Abstract
BACKGROUND/AIMS—Clearance of hepatitis B virus (HBV) is characterised by a strong cytotoxic T cell response. Persistence of HBV in chronic hepatitis B carriers may be related to failure of this response. The aim of this study was to determine whether HLA class I restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses persist in anti-hepatitis B e (HBe) positive / HBV DNA negative individuals, and to correlate the presence of viral CTL epitope mutation with clinical outcome. METHODS—An HLA/HBV dual transfectant model was used to demonstrate these CTL responses in individuals chronically infected with HBV. Subsequently, a known hepatitis B core (HBc) CTL epitope was sequenced in a family of five chronically infected individuals all sharing a HLA allele (HLA-A68.1). RESULTS—Low level HLA class I restricted cytotoxic T cell responses were detected in the peripheral blood of five of eight anti-HBe positive individuals. In the family of HLA-A68.1 positive chronically infected individuals, mutation of the HLA-A68.1 restricted hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg) CTL epitope STLPETTVVRR was found in all four anti-HBe positive individuals but not in the sole hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) positive patient. CONCLUSION—These data are consistent with a continued immune selection pressure on HBV in anti-HBe positive chronically infected individuals with low replicating HBV infection and suggest that mutation of a CTL epitope may be a consequence of the immune response, as opposed to the cause of viral persistence. Keywords: hepatitis B virus; HLA; hepatitis B core antigen; cytotoxicity; mutant
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (162.8 KB).
