Abstract
BACKGROUND—Obstructive jaundice is associated with postoperative complications related to increased endotoxaemia and the inflammatory response. In animals obstructive jaundice is associated with endotoxaemia and cytokine induction, which are reversed by internal biliary drainage. AIMS—To study endotoxaemia and the subsequent inflammatory response in obstructive jaundiced patients and after endoscopic biliary drainage. METHODS—In 15 patients with malignant distal obstructive jaundice, inflammatory and bacteriological parameters were assessed before endoscopic stent placement and after three weeks endoscopic drainage. RESULTS—Drainage reduced bilirubin from 252.5 to 45.1 µmol/l. At baseline low level endotoxaemia was detected (4.3 pg/ml) which was not affected after drainage (4.5 pg/ml). Serum interleukin 8 (IL-8) and endotoxin binding proteins were increased in jaundice and reduced after drainage (IL-8 113.6 to 20.7 pg/ml; lipopolysaccharide binding protein 24.2 to 16.5 µg/ml; sCD14 17.4 to 7.6 µg/ml; bactericidal/permeability increasing protein 2.9 to 1.8 ng/ml). Levels of other cytokines, augmented in animals, were only slightly increased and not changed after drainage (tumour necrosis factor (TNF): 21.7 and 18.4 pg/ml; sTNFr p55/75: 2.9/7.0 and 2.7/5.6 ng/ml; IL-6: 4.2 and 6.1 pg/ml; IL-10: 4.5 and 2.7 pg/ml). Elastase and lactoferrin tended towards reduction after drainage. All bile cultures were positive after stenting. CONCLUSIONS—The effects of obstructive jaundice in humans on endotoxin and cytokines are different from those in animal models. Obstructive jaundice causes alterations in circulating endotoxin binding proteins and IL-8. Concentrations of other mediators (TNF, previously suggested as being responsible for systemic endotoxaemia effects) are low and not affected by drainage. Keywords: endotoxin; obstructive jaundice; cytokines; endotoxin binding proteins
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (148.5 KB).
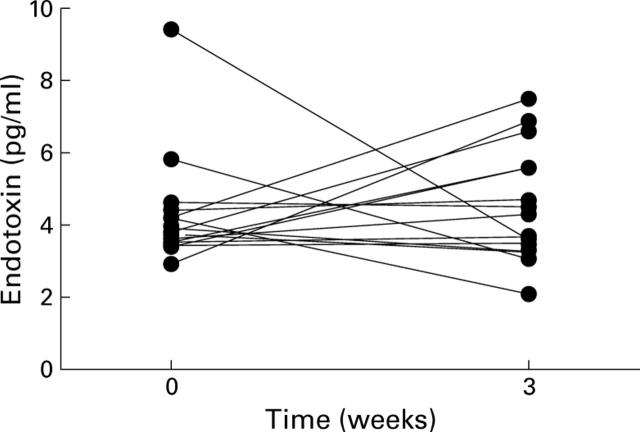
Figure 1 .
Endotoxin concentrations in systemic blood as measured by the LAL assay. p=0.7.
Figure 2 .
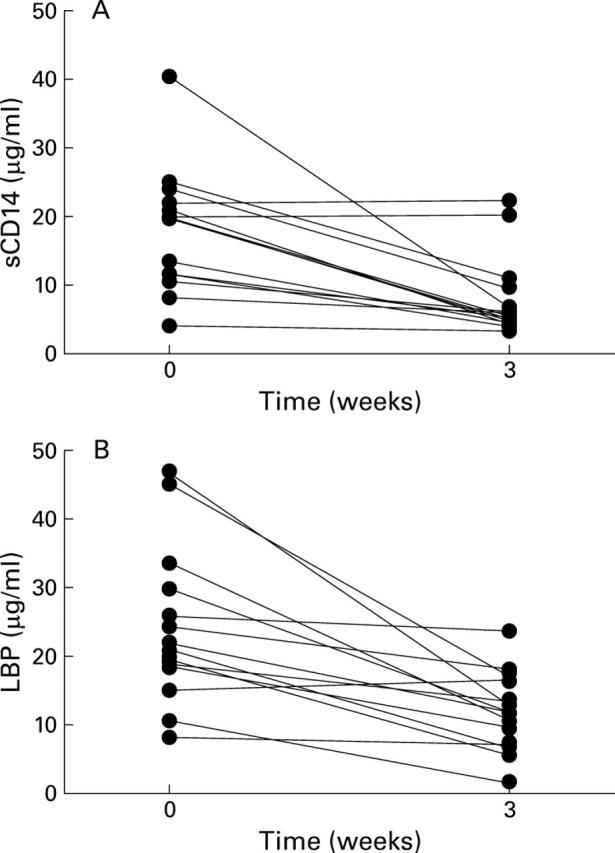
(A) Lipopolysaccharide binding protein (LBP) and (B) soluble CD14 concentrations in obstructive jaundice and after biliary drainage.
