Abstract
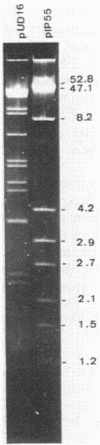
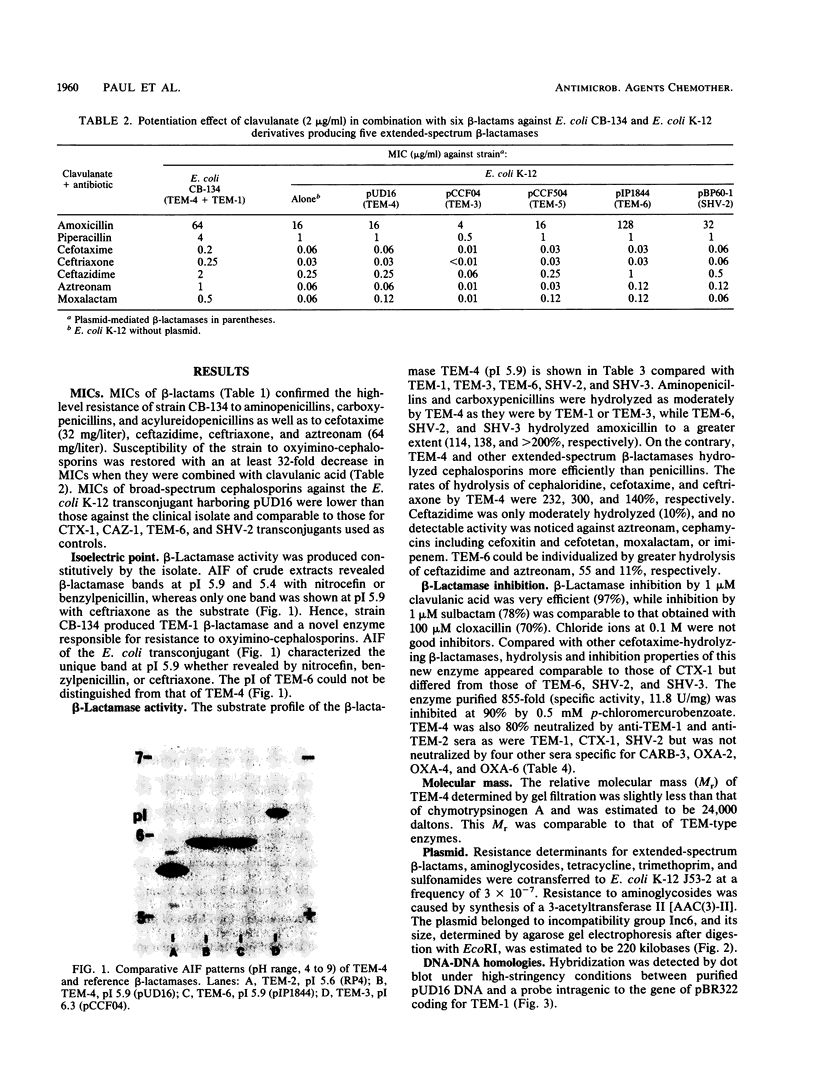
A clinical isolate of Escherichia coli, strain CB-134, recovered in 1986 from an abdominal abscess, exhibited resistance to penams, oxyimino-beta-lactams including broad-spectrum cephalosporins (cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, ceftazidime), and aztreonam but remained susceptible to cephamycins (cefoxitin, cefotetan) and to moxalactam and imipenem. Clavulanate (2 micrograms/ml) restored the susceptibility of the strain to broad-spectrum cephalosporins and aztreonam. A beta-lactamase with an isoelectric point (pI) of 5.9 was detected in strain CB-134, and the corresponding gene was transferred by conjugation to E. coli together with the associated aminoglycoside resistance determinant [AAC(3)-II] and tetracycline, trimethoprim, and sulfonamide resistance. The beta-lactamase efficiently hydrolyzed cefotaxime and ceftriaxone but only moderately hydrolyzed ceftazidime and was inhibited by clavulanate and sulbactam (1 microM) and by anti-TEM-1 and anti-TEM-2 sera. This extended-spectrum beta-lactamase, conferring resistance to cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, ceftazidime, and aztreonam, was comparable to CTX-1 (TEM-3) but differed from it by pI. Agarose gel electrophoresis of the plasmid DNA indicated that this new enzyme was coded by pUD16, a plasmid of 220 kilobases which belongs to the Inc6 incompatibility group. Hybridization with an intragenic probe for TEM-1 revealed that this beta-lactamase derives from TEM-type beta-lactamases and hence it was named TEM-4.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakken J. S., Sanders C. C., Thomson K. S. Selective ceftazidime resistance in Escherichia coli: association with changes in outer membrane protein. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1220–1225. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthelemy M., Guionie M., Labia R. Beta-lactamases: determination of their isoelectric points. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):695–698. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthélémy M., Péduzzi J., Ben Yaghlane H., Labia R. Single amino acid substitution between SHV-1 beta-lactamase and cefotaxime-hydrolyzing SHV-2 enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 11;231(1):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80734-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind A., Hörl G. Novel R-factor borne beta-lactamase of Escherichia coli confering resistance to cephalosporins. Infection. 1987 Jul-Aug;15(4):257–259. doi: 10.1007/BF01644127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben Redjeb S., Ben Yaghlane H., Boujnah A., Philippon A., Labia R. Synergy between clavulanic acid and newer beta-lactams on nine clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium resistant to third-generation cephalosporins. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Feb;21(2):263–266. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun-Buisson C., Legrand P., Philippon A., Montravers F., Ansquer M., Duval J. Transferable enzymatic resistance to third-generation cephalosporins during nosocomial outbreak of multiresistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Lancet. 1987 Aug 8;2(8554):302–306. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90891-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buré A., Legrand P., Arlet G., Jarlier V., Paul G., Philippon A. Dissemination in five French hospitals of Klebsiella pneumoniae serotype K25 harbouring a new transferable enzymatic resistance to third generation cephalosporins and aztreonam. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;7(6):780–782. doi: 10.1007/BF01975048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabbert Y. A., Scavizzi M. R., Witchitz J. L., Gerbaud G. R., Bouanchaud D. H. Incompatibility groups and the classification of fi - resistance factors. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):666–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.666-675.