Abstract
BACKGROUND—Biopsy specimens obtained from the gastro-oesophageal junction can reveal intestinal metaplasia in patients presenting for routine upper endoscopy. The site of biopsy may play a critical role in determining the dysplasia risk of a patient. AIMS—To evaluate prospectively the dysplasia risk in patients with intestinal metaplasia of the distal oesophagus or within the gastric cardia. METHODS—Patients with short segment Barrett's oesophagus (SSBO) and cardia intestinal metaplasia (CIM) were followed prospectively. RESULTS—177 patients with SSBO were identified (mean age 62 years, range 38-82; 91% whites). Twenty prevalence cases of dysplasia in SSBO were detected: 17 low grade dysplasia (LGD), three high grade dysplasia (HGD). Seventy six patients with CIM were identified (mean age 67 years, range 37-81; 81% whites). A single prevalence case of LGD in CIM was detected. During follow up of 78 SSBO and 34 CIM patients, dysplasia developed in nine (seven LGD, two HGD) with SSBO and in one (LGD) with CIM. There were significant differences between the two groups with respect to age, ethnicity, dysplasia prevalence, and incidence. Time to dysplasia progression was significantly longer in CIM compared with SSBO patients. Of the five patients with SSBO and HGD, one developed adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus on follow up. No HGD or cancers have been detected over this time period in CIM patients. CONCLUSIONS—The dysplasia risk is significantly greater in SSBO than in CIM patients, indicating two potentially different clinical processes. Future studies should separate SSBO from CIM in order to enhance the understanding of the pathophysiology and malignant potential of each entity. Keywords: high grade dysplasia; low grade dysplasia; metaplasia; Barrett's oesophagus; gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (84.4 KB).
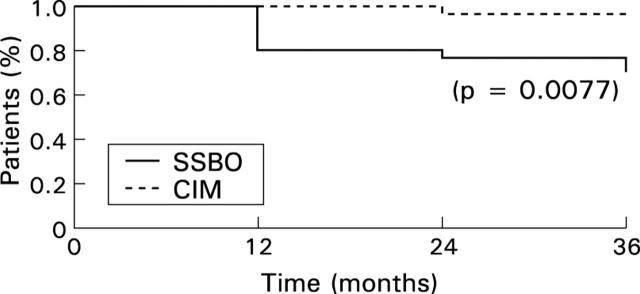
Figure 1 .
Dysplasia free interval. SSBO, short segment Barrett's oesophagus; CIM, cardia intestinal metaplasia.
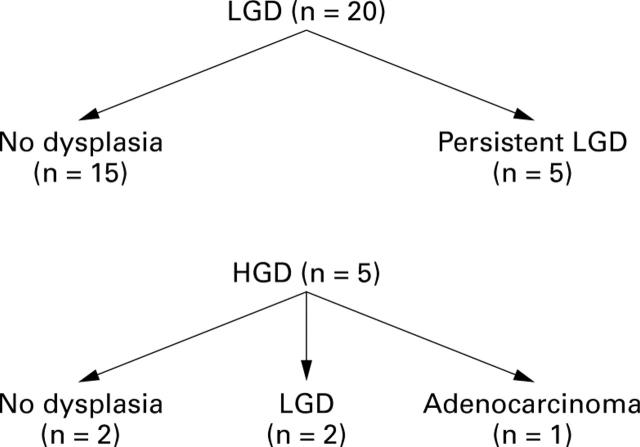
Figure 2 .
