Abstract
BACKGROUND—Intestinal tuberculosis and Crohn's disease are chronic granulomatous disorders that are difficult to differentiate histologically. AIMS—To characterise distinctive diagnostic features of tuberculosis and Crohn's disease in mucosal biopsy specimens obtained at colonoscopy. METHODS—Selected histological parameters were evaluated retrospectively in a total of 61 biopsy sites from 20 patients with tuberculosis and 112 biopsy sites from 20 patients with Crohn's disease. The patients were chosen on the basis of clinical history, colonoscopic findings, diagnostic histology, and response to treatment. RESULTS—The histological parameters characteristic of tuberculosis were multiple (mean number of granulomas per section: 5.35), large (mean widest diameter: 193 µm), confluent granulomas often with caseating necrosis. Other features were ulcers lined by conglomerate epithelioid histiocytes and disproportionate submucosal inflammation. The features characteristic of Crohn's disease were infrequent (mean number of granulomas per section: 0.75), small (mean widest diameter: 95 µm) granulomas, microgranulomas (defined as poorly organised collections of epithelioid histiocytes), focally enhanced colitis, and a high prevalence of chronic inflammation, even in endoscopically normal appearing areas. CONCLUSIONS—The type and frequency of granulomas, presence or absence of ulcers lined by epithelioid histiocytes and microgranulomas, and the distribution of chronic inflammation have been identified as histological parameters that can be used to differentiate tuberculosis and Crohn's disease in mucosal biopsy specimens obtained at colonoscopy. Keywords: tuberculosis; Crohn's disease; mucosal biopsy; histology
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (190.2 KB).
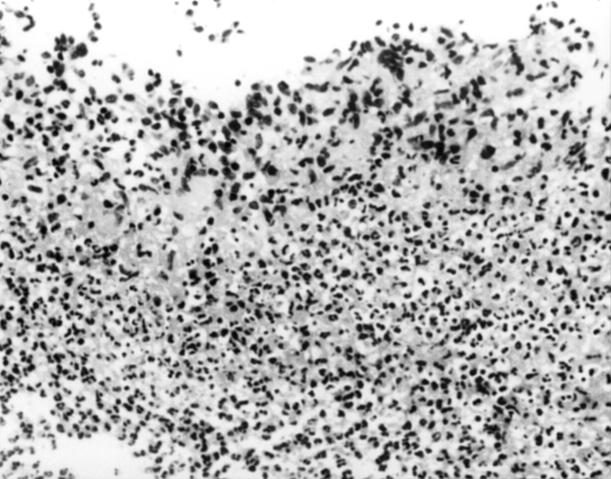
Figure 1 .
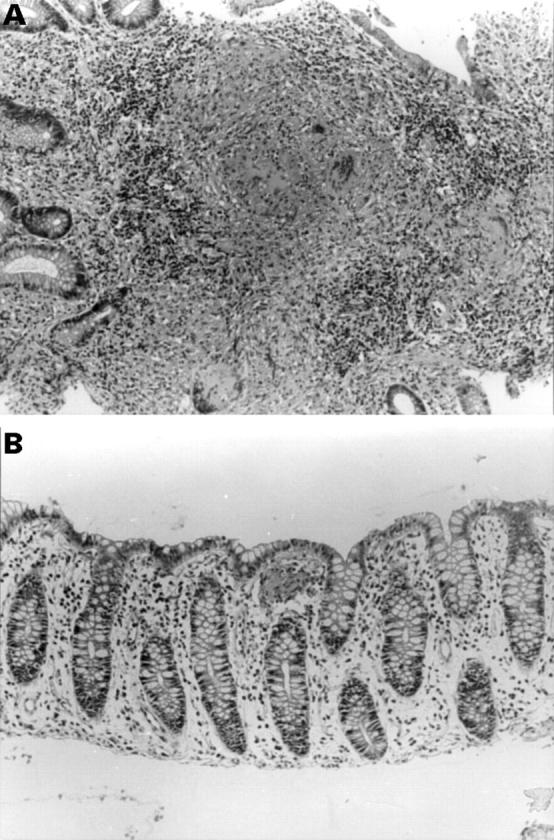
(A) Colonic mucosal biopsy of a patient with tuberculosis showing multiple, large, confluent granulomas (maximum diameter of largest granuloma: 438 µm). (B) Colonic mucosal biopsy of a patient with Crohn's disease showing a single, small, naked granuloma in the mucosa (maximum diameter: 65 µm).
