profiles of bile acids in urine using a lipophilic anion exchanger and computerized gas-liquid chromatorgaphy-mass spectrometry. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):339–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alsulyman O. M., Ouzounian J. G., Ames-Castro M., Goodwin T. M. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: perinatal outcome associated with expectant management. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1996 Oct;175(4 Pt 1):957–960. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(96)80031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back P., Walter K. Developmental pattern of bile acid metabolism as revealed by bile acid analysis of meconium. Gastroenterology. 1980 Apr;78(4):671–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beke R., De Weerdt G. A., Parijs J., Huybrechts W., Barbier F. Separation of conjugated and unconjugated bile acids by thin-layer chromatography. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Jul 1;70(1):197–199. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brites D., Rodrigues C. M., Cardoso M. da C., Graça L. M. Unusual case of severe cholestasis of pregnancy with early onset, improved by ursodeoxycholic acid administration. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1998 Feb;76(2):165–168. doi: 10.1016/s0301-2115(97)00185-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brites D., Rodrigues C. M. Elevated levels of bile acids in colostrum of patients with cholestasis of pregnancy are decreased following ursodeoxycholic acid therapy [see comemnts]. J Hepatol. 1998 Nov;29(5):743–751. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(98)80255-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brites D., Rodrigues C. M., Oliveira N., Cardoso M., Graça L. M. Correction of maternal serum bile acid profile during ursodeoxycholic acid therapy in cholestasis of pregnancy. J Hepatol. 1998 Jan;28(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(98)80207-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo C., Zuliani G., Ronchi M., Breidenstein J., Setchell K. D. Biliary bile acid composition of the human fetus in early gestation. Pediatr Res. 1987 Feb;21(2):197–200. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198702000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. H., da Silva R. C., Jones S. R., Weaver J. B., Elias E. Fetal mortality associated with cholestasis of pregnancy and the potential benefit of therapy with ursodeoxycholic acid. Gut. 1995 Oct;37(4):580–584. doi: 10.1136/gut.37.4.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann D., Fenech C., Cuer J. F. Evaluation of a sample-preparation procedure for bile acids in serum and bile. Clin Chem. 1983 Sep;29(9):1694–1694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisk N. M., Storey G. N. Fetal outcome in obstetric cholestasis. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1988 Nov;95(11):1137–1143. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1988.tb06791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floreani A., Paternoster D., Grella V., Sacco S., Gangemi M., Chiaramonte M. Ursodeoxycholic acid in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1994 Jan;101(1):64–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1994.tb13012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkinen J., Mäentausta O., Tuimala R., Ylöstalo P., Jänne O. Amniotic fluid bile acids in normal and pathologic pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Jul;56(1):60–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano Y., Miyazaki H., Higashidate S., Nakayama F. Analysis of 3-sulfated and nonsulfated bile acids by one-step solvolysis and high performance liquid chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1987 Dec;28(12):1524–1529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Kimura A., Aoki K., Tohma M., Kato H. Developmental pattern of 3-oxo-delta 4 bile acids in neonatal bile acid metabolism. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1997 Jul;77(1):F52–F56. doi: 10.1136/fn.77.1.f52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jönsson G., Midtvedt A. C., Norman A., Midtvedt T. Intestinal microbial bile acid transformation in healthy infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1995 May;20(4):394–402. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199505000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Yamakawa R., Ushijima K., Fujisawa T., Kuriya N., Kato H., Inokuchi T., Mahara R., Kurosawa T., Tohma M. Fetal bile acid metabolism during infancy: analysis of 1 beta-hydroxylated bile acids in urine, meconium and feces. Hepatology. 1994 Oct;20(4 Pt 1):819–824. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840200408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa T., Mahara R., Nittono H., Tohma M. Synthesis of 6-hydroxylated bile acids and identification of 3 alpha,6 alpha,7 alpha,12 alpha-tetrahydroxy-5 beta-cholan-24-oic acid in human meconium and neonatal urine. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1989 Feb;37(2):557–559. doi: 10.1248/cpb.37.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laatikainen T. J. Fetal bile acid levels in pregnancies complicated by maternal intrahepatic cholestasis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1975 Aug 1;122(7):852–856. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(75)90727-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laatikainen T. J., Lehtonen P. J., Hesso A. E. Fetal sulfated and nonsulfated bile acids in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Aug;92(2):185–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé D., Gerhardt M. F., Myara A., Vercambre C., Trivin F. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of tauro- and glyco-conjugated bile acids in human serum. J Chromatogr. 1989 May 30;490(2):275–284. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)82785-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R., St Pyrek J., Little J. M., Adcock E. W. Nature of bile acids in the fetus and newborn infant. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1983;2 (Suppl 1):S197–S206. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198300201-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashige F., Imai K., Osuga T. A simple and sensitive assay of total serum bile acids. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Jul 1;70(1):79–86. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzella G., Rizzo N., Salzetta A., Iampieri R., Bovicelli L., Roda E. Management of intrahepatic cholestasis in pregnancy. Lancet. 1991 Dec 21;338(8782-8783):1594–1595. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92415-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng L. J., Reyes H., Axelson M., Palma J., Hernandez I., Ribalta J., Sjövall J. Progesterone metabolites and bile acids in serum of patients with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: effect of ursodeoxycholic acid therapy. Hepatology. 1997 Dec;26(6):1573–1579. doi: 10.1002/hep.510260627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng L. J., Reyes H., Palma J., Hernandez I., Ribalta J., Sjövall J. Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid on conjugated bile acids and progesterone metabolites in serum and urine of patients with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. J Hepatol. 1997 Dec;27(6):1029–1040. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(97)80147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai T., Mahara R., Kurosawa T., Kimura A., Tohma M. Determination of fetal bile acids in biological fluids from neonates by gas chromatography-negative ion chemical ionization mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 1997 Mar 28;691(1):13–22. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(96)00384-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair P. P., Garcia C. A modified gas-liquid chromatographic procedure for the rapid determination of bile acids in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1969 Apr 11;29(1):164–166. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palma J., Reyes H., Ribalta J., Hernández I., Sandoval L., Almuna R., Liepins J., Lira F., Sedano M., Silva O. Ursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of cholestasis of pregnancy: a randomized, double-blind study controlled with placebo. J Hepatol. 1997 Dec;27(6):1022–1028. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(97)80146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palma J., Reyes H., Ribalta J., Iglesias J., Gonzalez M. C., Hernandez I., Alvarez C., Molina C., Danitz A. M. Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid in patients with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Hepatology. 1992 Jun;15(6):1043–1047. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes H., Gonzalez M. C., Ribalta J., Aburto H., Matus C., Schramm G., Katz R., Medina E. Prevalence of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy in Chile. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Apr;88(4):487–493. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-4-487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes H., Radrigan M. E., Gonzalez M. C., Latorre R., Ribalta J., Segovia N., Alvarez C., Andresen M., Figueroa D., Lorca B. Steatorrhea in patients with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Gastroenterology. 1987 Sep;93(3):584–590. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90922-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes H. The enigma of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: lessons from Chile. Hepatology. 1982 Jan-Feb;2(1):87–96. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano M. A., Brites D., Larena M. G., Monte M. J., Bravo M. P., Oliveira N., Marin J. J. Beneficial effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on alterations induced by cholestasis of pregnancy in bile acid transport across the human placenta. J Hepatol. 1998 May;28(5):829–839. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(98)80234-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Dumaswala R., Colombo C., Ronchi M. Hepatic bile acid metabolism during early development revealed from the analysis of human fetal gallbladder bile. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16637–16644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Lawson A. M., Tanida N., Sjövall J. General methods for the analysis of metabolic profiles of bile acids and related compounds in feces. J Lipid Res. 1983 Aug;24(8):1085–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell R. B., Hardy K. J., Smallwood R. A., Hoffman N. E. Fetal bile salt metabolism: placental transfer of dihydroxy bile salts in sheep. Am J Physiol. 1982 Aug;243(2):G172–G175. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1982.243.2.G172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D., Frohlich J., Wittmann B. A., Willms M. A prospective study of 18 patients with cholestasis of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982 Mar 15;142(6 Pt 1):621–625. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)32430-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]