Abstract
BACKGROUND—Barrett's oesophagus, columnar metaplasia of the epithelium, is a premalignant condition with a 50-100-fold increased risk of cancer. The condition is caused by chronic gastro-oesophageal reflux. Regression of metaplasia may decrease the cancer risk. AIMS—To determine whether elimination of acid gastro-oesophageal reflux induces a regression of metaplastic epithelium. METHODS—Sixty eight patients with acid reflux and proven Barrett's oesophagus were included in a prospective, randomised, double blind study with parallel groups, and were treated with profound acid secretion suppression with omeprazole 40 mg twice daily, or with mild acid secretion suppression with ranitidine 150 mg twice daily, for 24 months. Endoscopy was performed at 0, 3, 9, 15, and 24 months with measurement of length and surface area of Barrett's oesophagus; pH-metry was performed at 0 and 3 months. Per protocol analysis was performed on 26 patients treated with omeprazole, and 27 patients treated with ranitidine. RESULTS—Omeprazole reduced reflux to 0.1%, ranitidine to 9.4% per 24 hours. Symptoms were ameliorated in both groups. There was a small, but statistically significant regression of Barrett's oesophagus in the omeprazole group, both in length and in area. No change was observed in the ranitidine group. The difference between the regression in the omeprazole and ranitidine group was statistically significant for the area of Barrett's oesophagus (p=0.02), and showed a trend in the same direction for the length of Barrett's oesophagus (p=0.06). CONCLUSIONS—Profound suppression of acid secretion, leading to elimination of acid reflux, induces partial regression of Barrett's oesophagus. Keywords: acid reflux; Barrett's oesophagus; omeprazole; regression
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (116.3 KB).
Figure 1 .
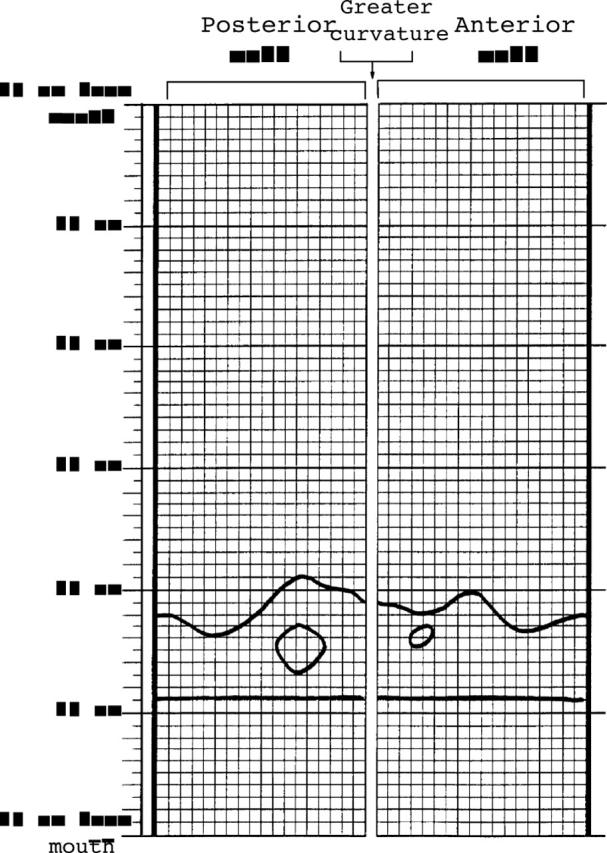
Example of a drawing, sketched on graph paper, with the squamocolumnar junction, two squamous islands within Barrett's epithelium, and the oesophagogastric junction.
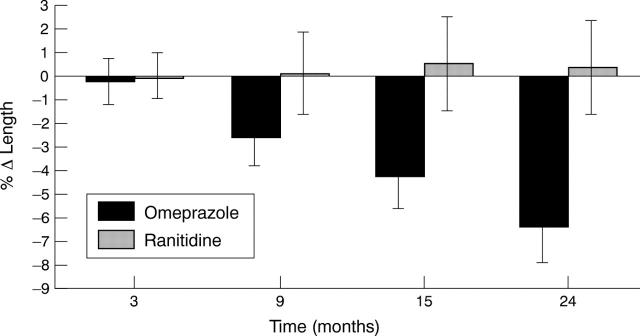
Figure 2 .
Relative changes in length of Barrett's oesophagus in the omeprazole and ranitidine treated patients (mean values (SEM)) at 3, 9, 15 and 24 months, compared with baseline.
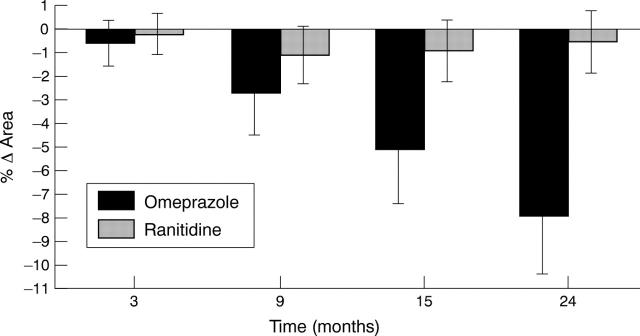
Figure 3 .
