Abstract
BACKGROUND—Intrasphincteric injection of botulinum toxin (Botx) has been proposed as treatment for oesophageal achalasia. However, the predictors of response and optimal dose remain unclear. AIMS—To compare the effect of different doses of Botx and to identify predictors of response. PATIENTS/METHODS—A total of 118 achalasic patients were randomised to receive one of three doses of Botx in a single injection: 50 U (n=40), 100 U (n=38), and 200 U (n=40). Of those who received 100 U, responsive patients were reinjected with an identical dose after 30 days. Clinical and manometric assessments were performed at baseline, 30 days after the initial injection of botulinum toxin, and at the end of follow up (mean 12 months; range 7-24 months). RESULTS—Thirty days after the initial injection, 82% of patients were considered responders without a clear dose related effect. At the end of follow up however, relapse of symptoms was evident in 19% of patients who received two injections of 100 U compared with 47% and 43% in the 50 U and 200 U groups, respectively. Using Kaplan-Meier analysis, patients in the 100×2 U group were more likely to remain in remission at any time (p<0.04), with 68% (95% CI 59-83) still in remission at 24 months. In a multiple adjusted model, response to Botx was independently predicted by the occurrence of vigorous achalasia (odds ratio 3.3) and the 100×2 U regimen (odds ratio 3.2). CONCLUSIONS—Two injections of 100 U of Botx 30 days apart appeared to be the most effective therapeutic schedule. The presence of vigorous achalasia was the principal determinant of the response to Botx. Keywords: achalasia; botulinum toxin; oesophagus; dose ranging study
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (133.1 KB).
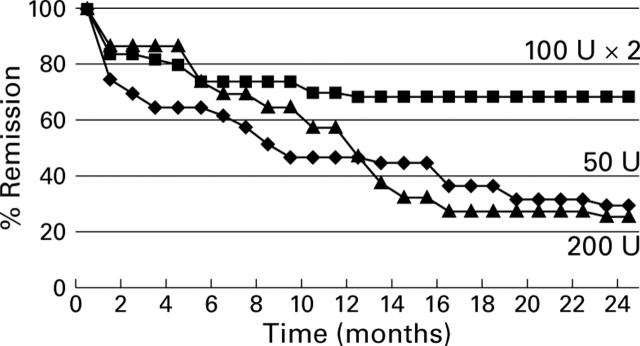
Figure 1 .
Remission curves using Kaplan-Meier analysis after Botx injection of 50 U, 100×2 U, or 200 U in the three groups of patients, obtained by censoring all non-responders.
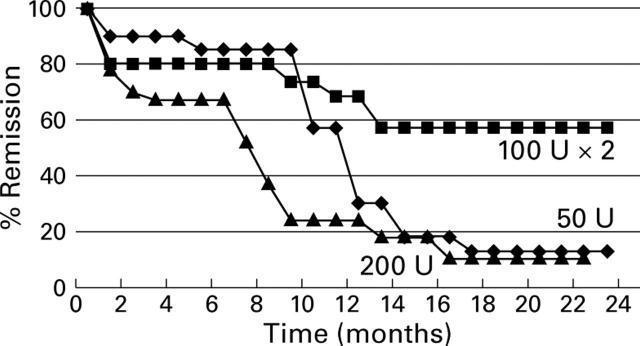
Figure 2 .
