Abstract
BACKGROUND/AIMS—The purpose of this study was to better define the long term prognosis of infection and disease in children with chronic hepatitis B treated with interferon (IFN) alpha. PATIENTS—A total of 107 children with chronic hepatitis B who received IFN alpha for three or six months in two clinical trials were followed for a mean period of 69 (17) months. Response to treatment was defined as loss of hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) within 12 months after stopping treatment. A control group of 59 patients was also followed for a shorter mean time (46 (19) months). RESULTS—Sixteen (15%) treated children responded during therapy and 18 (17%) during post-treatment follow up; 31 (29%) non-responders lost HBeAg during subsequent years. High pretreatment levels of transaminases and a greater histological activity index were predictors of response. Kaplan-Meier estimates of cumulative HBeAg clearance rates at five years were similar between treated patients (60%) and controls (65%). After HBeAg clearance, all cases lost hepatitis B virus DNA and 94% had normal transaminase levels. Loss of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) occurred in four (25%) patients who responded during treatment but in none of the other treated or untreated patients. CONCLUSIONS—After five years' observation, the proportion of treated children with sustained HBeAg clearance comprised an equal number of responders and non-responders and did not differ from that observed in untreated controls, suggesting that IFN simply accelerated a spontaneous event. However, IFN significantly improved the rate of HBsAg loss in cases with more prominent disease activity who were early responders, and may be particularly useful in this type of patient. Keywords: hepatitis B; interferon; children; hepatitis B virus
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (129.2 KB).
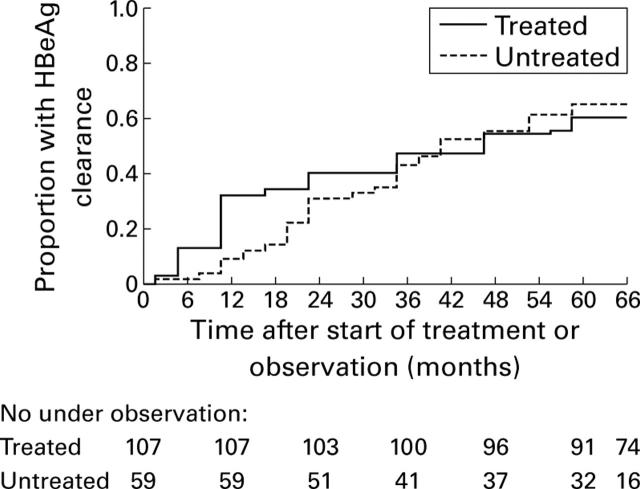
Figure 1 .
Cumulative proportion of treated and untreated patients who remained HBeAg positive during the survey (limited to 66 months), calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method. At the end of follow up, the rate of HBeAg clearance was 60% in treated and 65% in untreated patients (NS).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbera C., Bortolotti F., Crivellaro C., Coscia A., Zancan L., Cadrobbi P., Nebbia G., Pillan M. N., Lepore L., Parrella T. Recombinant interferon-alpha 2a hastens the rate of HBeAg clearance in children with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 1994 Aug;20(2):287–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley R. P. Hepatitis B virus. The major etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 1988 May 15;61(10):1942–1956. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880515)61:10<1942::aid-cncr2820611003>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortolotti F., Cadrobbi P., Crivellaro C., Guido M., Rugge M., Noventa F., Calzia R., Realdi G. Long-term outcome of chronic type B hepatitis in patients who acquire hepatitis B virus infection in childhood. Gastroenterology. 1990 Sep;99(3):805–810. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90972-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortolotti F., Jara P., Crivellaro C., Hierro L., Cadrobbi P., Frauca E., Camarena C., De La Vega A., Diaz C., De Moliner L. Outcome of chronic hepatitis B in Caucasian children during a 20-year observation period. J Hepatol. 1998 Aug;29(2):184–190. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(98)80002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortolotti F., Wirth S., Crivellaro C., Alberti A., Martine U., de Moliner L. Long-term persistence of hepatitis B virus DNA in the serum of children with chronic hepatitis B after hepatitis B e antigen to antibody seroconversion. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1996 Apr;22(3):270–274. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199604000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groote J., Desmet V. J., Gedigk P., Korb G., Popper H., Poulsen H., Scheuer P. J., Schmid M., Thaler H., Uehlinger E. A classification of chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1968 Sep 14;2(7568):626–628. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90710-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmet V. J., Gerber M., Hoofnagle J. H., Manns M., Scheuer P. J. Classification of chronic hepatitis: diagnosis, grading and staging. Hepatology. 1994 Jun;19(6):1513–1520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregorio G. V., Jara P., Hierro L., Diaz C., de la Vega A., Vegnente A., Iorio R., Bortolotti F., Crivellaro C., Zancan L. Lymphoblastoid interferon alfa with or without steroid pretreatment in children with chronic hepatitis B: a multicenter controlled trial. Hepatology. 1996 Apr;23(4):700–707. doi: 10.1002/hep.510230407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenman J., Baker B., Waggoner J., Everhart J. E., Di Bisceglie A. M., Hoofnagle J. H. Long-term remission of chronic hepatitis B after alpha-interferon therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Apr 15;114(8):629–634. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-8-629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. L., Lin H. J., Lau J. N., Flok A. S., Wu P. C., Chung H. T., Wong L. K., Leung M. P., Yeung C. Y. Effect of recombinant alpha 2 interferon with or without prednisone in Chinese HBsAg carrier children. Q J Med. 1991 Feb;78(286):155–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau D. T., Everhart J., Kleiner D. E., Park Y., Vergalla J., Schmid P., Hoofnagle J. H. Long-term follow-up of patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with interferon alfa. Gastroenterology. 1997 Nov;113(5):1660–1667. doi: 10.1053/gast.1997.v113.pm9352870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederau C., Heintges T., Lange S., Goldmann G., Niederau C. M., Mohr L., Häussinger D. Long-term follow-up of HBeAg-positive patients treated with interferon alfa for chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 1996 May 30;334(22):1422–1427. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199605303342202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Moreno M., Camps T., Aguado J. G., Porres J. C., Oliva H., Bartolomé J., Carreño V. Serological and histological follow up of chronic hepatitis B infection. Arch Dis Child. 1989 Aug;64(8):1165–1169. doi: 10.1136/adc.64.8.1165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Moreno M., Camps T., Jimenez J., López R., Castillo I., Bartolomé J., Carreño V. Factors predictive of response to interferon therapy in children with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 1995 May;22(5):540–544. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(95)80448-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Moreno M., Rua M. J., Molina J., Moraleda G., Moreno A., García-Aguado J., Carreño V. Prospective, randomized controlled trial of interferon-alpha in children with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 1991 Jun;13(6):1035–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokal E. M., Conjeevaram H. S., Roberts E. A., Alvarez F., Bern E. M., Goyens P., Rosenthal P., Lachaux A., Shelton M., Sarles J. Interferon alfa therapy for chronic hepatitis B in children: a multinational randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 1998 May;114(5):988–995. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70318-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]