Relative changes in surface area of Barrett's oesophagus in the omeprazole and ranitidine treated patients (mean values (SEM)) at 3, 9, 15, and 24 months, compared with baseline.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barham C. P., Jones R. L., Biddlestone L. R., Hardwick R. H., Shepherd N. A., Barr H. Photothermal laser ablation of Barrett's oesophagus: endoscopic and histological evidence of squamous re-epithelialisation. Gut. 1997 Sep;41(3):281–284. doi: 10.1136/gut.41.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr H., Shepherd N. A., Dix A., Roberts D. J., Tan W. C., Krasner N. Eradication of high-grade dysplasia in columnar-lined (Barrett's) oesophagus by photodynamic therapy with endogenously generated protoporphyrin IX. Lancet. 1996 Aug 31;348(9027):584–585. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)03054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenson M. M., Johnson T. D., Markowitz N. R., Buchi K. N., Samowitz W. S. Restoration of squamous mucosa after ablation of Barrett's esophageal epithelium. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jun;104(6):1686–1691. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90646-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow W. H., Finkle W. D., McLaughlin J. K., Frankl H., Ziel H. K., Fraumeni J. F., Jr The relation of gastroesophageal reflux disease and its treatment to adenocarcinomas of the esophagus and gastric cardia. JAMA. 1995 Aug 9;274(6):474–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deviere J., Buset M., Dumonceau J. M., Rickaert F., Cremer M. Regression of Barrett's epithelium with omeprazole. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 1;320(22):1497–1498. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906013202218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gore S., Healey C. J., Sutton R., Eyre-Brook I. A., Gear M. W., Shepherd N. A., Wilkinson S. P. Regression of columnar lined (Barrett's) oesophagus with continuous omeprazole therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1993 Dec;7(6):623–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1993.tb00143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iftikhar S. Y., James P. D., Steele R. J., Hardcastle J. D., Atkinson M. Length of Barrett's oesophagus: an important factor in the development of dysplasia and adenocarcinoma. Gut. 1992 Sep;33(9):1155–1158. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.9.1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. A., Winters C., Spurling T. J., Chobanian S. J., Cattau E. L., Jr Esophageal acid sensitivity in Barrett's esophagus. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1987 Feb;9(1):23–27. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198702000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzka D. A., Castell D. O. Successful elimination of reflux symptoms does not insure adequate control of acid reflux in patients with Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994 Jul;89(7):989–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim R., Baggott B. B., Rose S., Shar A. O., Mallory D. L., Lasky S. S., Kressloff M., Faccenda L. Y., Reynolds J. C. Quantitative endoscopy: precise computerized measurement of metaplastic epithelial surface area in Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 1995 Feb;108(2):360–366. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malesci A., Savarino V., Zentilin P., Belicchi M., Mela G. S., Lapertosa G., Bocchia P., Ronchi G., Franceschi M. Partial regression of Barrett's esophagus by long-term therapy with high-dose omeprazole. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996 Dec;44(6):700–705. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(96)70055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menke-Pluymers M. B., Hop W. C., Dees J., van Blankenstein M., Tilanus H. W. Risk factors for the development of an adenocarcinoma in columnar-lined (Barrett) esophagus. The Rotterdam Esophageal Tumor Study Group. Cancer. 1993 Aug 15;72(4):1155–1158. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930815)72:4<1155::aid-cncr2820720404>3.0.co;2-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann C. S., Iqbal T. H., Cooper B. T. Long term continuous omeprazole treatment of patients with Barrett's oesophagus. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1995 Aug;9(4):451–454. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1995.tb00405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr W. C., Lackey C., Robinson M. G., Johnson L. F., Welsh J. D. Esophageal acid clearance during sleep in patients with Barrett's esophagus. Dig Dis Sci. 1988 Jun;33(6):654–659. doi: 10.1007/BF01540426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottenjann R., Heidt H. Regression der Zylinderepithel-Metaplasie bei Barrett-Osophagus. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1990 Jun 8;115(23):916–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overholt B. F., Panjehpour M. Photodynamic therapy for Barrett's esophagus: clinical update. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996 Sep;91(9):1719–1723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paull A., Trier J. S., Dalton M. D., Camp R. C., Loeb P., Goyal R. K. The histologic spectrum of Barrett's esophagus. N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 26;295(9):476–480. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608262950904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritenbaugh C., Sampliner R., Aickin M., Garewal H., Meyskens F. Risk factors for Barrett's oesophagus: a life history approach to behavioural assessment in the distant past. Eur J Cancer Prev. 1995 Dec;4(6):459–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampliner R. E. Effect of up to 3 years of high-dose lansoprazole on Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994 Oct;89(10):1844–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma P., Morales T. G., Bhattacharyya A., Garewal H. S., Sampliner R. E. Squamous islands in Barrett's esophagus: what lies underneath? Am J Gastroenterol. 1998 Mar;93(3):332–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma P., Sampliner R. E., Camargo E. Normalization of esophageal pH with high-dose proton pump inhibitor therapy does not result in regression of Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997 Apr;92(4):582–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J., Robbins A. H., Rubins H. B., Vincent M. E., Heeren T., Doos W. G., Colton T., Schimmel E. M. Adenocarcinoma and Barrett's esophagus. An overrated risk? Gastroenterology. 1984 Oct;87(4):927–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]