Remission curves by Kaplan-Meier analysis after Botx injection of 50 U, 100×2 U, or 200 U in the three groups of patients, obtained in the main centre of the study (S Giovanni Rotondo). Values did not differ significantly from those of the whole population (p=0.6) or other centres (data not shown).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annese V., Basciani M., Borrelli O., Leandro G., Simone P., Andriulli A. Intrasphincteric injection of botulinum toxin is effective in long-term treatment of esophageal achalasia. Muscle Nerve. 1998 Nov;21(11):1540–1542. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4598(199811)21:11<1540::aid-mus27>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Annese V., Basciani M., Lombardi G., Caruso N., Perri F., Simone P., Andriulli A. Perendoscopic injection of botulinum toxin is effective in achalasia after failure of myotomy or pneumatic dilation. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996 Oct;44(4):461–465. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(96)70100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Annese V., Basciani M., Perri F., Lombardi G., Frusciante V., Simone P., Andriulli A., Vantrappen G. Controlled trial of botulinum toxin injection versus placebo and pneumatic dilation in achalasia. Gastroenterology. 1996 Dec;111(6):1418–1424. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(96)70002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassotti G., Battaglia E., Debernardi V., Germani U., Quiriconi F., Dughera L., Buonafede G., Puiatti P., Morelli A., Spinozzi F. Esophageal dysfunction in scleroderma: relationship with disease subsets. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Dec;40(12):2252–2259. doi: 10.1002/art.1780401222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brin M. F. Botulinum toxin: chemistry, pharmacology, toxicity, and immunology. Muscle Nerve Suppl. 1997;6:S146–S168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell D. O., Katzka D. A. Botulinum toxin for achalasia: to be or not to be? Gastroenterology. 1996 May;110(5):1650–1652. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.agast961650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Parkman H. P. Treatment of achalasia--whalebone to botulinum toxin. N Engl J Med. 1995 Mar 23;332(12):815–816. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199503233321211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuillière C., Ducrotté P., Zerbib F., Metman E. H., de Looze D., Guillemot F., Hudziak H., Lamouliatte H., Grimaud J. C., Ropert A. Achalasia: outcome of patients treated with intrasphincteric injection of botulinum toxin. Gut. 1997 Jul;41(1):87–92. doi: 10.1136/gut.41.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman V. M., Parkman H. P., Schiano T. D., Hills C., Dabezies M. A., Cohen S., Fisher R. S., Miller L. S. Symptomatic improvement in achalasia after botulinum toxin injection of the lower esophageal sphincter. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996 Sep;91(9):1724–1730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg S. P., Burrell M., Fette G. G., Vos C., Traube M. Classic and vigorous achalasia: a comparison of manometric, radiographic, and clinical findings. Gastroenterology. 1991 Sep;101(3):743–748. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90534-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. M., Eaker E. Y. Prospective study of esophageal botulinum toxin injection in high-risk achalasia patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997 Oct;92(10):1812–1817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene P., Fahn S., Diamond B. Development of resistance to botulinum toxin type A in patients with torticollis. Mov Disord. 1994 Mar;9(2):213–217. doi: 10.1002/mds.870090216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankovic J. Botulinum toxin in movement disorders. Curr Opin Neurol. 1994 Aug;7(4):358–366. doi: 10.1097/00019052-199408000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankovic J., Brin M. F. Therapeutic uses of botulinum toxin. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 25;324(17):1186–1194. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104253241707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasricha P. J., Rai R., Ravich W. J., Hendrix T. R., Kalloo A. N. Botulinum toxin for achalasia: long-term outcome and predictors of response. Gastroenterology. 1996 May;110(5):1410–1415. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8613045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasricha P. J., Ravich W. J., Hendrix T. R., Sostre S., Jones B., Kalloo A. N. Intrasphincteric botulinum toxin for the treatment of achalasia. N Engl J Med. 1995 Mar 23;332(12):774–778. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199503233321203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasricha P. J., Ravich W. J., Hendrix T. R., Sostre S., Jones B., Kalloo A. N. Treatment of achalasia with intrasphincteric injection of botulinum toxin. A pilot trial. Ann Intern Med. 1994 Oct 15;121(8):590–591. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-121-8-199410150-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasricha P. J., Ravich W. J., Kalloo A. N. Effects of intrasphincteric botulinum toxin on the lower esophageal sphincter in piglets. Gastroenterology. 1993 Oct;105(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90947-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaezi M. F., Richter J. E. Current therapies for achalasia: comparison and efficacy. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1998 Jul;27(1):21–35. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199807000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaezi M. F., Richter J. E., Wilcox C. M., Schroeder P. L., Birgisson S., Slaughter R. L., Koehler R. E., Baker M. E. Botulinum toxin versus pneumatic dilatation in the treatment of achalasia: a randomised trial. Gut. 1999 Feb;44(2):231–239. doi: 10.1136/gut.44.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]