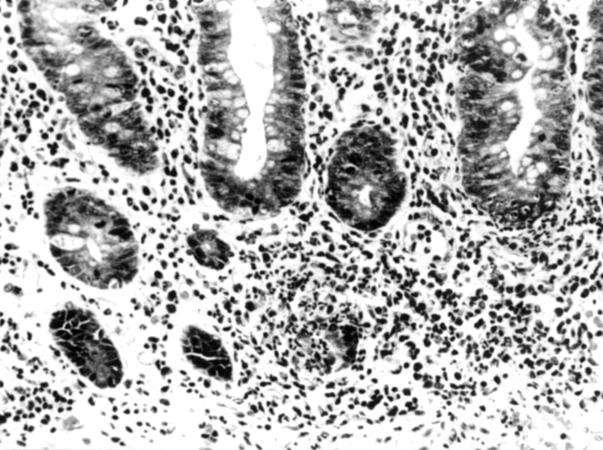
Figure 2 .
Colonic mucosa of a patient with Crohn's disease, showing an ill formed microgranuloma over a lymphoid follicle (maximum diameter: 75 µm).
Figure 3 .
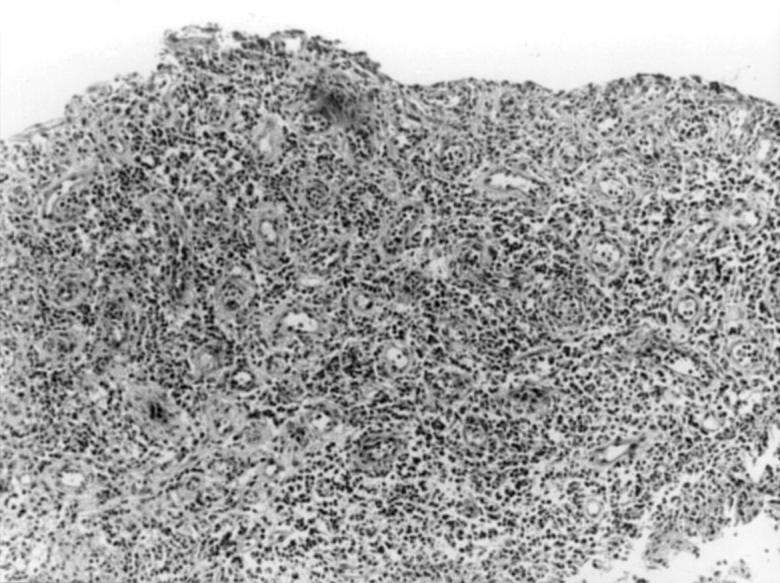

Mucosal biopsy specimen from a patient with Crohn's disease, showing inflammatory granulation tissue from a site of deep ulceration.
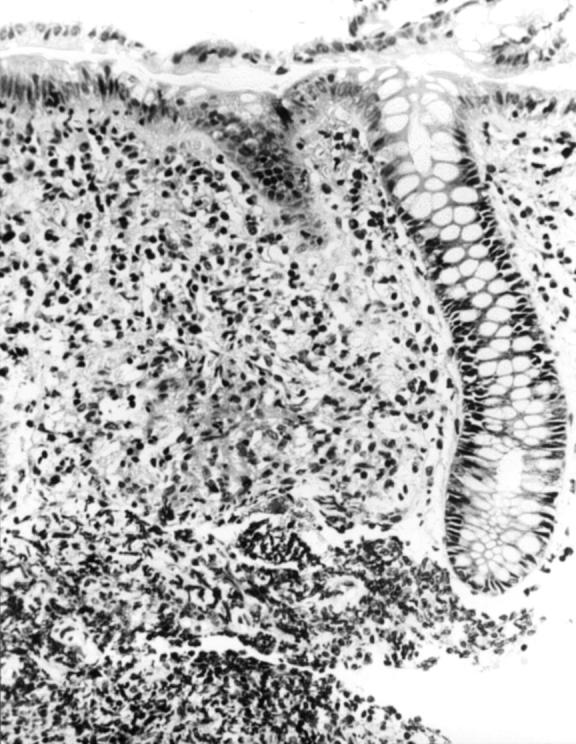
Figure 4 .
Mucosal biopsy of a patient with tuberculosis, showing a conglomerate band of epithelioid histiocytes at a site of ulceration.
Figure 5 .
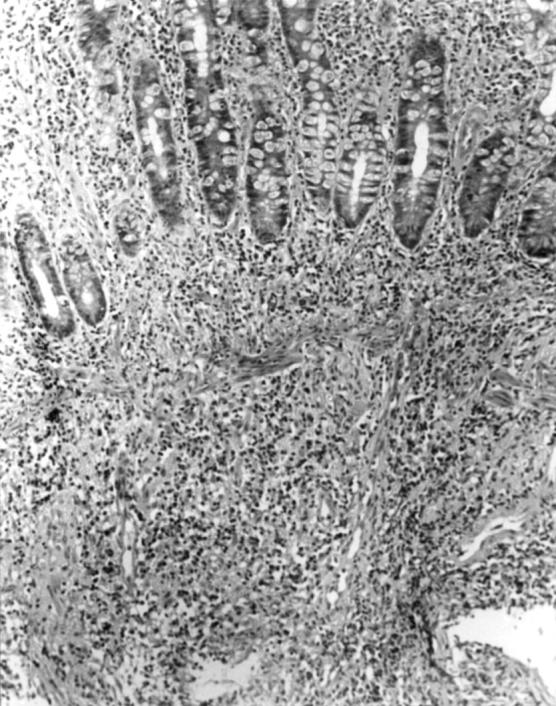
Ileal mucosal biopsy specimen from a patient with tuberculosis, showing disproportionate submucosal inflammation.