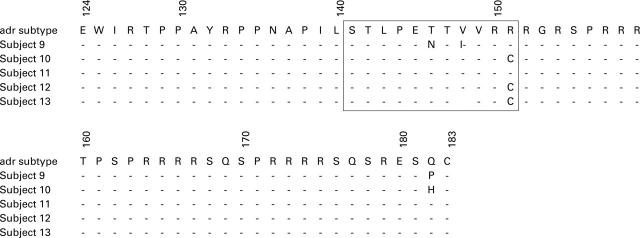
Figure 1 .
Cytotoxicity assay of an individual with acute hepatitis B. (A) Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were stimulated with the HBc/HLA B*0702 dual transfectant and then tested against HBc/B*0702 dual transfectant, vector/B*0702 dual transfectant, or L721.221/HBc single transfectant. Cold targets were used at a ratio of 10:1 to hot targets. (B) To confirm the presence of a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I restricted cytotoxic response, the culture was restimulated with the dual transfectant line and retested in the presence of the anti-MHC class I antibody W6/32, an isotype matched control antibody, or no antibody.
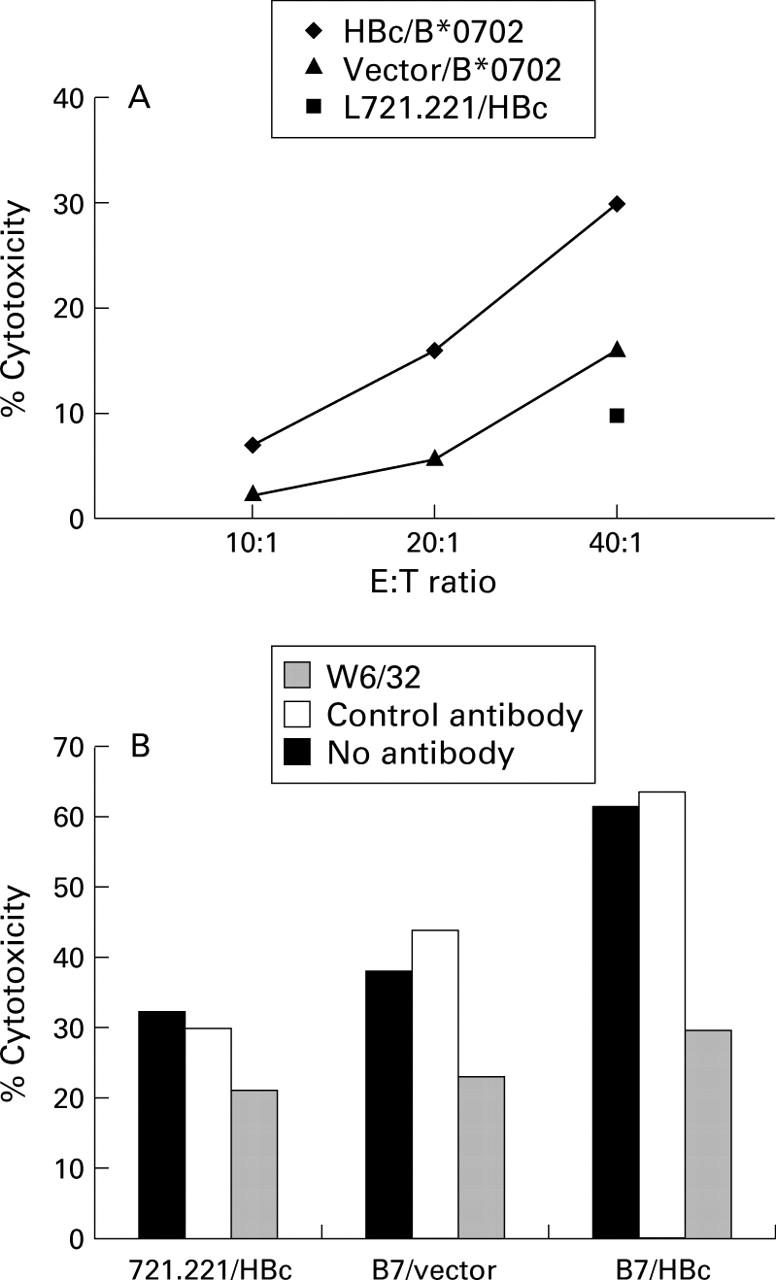
Figure 2 .
Summary of the cytotoxicity results of the HLA-B7 positive (A), HLA-A2 positive (B), and HLA-A68.1 (C) individuals. Subject No 4 was HBeAg positive, and the remainder were anti-HBe positive, except where indicated. Results are expressed as percentage specific cytotoxicity against the HBc/HLA transfectant cell line compared with that of the vector/HLA dual transfectant. In (B), 5A indicates the result when peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from subject No 5 were stimulated with the HBc/HLA dual transfectant and 5B the result when PBMC from the same individual were stimulated with the vector/HLA dual transfectant as a control for an allospecific response. In (C), subject No 12 was HBeAg positive, and subject Nos 11 and 13 anti-HBe positive. Assays were performed at effector to target ratios of 40:1 using cold targets at a ratio of 10:1 to hot targets.
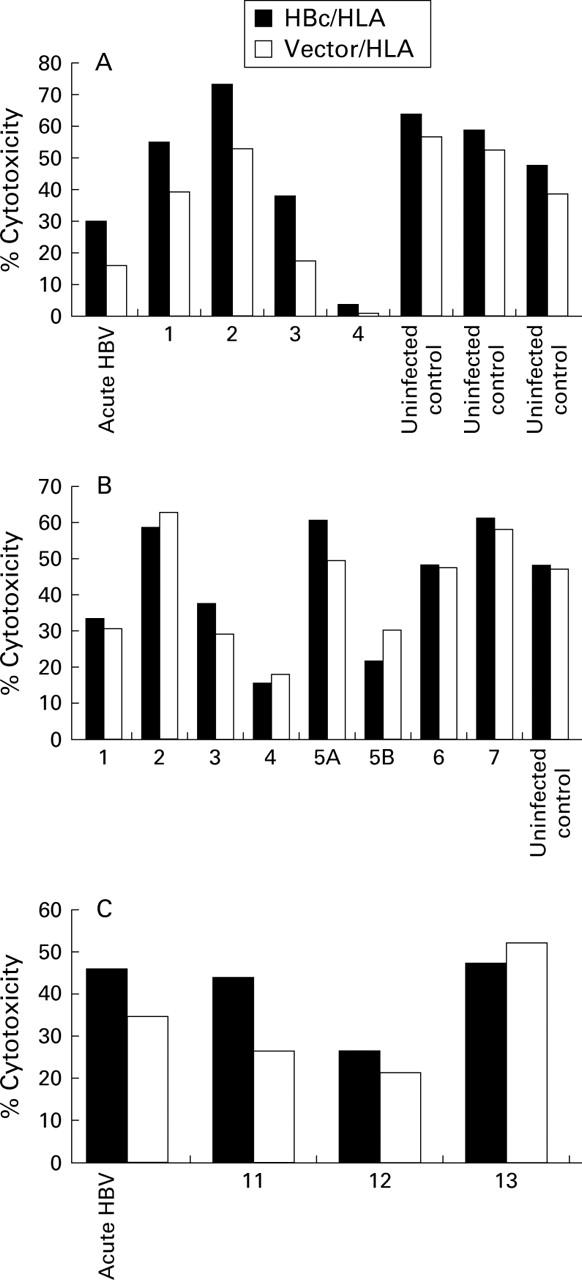
Figure 3 .