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanal C. M., Sirot D. L., Labia R., Petit A., Morand A., Sirot J. L., Cluzel R. A. Comparative study of a novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase, CAZ-2, and the CTX-1 and CAZ-1 enzymes conferring resistance to broad-spectrum cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Nov;32(11):1660–1665. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.11.1660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courvalin P., Weisblum B., Davies J. Aminoglycoside-modifying enzyme of an antibiotic-producing bacterium acts as a determinant of antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):999–1003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Kitzis M. D., Billot-Klein D., Goldstein F., Tran Van Nhieu G., Lu T., Carlet J., Collatz E., Williamson R. Plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase (TEM-7) involved in resistance to ceftazidime and aztreonam. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):860–866. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. J., Dowding J. E. Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:611–628. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Datta N., Kontomichalou P., Smith J. T. Molecular specificities of R factor-determined beta-lactamases: correlation with plasmid compatibility. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):56–62. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.56-62.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarlier V., Nicolas M. H., Fournier G., Philippon A. Extended broad-spectrum beta-lactamases conferring transferable resistance to newer beta-lactam agents in Enterobacteriaceae: hospital prevalence and susceptibility patterns. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):867–878. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitzis M. D., Billot-Klein D., Goldstein F. W., Williamson R., Tran Van Nhieu G., Carlet J., Acar J. F., Gutmann L. Dissemination of the novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase CTX-1, which confers resistance to broad-spectrum cephalosporins, and its inhibition by beta-lactamase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):9–14. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliebe C., Nies B. A., Meyer J. F., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Evolution of plasmid-coded resistance to broad-spectrum cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):302–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knothe H., Shah P., Krcmery V., Antal M., Mitsuhashi S. Transferable resistance to cefotaxime, cefoxitin, cefamandole and cefuroxime in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Serratia marcescens. Infection. 1983 Nov-Dec;11(6):315–317. doi: 10.1007/BF01641355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Guionie M., Barthélémy M. Properties of three carbenicillin-hydrolysing beta-lactamases (CARB) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: identification of a new enzyme. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Jan;7(1):49–56. doi: 10.1093/jac/7.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Morand A., Tiwari K., Pitton J. S., Sirot D., Sirot J. Kinetic properties of two plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases from Klebsiella pneumoniae with strong activity against third-generation cephalosporins. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Mar;21(3):301–307. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.3.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labigne-Roussel A., Gerbaud G., Courvalin P. Translocation of sequences encoding antibiotic resistance from the chromosome to a receptor plasmid in Salmonella ordonez. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(3):390–408. doi: 10.1007/BF00293927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesage D. D., Gerbaud G. R., Chabbert Y. A. Carte génétique et strucutre chez Escherichia coli K12 d'un plasmide de résistance isolé de Salmonella ordonez. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1975 May-Jun;126A(4):435–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew A., Harris A. M., Marshall M. J., Ross G. W. The use of analytical isoelectric focusing for detection and identification of beta-lactamases. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):169–178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul G., Barthélémy M., Philippon A., Peduzzi J., Gilly L., Labia R., Névot P. Immunological comparison of constitutive beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria by neutralization in zymogram gels: properties of anti-TEM-1 and anti-TEM-2 sera. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1988 Jul-Aug;139(4):435–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit A., Sirot D. L., Chanal C. M., Sirot J. L., Labia R., Gerbaud G., Cluzel R. A. Novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae more resistant to ceftazidime than to other broad-spectrum cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):626–630. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippon A. M., Paul G. C., Jacoby G. A. Properties of PSE-2 beta-lactamase and genetic basis for its production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Sep;24(3):362–369. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.3.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippon A., Paul G., Vedel G., Nevot P. Résistance plasmidique aux céphalosporines de 3e génération. Presse Med. 1988 Oct 26;17(37):1883–1889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C. Chromosomal cephalosporinases responsible for multiple resistance to newer beta-lactam antibiotics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:573–593. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Emergence of resistance during therapy with the newer beta-lactam antibiotics: role of inducible beta-lactamases and implications for the future. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):639–648. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah P. M., Stille W. Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae strains more susceptible to cefoxitin than to third generation cephalosporins. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Jun;11(6):597–598. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.6.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirot D., Sirot J., Labia R., Morand A., Courvalin P., Darfeuille-Michaud A., Perroux R., Cluzel R. Transferable resistance to third-generation cephalosporins in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae: identification of CTX-1, a novel beta-lactamase. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Sep;20(3):323–334. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirot J., Chanal C., Petit A., Sirot D., Labia R., Gerbaud G. Klebsiella pneumoniae and other Enterobacteriaceae producing novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases markedly active against third-generation cephalosporins: epidemiologic studies. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):850–859. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sougakoff W., Goussard S., Gerbaud G., Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated resistance to third-generation cephalosporins caused by point mutations in TEM-type penicillinase genes. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):879–884. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sougakoff W., Petit A., Goussard S., Sirot D., Bure A., Courvalin P. Characterization of the plasmid genes blaT-4 and blaT-5 which encode the broad-spectrum beta-lactamases TEM-4 and TEM-5 in enterobacteriaceae. Gene. 1989 May 30;78(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90236-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer R. C., Wheat P. F., Winstanley T. G., Cox D. M., Plested S. J. Novel beta-lactamase in a clinical isolate of Klebsiella pneumoniae conferring unusual resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Dec;20(6):919–921. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.6.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thabaut A., Acar J., Arlet G., Berardi-Grassias L., Bergogne-Bérézin E., Brun Y., Buisson Y., Chabanon G., Cluzel R., Courtieu A. Sensibilité des Pseudomonas aeruginosa et des Klebsiella à la ceftazidime. Etat actuel en France. Presse Med. 1988 Oct 26;17(37):1895–1899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]