Figure 6 .
Colonic mucosal biopsy specimen of a patient with Crohn's disease, showing focal overrunning of crypts by neutrophils associated with increased chronic inflammatory cells in the adjacent lamina propria (focally enhanced colitis).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addison N. V. Abdominal tuberculosis--a disease revived. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1983 Mar;65(2):105–111. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava D. K., Tandon H. D., Chawla T. C., Shriniwas, Tandon B. N., Kapur B. M. Diagnosis of ileocecal and colonic tuberculosis by colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1985 Apr;31(2):68–70. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(85)71995-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Morson B. C. The granuloma in Crohn's disease. Gut. 1979 Apr;20(4):269–274. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.4.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook M. G., Dixon M. F. An analysis of the reliability of detection and diagnostic value of various pathological features in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1973 Apr;14(4):255–262. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.4.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer N. H., Stansfeld A. G., Dawson A. M. The value of rectal biopsy in the diagnosis of Crohn's disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1970;5(6):491–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geboes K., Ectors N., D'Haens G., Rutgeerts P. Is ileoscopy with biopsy worthwhile in patients presenting with symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease? Am J Gastroenterol. 1998 Feb;93(2):201–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman H. Interpretation of large intestinal mucosal biopsy specimens. Hum Pathol. 1994 Nov;25(11):1150–1159. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOON J. R., DOCKERTY M. B., PEMBERTON J. de J. Ileocecal tuberculosis including a comparison of this disease with nonspecific regional enterocolitis and noncaseous tuberculated enterocolitis. Int Abstr Surg. 1950 Nov;91(5):417–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL J. S., KNAPTON P. J. ILEO-CAECAL TUBERCULOSIS. Gut. 1964 Dec;5:524–529. doi: 10.1136/gut.5.6.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE F. D., ROY A. D. ILEO-CAECAL GRANULOMATA. Gut. 1964 Dec;5:517–523. doi: 10.1136/gut.5.6.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOCKHART-MUMMERY H. E., MORSON B. C. CROHN'S DISEASE OF THE LARGE INTESTINE. Gut. 1964 Dec;5:493–509. doi: 10.1136/gut.5.6.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Berre N., Heresbach D., Kerbaol M., Caulet S., Bretagne J. F., Chaperon J., Gosselin M., Ramée M. P. Histological discrimination of idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease from other types of colitis. J Clin Pathol. 1995 Aug;48(8):749–753. doi: 10.1136/jcp.48.8.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malatjalian D. A. Pathology of inflammatory bowel disease in colorectal mucosal biopsies. Dig Dis Sci. 1987 Dec;32(12 Suppl):5S–15S. doi: 10.1007/BF01312459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhuber G., Püspök A., Oesterreicher C., Novacek G., Zauner C., Burghuber M., Vogelsang H., Pötzi R., Stolte M., Wrba F. Focally enhanced gastritis: a frequent type of gastritis in patients with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1997 Mar;112(3):698–706. doi: 10.1053/gast.1997.v112.pm9041230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer K. R., Patil D. H., Basran G. S., Riordan J. F., Silk D. B. Abdominal tuberculosis in urban Britain--a common disease. Gut. 1985 Dec;26(12):1296–1305. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.12.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotterdam H., Korelitz B. I., Sommers S. C. Microgranulomas in grossly normal rectal mucosa in Crohn's disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977 Jun;67(6):550–554. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/67.6.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz-Moormann P., Schäg M. Histology of the lower intestinal tract in Crohn's disease of children and adolescents. Multicentric Paediatric Crohn's Disease Study. Pathol Res Pract. 1990 Aug;186(4):479–484. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(11)80467-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah S., Thomas V., Mathan M., Chacko A., Chandy G., Ramakrishna B. S., Rolston D. D. Colonoscopic study of 50 patients with colonic tuberculosis. Gut. 1992 Mar;33(3):347–351. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.3.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd N. A. Pathological mimics of chronic inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Sep;44(9):726–733. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.9.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Riddell R. H. The pathological diagnosis and differential diagnosis of Crohn's disease. Hepatogastroenterology. 1990 Feb;37(1):18–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandon H. D., Prakash A. Pathology of intestinal tuberculosis and its distinction from Crohn's disease. Gut. 1972 Apr;13(4):260–269. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.4.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS W. J. HISTOLOGY OF CROHN'S SYNDROME. Gut. 1964 Dec;5:510–516. doi: 10.1136/gut.5.6.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]