Abstract
AIMS—To assess the long term therapeutic effectiveness, safety, and tolerability of low daily doses of isosmotic PEG electrolyte solutions (PMF-100) administered for a six month period for the treatment of functional constipation, in a double blind, placebo controlled, parallel group study. METHODS—After an initial four week run in period with PMF-100 (250 ml twice daily; PEG 14.6 g twice daily), 70 patients suffering from chronic constipation (58 females, aged 42 (15) years) with normalised bowel frequency (>3 bowel movements (bm)/week) were randomly allocated to receive either PMF-100 or placebo, contained in sachets (one sachet in 250 ml of water twice daily) for 20 weeks. Patients were assessed at four week intervals, and reported frequency and modality of evacuation, laxative use, and relevant symptoms on a diary card. At weeks 1, 12, and 24, a physical examination and laboratory tests were performed. RESULTS—Complete remission of constipation was reported by a significantly (p<0.01) higher number of patients treated with PMF-100 compared with placebo at each four week visit. At the end of the study, 77% of the PMF-100 group and 20% of the placebo group were asymptomatic. Compared with placebo, patients treated with PMF-100 reported hard/pellety stools and straining at defecation less frequently, a significantly higher bowel frequency (week 12: 7.4 (3.1) v 4.3 (2.5) bm/week, 95% CI 1.64, 4.42; week 24: 7.4 (3.2) v 5.4 (2.1) bm/week, 95% CI 0.13,3.93), reduced consumption of laxative/four weeks (week 12: 0.7 (2.7) v 2.2 (3.3), 95% CI −2.29, 0.03; week 24: 0.2 (0.8) v 1.4 (2), 95% CI −2.07, −0.023), reduced mean number of sachets used (week 12: 33 (13) v 43 (12), 95% CI −17.24, 4.56; week 24: 33 (13) v 44 (12), 95% CI −19.68, −2.24), and reduced number of drop outs for therapy failure (16 v 3; p<0.005). Adverse events, physical findings, laboratory values, palatability, and overall tolerance of the solutions did not differ between groups. CONCLUSIONS—Administration of small daily doses of isosmotic PEG electrolyte balanced solutions was effective over a six month period for the treatment of functional constipation. A mean daily dose of approximately 300 ml of PEG solution (PEG 17.52 g) appeared to be safe, well tolerated, and devoid of significant side effects. Keywords: constipation; polyethylene glycol; safety; tolerability
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (143.0 KB).
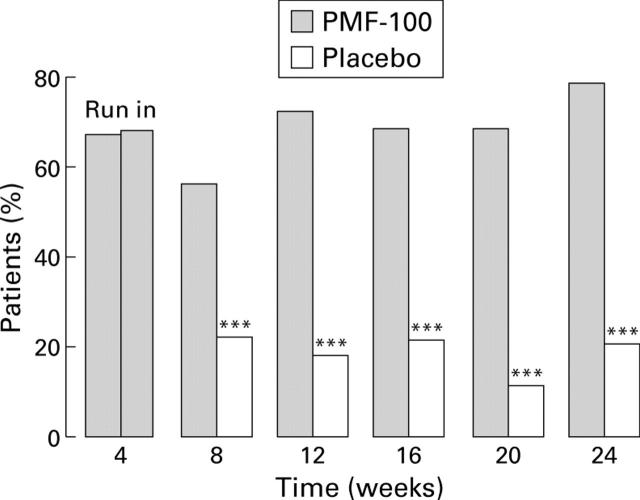
Figure 1 .
Percentage of patients with complete remission of constipation symptoms consisting of more than three bowel movements per week, no use of laxatives, no straining at defecation, feeling of complete evacuation, and no hard/pellety stools during PMF-100 and placebo treatment. The two groups did not differ at the end of the run in period; a significantly higher number of patients with complete remission of constipation was observed in the PMF-100 group at each visit throughout the study (***p<0.001).
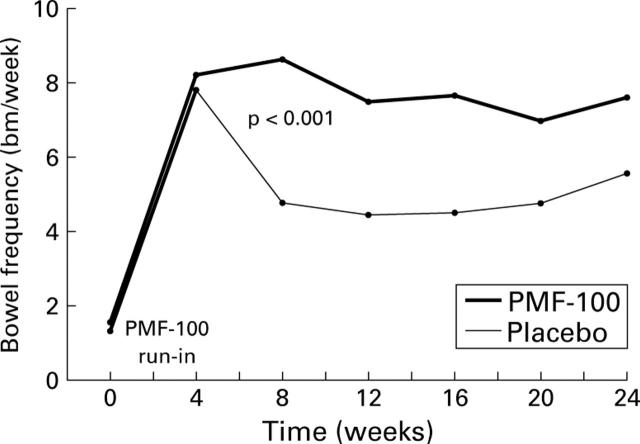
Figure 2 .
Bowel frequency during the run in and study periods with PMF-100 and placebo treatments. After the run in period, bowel frequency was significantly higher in the PMF-100 group throughout the study.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andorsky R. I., Goldner F. Colonic lavage solution (polyethylene glycol electrolyte lavage solution) as a treatment for chronic constipation: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990 Mar;85(3):261–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attar A., Lémann M., Ferguson A., Halphen M., Boutron M. C., Flourié B., Alix E., Salmeron M., Guillemot F., Chaussade S. Comparison of a low dose polyethylene glycol electrolyte solution with lactulose for treatment of chronic constipation. Gut. 1999 Feb;44(2):226–230. doi: 10.1136/gut.44.2.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badiali D., Corazziari E., Habib F. I., Tomei E., Bausano G., Magrini P., Anzini F., Torsoli A. Effect of wheat bran in treatment of chronic nonorganic constipation. A double-blind controlled trial. Dig Dis Sci. 1995 Feb;40(2):349–356. doi: 10.1007/BF02065421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldonedo Y. C., Lugo E., Uzcátegui A. A., Guelrud M., Skornicki J. Evaluación y uso del polietilen glicol en pacientes constipados. G E N. 1991 Oct-Dec;45(4):294–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corazziari E., Badiali D., Habib F. I., Reboa G., Pitto G., Mazzacca G., Sabbatini F., Galeazzi R., Cilluffo T., Vantini I. Small volume isosmotic polyethylene glycol electrolyte balanced solution (PMF-100) in treatment of chronic nonorganic constipation. Dig Dis Sci. 1996 Aug;41(8):1636–1642. doi: 10.1007/BF02087913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G. J., Crowder M., Reid B., Dickerson J. W. Bowel function measurements of individuals with different eating patterns. Gut. 1986 Feb;27(2):164–169. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.2.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gear J. S., Brodribb A. J., Ware A., Mann J. I. Fibre and bowel transit times. Br J Nutr. 1981 Jan;45(1):77–82. doi: 10.1079/bjn19810078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebo K. B., Heyman M. B. Polyethylene glycol-electrolyte solution for intestinal clearance in children with refractory encopresis. A safe and effective therapeutic program. Am J Dis Child. 1988 Mar;142(3):340–342. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1988.02150030114035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar A. J., Rode H., Buchler J., Cywes S. Whole-gut lavage in children using an iso-osmolar solution containing polyethelene glycol (Golytely). J Pediatr Surg. 1988 Sep;23(9):822–824. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(88)80231-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. G., Currie J. E., Walls A. D. Whole gut irrigation: a new treatment for constipation. Br Med J. 1978 Aug 5;2(6134):396–397. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6134.396-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolia V., Lin C. H., Elitsur Y. A prospective randomized study with mineral oil and oral lavage solution for treatment of faecal impaction in children. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1993 Oct;7(5):523–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1993.tb00128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]