Outcome of dysplasia in patients with short segment Barrett's oesophagus. HGD, high grade dysplasia; LGD, low grade dysplasia
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blot W. J., Devesa S. S., Fraumeni J. F., Jr Continuing climb in rates of esophageal adenocarcinoma: an update. JAMA. 1993 Sep 15;270(11):1320–1320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blot W. J., Devesa S. S., Kneller R. W., Fraumeni J. F., Jr Rising incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and gastric cardia. JAMA. 1991 Mar 13;265(10):1287–1289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalasani N., Wo J. M., Hunter J. G., Waring J. P. Significance of intestinal metaplasia in different areas of esophagus including esophagogastric junction. Dig Dis Sci. 1997 Mar;42(3):603–607. doi: 10.1023/a:1018863529777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. W., Smyrk T. C., Burdiles P., Hoeft S. F., Peters J. H., Kiyabu M., Hinder R. A., Bremner C. G., DeMeester T. R. Is Barrett's metaplasia the source of adenocarcinomas of the cardia? Arch Surg. 1994 Jun;129(6):609–614. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1994.01420300051007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum J. R., Vicari J. J., Falk G. W., Rice T. W., Peek R. M., Easley K., Richter J. E. Inflammation and intestinal metaplasia of the gastric cardia: the role of gastroesophageal reflux and H. pylori infection. Gastroenterology. 1998 Apr;114(4):633–639. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackelsberger A., Günther T., Schultze V., Manes G., Dominguez-Muñoz J. E., Roessner A., Malfertheiner P. Intestinal metaplasia at the gastro-oesophageal junction: Helicobacter pylori gastritis or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease? Gut. 1998 Jul;43(1):17–21. doi: 10.1136/gut.43.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. R., Smith R. R., Cameron J. L. Prevalence and characteristics of Barrett esophagus in patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus or esophagogastric junction. Hum Pathol. 1988 Aug;19(8):942–948. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota W. K., Loughney T. M., Lazas D. J., Maydonovitch C. L., Rholl V., Wong R. K. Specialized intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia, and cancer of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction: prevalence and clinical data. Gastroenterology. 1999 Feb;116(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(99)70123-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. H., Hammond A. S., Laskin W., Jones D. M. The prevalence and clinical characteristics of short segments of specialized intestinal metaplasia in the distal esophagus on routine endoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996 Aug;91(8):1507–1511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClave S. A., Boyce H. W., Jr, Gottfried M. R. Early diagnosis of columnar-lined esophagus: a new endoscopic diagnostic criterion. Gastrointest Endosc. 1987 Dec;33(6):413–416. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(87)71676-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morales T. G., Sampliner R. E., Bhattacharyya A. Intestinal metaplasia of the gastric cardia. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997 Mar;92(3):414–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pera M., Cameron A. J., Trastek V. F., Carpenter H. A., Zinsmeister A. R. Increasing incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction. Gastroenterology. 1993 Feb;104(2):510–513. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90420-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira A. D., Suspiro A., Chaves P., Saraiva A., Glória L., de Almeida J. C., Leitão C. N., Soares J., Mira F. C. Short segments of Barrett's epithelium and intestinal metaplasia in normal appearing oesophagogastric junctions: the same or two different entities? Gut. 1998 May;42(5):659–662. doi: 10.1136/gut.42.5.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid B. J. Barrett's esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1991 Dec;20(4):817–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddell R. H., Goldman H., Ransohoff D. F., Appelman H. D., Fenoglio C. M., Haggitt R. C., Ahren C., Correa P., Hamilton S. R., Morson B. C. Dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease: standardized classification with provisional clinical applications. Hum Pathol. 1983 Nov;14(11):931–968. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(83)80175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell T. G., Sontag S. J., Chejfec G. Adenocarcinomas arising in tongues or short segments of Barrett's esophagus. Dig Dis Sci. 1992 Jan;37(1):137–143. doi: 10.1007/BF01308357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma P., Morales T. G., Bhattacharyya A., Garewal H. S., Sampliner R. E. Dysplasia in short-segment Barrett's esophagus: a prospective 3-year follow-up. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997 Nov;92(11):2012–2016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma P., Morales T. G., Sampliner R. E. Short segment Barrett's esophagus--the need for standardization of the definition and of endoscopic criteria. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998 Jul;93(7):1033–1036. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J., Goyal R. K. Barrett's esophagus. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 7;315(6):362–371. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608073150605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J., Zeroogian J. M., Antonioli D. A., Wang H. H., Goyal R. K. Prevalence of metaplasia at the gastro-oesophageal junction. Lancet. 1994 Dec 3;344(8936):1533–1536. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90349-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston A. P., Krmpotich P. T., Cherian R., Dixon A., Topalosvki M. Prospective long-term endoscopic and histological follow-up of short segment Barrett's esophagus: comparison with traditional long segment Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997 Mar;92(3):407–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston A. P., Krmpotich P., Makdisi W. F., Cherian R., Dixon A., McGregor D. H., Banerjee S. K. Short segment Barrett's esophagus: clinical and histological features, associated endoscopic findings, and association with gastric intestinal metaplasia. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996 May;91(5):981–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]