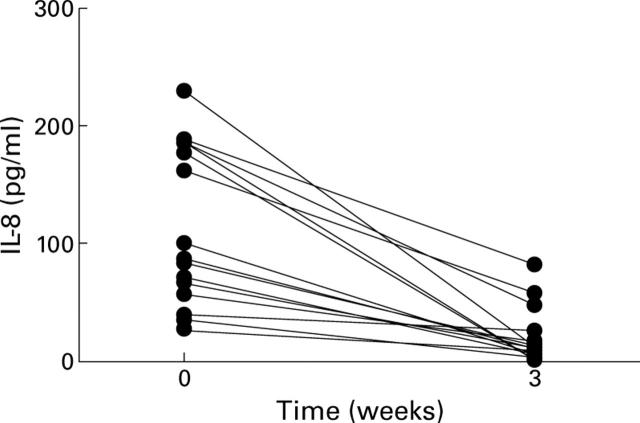
Figure 3 .
Interleukin (IL) 8 concentrations before and after biliary drainage. p<0.001.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballinger A. B., Woolley J. A., Ahmed M., Mulcahy H., Alstead E. M., Landon J., Clark M. L., Farthing M. J. Persistent systemic inflammatory response after stent insertion in patients with malignant bile duct obstruction. Gut. 1998 Apr;42(4):555–559. doi: 10.1136/gut.42.4.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bemelmans M. H., Gouma D. J., Greve J. W., Buurman W. A. Cytokines tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 in experimental biliary obstruction in mice. Hepatology. 1992 Jun;15(6):1132–1136. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bemelmans M. H., Greve J. W., Gouma D. J., Buurman W. A. Increased concentrations of tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and soluble TNF receptors in biliary obstruction in mice; soluble TNF receptors as prognostic factors for mortality. Gut. 1996 Mar;38(3):447–453. doi: 10.1136/gut.38.3.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blamey S. L., Fearon K. C., Gilmour W. H., Osborne D. H., Carter D. C. Prediction of risk in biliary surgery. Br J Surg. 1983 Sep;70(9):535–538. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800700910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitch E. A., Sittig K., Li M., Berg R., Specian R. D. Obstructive jaundice promotes bacterial translocation from the gut. Am J Surg. 1990 Jan;159(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(05)80610-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dentener M. A., Francot G. J., Smit F. T., Froon A. H., Pennings H. J., Wouters E. F., Buurman W. A. Presence of bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein in disease: detection by ELISA. J Infect Dis. 1995 Mar;171(3):739–743. doi: 10.1093/infdis/171.3.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond T., Rowlands B. J. Endotoxaemia in obstructive jaundice. HPB Surg. 1991 Jun;4(2):81–94. doi: 10.1155/1991/48672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding J. W., Andersson R., Soltesz V., Willén R., Bengmark S. Obstructive jaundice impairs reticuloendothelial function and promotes bacterial translocation in the rat. J Surg Res. 1994 Aug;57(2):238–245. doi: 10.1006/jsre.1994.1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding J. W., Andersson R., Soltesz V., Willén R., Bengmark S. The role of bile and bile acids in bacterial translocation in obstructive jaundice in rats. Eur Surg Res. 1993 Jan-Feb;25(1):11–19. doi: 10.1159/000129252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding J. W., Andersson R., Stenram U., Lunderquist A., Bengmark S. Effect of biliary decompression on reticuloendothelial function in jaundiced rats. Br J Surg. 1992 Jul;79(7):648–652. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800790718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froon A. H., Dentener M. A., Greve J. W., Ramsay G., Buurman W. A. Lipopolysaccharide toxicity-regulating proteins in bacteremia. J Infect Dis. 1995 May;171(5):1250–1257. doi: 10.1093/infdis/171.5.1250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouma D. J., Coelho J. C., Schlegel J. F., Li Y. F., Moody F. G. The effect of preoperative internal and external biliary drainage on mortality of jaundiced rats. Arch Surg. 1987 Jun;122(6):731–734. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1987.01400180113022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve J. W., Maessen J. G., Tiebosch T., Buurman W. A., Gouma D. J. Prevention of postoperative complications in jaundiced rats. Internal biliary drainage versus oral lactulose. Ann Surg. 1990 Aug;212(2):221–227. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199008000-00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hack C. E., Paardekooper J., Eerenberg A. J., Navis G. O., Nijsten M. W., Thijs L. G., Nuijens J. H. A modified competitive inhibition radioimmunoassay for the detection of C3a. Use of 125I-C3 instead of 125I-C3a. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Apr 6;108(1-2):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90405-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hechtman D. H., Cybulsky M. I., Fuchs H. J., Baker J. B., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Intravascular IL-8. Inhibitor of polymorphonuclear leukocyte accumulation at sites of acute inflammation. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 1;147(3):883–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa A., Kinoshita H., Hirohashi K., Kubo S., Tsukamoto T., Hamba H., Shuto T. Concentrations of bile and serum endotoxin and serum cytokines after biliary drainage for acute cholangitis. Osaka City Med J. 1997 Jun;43(1):15–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsten T. M., Allema J. H., Reinders M., van Gulik T. M., de Wit L. T., Verbeek P. C., Huibregtse K., Tytgat G. N., Gouma D. J. Preoperative biliary drainage, colonisation of bile and postoperative complications in patients with tumours of the pancreatic head: a retrospective analysis of 241 consecutive patients. Eur J Surg. 1996 Nov;162(11):881–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsten T. M., Coene P. P., van Gulik T. M., Bosma A., van Marle J., James J., Lygidakis N. J., Klopper P. J., van der Heyde M. N. Morphologic changes of extrahepatic bile ducts during obstruction and subsequent decompression by endoprosthesis. Surgery. 1992 May;111(5):562–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura F., Miyazaki M., Suwa T., Itoh H., Ambiru S., Shimizu H., Nakagawa K. Hyperactive cytokine response after partial hepatectomy in patients with biliary obstruction. Eur Surg Res. 1998;30(4):259–267. doi: 10.1159/000008585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger C., Schütt C., Obertacke U., Joka T., Müller F. E., Knöller J., Köller M., König W., Schönfeld W. Serum CD14 levels in polytraumatized and severely burned patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Aug;85(2):297–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05722.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E. C., Mok F. P., Fan S. T., Lo C. M., Chu K. M., Liu C. L., Wong J. Preoperative endoscopic drainage for malignant obstructive jaundice. Br J Surg. 1994 Aug;81(8):1195–1198. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800810839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantz M., Gullberg U., Nilsson E., Olsson I. Characterization in vitro of a human tumor necrosis factor-binding protein. A soluble form of a tumor necrosis factor receptor. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1396–1402. doi: 10.1172/JCI114853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra M. N., Wilde C. G., Collins M. S., Snable J. L., Thornton M. B., Scott R. W. The role of bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein as a natural inhibitor of bacterial endotoxin. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):532–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Tobias P. S., Wolfson E., Ulevitch R. J. Plasma lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein. A key component in macrophage recognition of gram-negative LPS. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 1;149(1):200–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motte S., Deviere J., Dumonceau J. M., Serruys E., Thys J. P., Cremer M. Risk factors for septicemia following endoscopic biliary stenting. Gastroenterology. 1991 Nov;101(5):1374–1381. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mészáros K., Aberle S., White M., Parent J. B. Immunoreactivity and bioactivity of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein in normal and heat-inactivated sera. Infect Immun. 1995 Jan;63(1):363–365. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.1.363-365.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuijens J. H., Abbink J. J., Wachtfogel Y. T., Colman R. W., Eerenberg A. J., Dors D., Kamp A. J., Strack van Schijndel R. J., Thijs L. G., Hack C. E. Plasma elastase alpha 1-antitrypsin and lactoferrin in sepsis: evidence for neutrophils as mediators in fatal sepsis. J Lab Clin Med. 1992 Feb;119(2):159–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain J. A. Reticulo-endothelial function in obstructive jaundice. Br J Surg. 1987 Dec;74(12):1091–1094. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800741207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puntis M. C., Jiang W. G. Plasma cytokine levels and monocyte activation in patients with obstructive jaundice. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996 Jan;11(1):7–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1996.tb00003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H. R., Winkle P. J., Kendall B. J., Diehl D. L. Biliary interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in patients undergoing endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Dig Dis Sci. 1997 Jun;42(6):1290–1294. doi: 10.1023/a:1018822628096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinas G. A., Keller U., Brockhaus M. Release of soluble receptors for tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in relation to circulating TNF during experimental endotoxinemia. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):533–536. doi: 10.1172/JCI115891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain M. G., Tjandra K., Kanwar S., Kubes P. Neutrophil adhesion is impaired in rat model of cholestasis. Gastroenterology. 1995 Sep;109(3):923–932. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90403-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. L., Hoper M., Diamond T., Rowlands B. J. Development and reversibility of T lymphocyte dysfunction in experimental obstructive jaundice. Br J Surg. 1990 Nov;77(11):1229–1232. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800771112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias P. S., Soldau K., Gegner J. A., Mintz D., Ulevitch R. J. Lipopolysaccharide binding protein-mediated complexation of lipopolysaccharide with soluble CD14. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 5;270(18):10482–10488. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.18.10482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trede M., Schwall G. The complications of pancreatectomy. Ann Surg. 1988 Jan;207(1):39–47. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198801000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. L., Ma J. K., Birr C. A., Trown P. W., Carroll S. F. Measurement of bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein in human body fluids by sandwich ELISA. J Immunol Methods. 1994 Jan 3;167(1-2):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(94)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D. CD14 and innate recognition of bacteria. J Immunol. 1995 Jul 1;155(1):6–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurfel M. M., Hailman E., Wright S. D. Soluble CD14 acts as a shuttle in the neutralization of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) by LPS-binding protein and reconstituted high density lipoprotein. J Exp Med. 1995 May 1;181(5):1743–1754. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.5.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurfel M. M., Kunitake S. T., Lichenstein H., Kane J. P., Wright S. D. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein is carried on lipoproteins and acts as a cofactor in the neutralization of LPS. J Exp Med. 1994 Sep 1;180(3):1025–1035. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.3.1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagitani K., Kubota Y., Tsuji K., Yamamoto S., Amoh Y., Takaoka M., Ogura M., Inoue K. Influence of biliary obstruction on neutrophil chemotaxis. J Gastroenterol. 1998 Aug;33(4):536–540. doi: 10.1007/s005350050128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Poll T., Jansen J., Levi M., ten Cate H., ten Cate J. W., van Deventer S. J. Regulation of interleukin 10 release by tumor necrosis factor in humans and chimpanzees. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1985–1988. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Poll T., Jansen J., van Leenen D., von der Möhlen M., Levi M., ten Cate H., Gallati H., ten Cate J. W., van Deventer S. J. Release of soluble receptors for tumor necrosis factor in clinical sepsis and experimental endotoxemia. J Infect Dis. 1993 Oct;168(4):955–960. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.4.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Möhlen M. A., Kimmings A. N., Wedel N. I., Mevissen M. L., Jansen J., Friedmann N., Lorenz T. J., Nelson B. J., White M. L., Bauer R. Inhibition of endotoxin-induced cytokine release and neutrophil activation in humans by use of recombinant bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein. J Infect Dis. 1995 Jul;172(1):144–151. doi: 10.1093/infdis/172.1.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]