Abstract
BACKGROUND—The phenotypic spectrum of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) varies from the classic appearance of hundreds of adenomatous colonic polyps in the young adult and early onset colorectal cancer, to the occurrence of sparse adenomas in the older adult, "attenuated" FAP, due to mutations at the 5' or 3' ends of the APC gene. AIMS—To investigate marked intrafamilial phenotypic variation occurring in a family with an APC gene mutation in exon 9. PATIENTS—An extended kindred of 22 people of whom 16 had colorectal neoplasia and/or were APC mutation carriers. RESULTS—Phenotypic manifestation varied from classic FAP to a complete lack of clinical or endoscopic, or bioptic disease in five people in three different generations. This occurred in four of them over two generations, in spite of having a confirmed 11 bp insertion causing a frame shift and stop codon (363) in exon 9 of the APC gene. CONCLUSIONS—At present, it is assumed that in this family there is alternative splicing of the APC gene, and/or unidentified modifying genetic factors. The family illustrates the importance of genetic testing in evaluating carrier status and not just clinical examination. This clinical observation also high- lights the dilemma in recognising the possible contribution of low penetrance germline APC mutations to what has been considered "sporadic" colorectal neoplasia. Keywords: APC gene; familial adenomatous polyposis; phenotype variation; modifying genes; alternative splicing
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (93.5 KB).
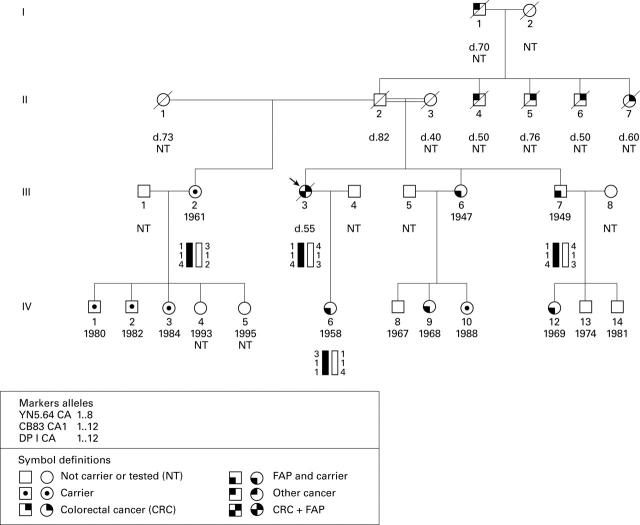
Figure 1 .
Family K pedigree. Note the common alleles of III.2, III.3, III.7, and IV.6 assumed to be from their common II.2 origin (black bar). The second allele of III.2 is dissimilar to those of III.3 and III.7 and is therefore assumed to be from their different mothers (blank bar). NT, not tested for APC mutation; d, died (age in years); arrow, propositus.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bisgaard M. L., Fenger K., Bülow S., Niebuhr E., Mohr J. Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP): frequency, penetrance, and mutation rate. Hum Mutat. 1994;3(2):121–125. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380030206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradburn D. M., Gunn A., Hastings A., Shepherd N. A., Chapman P. D., Burn J. Histological detection of microadenomas in the diagnosis of familial adenomatous polyposis. Br J Surg. 1991 Nov;78(11):1394–1395. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800781141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brensinger J. D., Laken S. J., Luce M. C., Powell S. M., Vance G. H., Ahnen D. J., Petersen G. M., Hamilton S. R., Giardiello F. M. Variable phenotype of familial adenomatous polyposis in pedigrees with 3' mutation in the APC gene. Gut. 1998 Oct;43(4):548–552. doi: 10.1136/gut.43.4.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunyan D. J., Shea-Simonds J., Reck A. C., Finnis D., Eccles D. M. Genotype-phenotype correlations of new causative APC gene mutations in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. J Med Genet. 1995 Sep;32(9):728–731. doi: 10.1136/jmg.32.9.728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspari R., Friedl W., Mandl M., Möslein G., Kadmon M., Knapp M., Jacobasch K. H., Ecker K. W., Kreissler-Haag D., Timmermanns G. Familial adenomatous polyposis: mutation at codon 1309 and early onset of colon cancer. Lancet. 1994 Mar 12;343(8898):629–632. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92634-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbie Z., Spycher M., Mary J. L., Häner M., Guldenschuh I., Hürliman R., Amman R., Roth J., Müller H., Scott R. J. Correlation between the development of extracolonic manifestations in FAP patients and mutations beyond codon 1403 in the APC gene. J Med Genet. 1996 Apr;33(4):274–280. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.4.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dove W. F., Cormier R. T., Gould K. A., Halberg R. B., Merritt A. J., Newton M. A., Shoemaker A. R. The intestinal epithelium and its neoplasms: genetic, cellular and tissue interactions. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1998 Jun 29;353(1370):915–923. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1998.0256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Guy S. P., Thakker N., Armstrong J. G., Dodd C., Davies D. R., Babbs C., Clancy T., Warnes T., Sloan P. Non-penetrance and late appearance of polyps in families with familial adenomatous polyposis. Gut. 1993 Oct;34(10):1389–1393. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.10.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frayling I. M., Beck N. E., Ilyas M., Dove-Edwin I., Goodman P., Pack K., Bell J. A., Williams C. B., Hodgson S. V., Thomas H. J. The APC variants I1307K and E1317Q are associated with colorectal tumors, but not always with a family history. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Sep 1;95(18):10722–10727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.18.10722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedl W., Meuschel S., Caspari R., Lamberti C., Krieger S., Sengteller M., Propping P. Attenuated familial adenomatous polyposis due to a mutation in the 3' part of the APC gene. A clue for understanding the function of the APC protein. Hum Genet. 1996 May;97(5):579–584. doi: 10.1007/BF02281864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giardiello F. M., Krush A. J., Petersen G. M., Booker S. V., Kerr M., Tong L. L., Hamilton S. R. Phenotypic variability of familial adenomatous polyposis in 11 unrelated families with identical APC gene mutation. Gastroenterology. 1994 Jun;106(6):1542–1547. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90408-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. R., Guillem J. G. The genetics of colorectal cancer. Surg Clin North Am. 1997 Feb;77(1):175–195. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(05)70538-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota O., Kino I. Depressed adenomas of the colon in familial adenomatous polyposis. Histology, immunohistochemical detection of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), and analysis of the background mucosa. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995 Mar;19(3):318–327. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199503000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch H. T., Lynch P. M., Follett K. L., Harris R. E. Familial polyposis coli: heterogeneous polyp expression in 2 kindreds. J Med Genet. 1979 Feb;16(1):1–7. doi: 10.1136/jmg.16.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch H. T., Smyrk T. C. Classification of familial adenomatous polyposis: a diagnostic nightmare. Am J Hum Genet. 1998 Jun;62(6):1288–1289. doi: 10.1086/301890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch H. T., Smyrk T., McGinn T., Lanspa S., Cavalieri J., Lynch J., Slominski-Castor S., Cayouette M. C., Priluck I., Luce M. C. Attenuated familial adenomatous polyposis (AFAP). A phenotypically and genotypically distinctive variant of FAP. Cancer. 1995 Dec 15;76(12):2427–2433. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19951215)76:12<2427::aid-cncr2820761205>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase H., Miyoshi Y., Horii A., Aoki T., Ogawa M., Utsunomiya J., Baba S., Sasazuki T., Nakamura Y. Correlation between the location of germ-line mutations in the APC gene and the number of colorectal polyps in familial adenomatous polyposis patients. Cancer Res. 1992 Jul 15;52(14):4055–4057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbold K. M., Warfield A. T., MacDonald F. Undifferentiated columnar cells in colorectal adenomas and familial adenomatous polyposis. J Pathol. 1989 Jun;158(2):93–96. doi: 10.1002/path.1711580203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul P., Letteboer T., Gelbert L., Groden J., White R., Coppes M. J. Identical APC exon 15 mutations result in a variable phenotype in familial adenomatous polyposis. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2(7):925–931. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.7.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praml C., Amler L. C., Dihlmann S., Finke L. H., Schlag P., Schwab M. Secretory type II phospholipase A2 (PLA2G2A) expression status in colorectal carcinoma derived cell lines and in normal colonic mucosa. Oncogene. 1998 Oct 15;17(15):2009–2012. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presciuttini S., Varesco L., Sala P., Gismondi V., Rossetti C., Bafico A., Ferrara G. B., Bertario L. Age of onset in familial adenomatous polyposis: heterogeneity within families and among APC mutations. Ann Hum Genet. 1994 Oct;58(Pt 4):331–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1994.tb00730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen P., Shomrat R., Strul H., Naiman T., Karminsky N., Legum C., Orr-Urtreger A. Prevalence of the I1307K APC gene variant in Israeli Jews of differing ethnic origin and risk for colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 1999 Jan;116(1):54–57. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(99)70228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro I. M., Groden J. Alternative splicing of the APC gene and its association with terminal differentiation. Cancer Res. 1997 Feb 1;57(3):488–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. J., van der Luijt R., Spycher M., Mary J. L., Müller A., Hoppeler T., Haner M., Müller H., Martinoli S., Brazzola P. L. Novel germline APC gene mutation in a large familial adenomatous polyposis kindred displaying variable phenotypes. Gut. 1995 May;36(5):731–736. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.5.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker A. R., Gould K. A., Luongo C., Moser A. R., Dove W. F. Studies of neoplasia in the Min mouse. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997 Apr 18;1332(2):F25–F48. doi: 10.1016/s0304-419x(96)00041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soravia C., Berk T., Madlensky L., Mitri A., Cheng H., Gallinger S., Cohen Z., Bapat B. Genotype-phenotype correlations in attenuated adenomatous polyposis coli. Am J Hum Genet. 1998 Jun;62(6):1290–1301. doi: 10.1086/301883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirio L. N., Dixon D. A., Robertson J., Robertson M., Barrows J., Traer E., Burt R. W., Leppert M. F., White R., Prescott S. M. The inducible prostaglandin biosynthetic enzyme, cyclooxygenase 2, is not mutated in patients with attenuated adenomatous polyposis coli. Cancer Res. 1998 Nov 1;58(21):4909–4912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirio L., Olschwang S., Groden J., Robertson M., Samowitz W., Joslyn G., Gelbert L., Thliveris A., Carlson M., Otterud B. Alleles of the APC gene: an attenuated form of familial polyposis. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):951–957. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90538-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson I. P., Beck N. E., Neale K., Bodmer W. F. Variants at the secretory phospholipase A2 (PLA2G2A) locus: analysis of associations with familial adenomatous polyposis and sporadic colorectal tumours. Ann Hum Genet. 1996 Sep;60(Pt 5):369–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1996.tb00434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walon C., Kartheuser A., Michils G., Smaers M., Lannoy N., Ngounou P., Mertens G., Verellen-Dumoulin C. Novel germline mutations in the APC gene and their phenotypic spectrum in familial adenomatous polyposis kindreds. Hum Genet. 1997 Oct;100(5-6):601–605. doi: 10.1007/s004390050560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S., Bubb V. J., Wyllie A. H. Germline APC mutation (Gln1317) in a cancer-prone family that does not result in familial adenomatous polyposis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1996 Feb;15(2):122–128. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2264(199602)15:2<122::AID-GCC7>3.0.CO;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J., Simms L. A., Tarish J., Buttenshaw R., Knight N., Anderson G. J., Bell A., Leggett B. A family with attenuated familial adenomatous polyposis due to a mutation in the alternatively spliced region of APC exon 9. Hum Mutat. 1998;11(6):450–455. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1998)11:6<450::AID-HUMU5>3.0.CO;2-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Luijt R. B., Vasen H. F., Tops C. M., Breukel C., Fodde R., Meera Khan P. APC mutation in the alternatively spliced region of exon 9 associated with late onset familial adenomatous polyposis. Hum Genet. 1995 Dec;96(6):705–710. doi: 10.1007/BF00210303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]