Deduced amino acid sequences of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) A68.1 cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) epitope from the HLA-A68.1 positive family compared with that of the HBV adr subtype.26 Numbering is from the start of the core gene and the A68.1 CTL epitope is boxed.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertoletti A., Chisari F. V., Penna A., Guilhot S., Galati L., Missale G., Fowler P., Schlicht H. J., Vitiello A., Chesnut R. C. Definition of a minimal optimal cytotoxic T-cell epitope within the hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid protein. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2376–2380. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2376-2380.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertoletti A., Sette A., Chisari F. V., Penna A., Levrero M., De Carli M., Fiaccadori F., Ferrari C. Natural variants of cytotoxic epitopes are T-cell receptor antagonists for antiviral cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1994 Jun 2;369(6479):407–410. doi: 10.1038/369407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum F., Nassal M. Hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid assembly: primary structure requirements in the core protein. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3319–3330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3319-3330.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozkaya H., Ayola B., Lok A. S. High rate of mutations in the hepatitis B core gene during the immune clearance phase of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 1996 Jul;24(1):32–37. doi: 10.1002/hep.510240107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carman W. F., Boner W., Fattovich G., Colman K., Dornan E. S., Thursz M., Hadziyannis S. Hepatitis B virus core protein mutations are concentrated in B cell epitopes in progressive disease and in T helper cell epitopes during clinical remission. J Infect Dis. 1997 May;175(5):1093–1100. doi: 10.1086/516447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carman W. F., Korula J., Wallace L., MacPhee R., Mimms L., Decker R. Fulminant reactivation of hepatitis B due to envelope protein mutant that escaped detection by monoclonal HBsAg ELISA. Lancet. 1995 Jun 3;345(8962):1406–1407. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)92599-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derso A., Boxall E. H., Tarlow M. J., Flewett T. H. Transmission of HBsAg from mother to infant in four ethnic groups. Br Med J. 1978 Apr 15;1(6118):949–952. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6118.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garboczi D. N., Ghosh P., Utz U., Fan Q. R., Biddison W. E., Wiley D. C. Structure of the complex between human T-cell receptor, viral peptide and HLA-A2. Nature. 1996 Nov 14;384(6605):134–141. doi: 10.1038/384134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett T. P., Saper M. A., Bjorkman P. J., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Specificity pockets for the side chains of peptide antigens in HLA-Aw68. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):692–696. doi: 10.1038/342692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo H. C., Jardetzky T. S., Garrett T. P., Lane W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Different length peptides bind to HLA-Aw68 similarly at their ends but bulge out in the middle. Nature. 1992 Nov 26;360(6402):364–366. doi: 10.1038/360364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günther S., Paulij W., Meisel H., Will H. Analysis of hepatitis B virus populations in an interferon-alpha-treated patient reveals predominant mutations in the C-gene and changing e-antigenicity. Virology. 1998 Apr 25;244(1):146–160. doi: 10.1006/viro.1998.9079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko S., Miller R. H., Feinstone S. M., Unoura M., Kobayashi K., Hattori N., Purcell R. H. Detection of serum hepatitis B virus DNA in patients with chronic hepatitis using the polymerase chain reaction assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):312–316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavathas P., Bach F. H., DeMars R. Gamma ray-induced loss of expression of HLA and glyoxalase I alleles in lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4251–4255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khakoo S. I., Soni P. N., Brown D., Dusheiko G. M. A clinical evaluation of a new method for HBV DNA quantitation in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Med Virol. 1996 Oct;50(2):112–116. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9071(199610)50:2<112::AID-JMV2>3.0.CO;2-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Conley A. J., Brewah Y. A., Jones G. M., Leath S., Boots L. J., Davey V., Pantaleo G., Demarest J. F., Carter C. Transfer of HIV-1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes to an AIDS patient leads to selection for mutant HIV variants and subsequent disease progression. Nat Med. 1995 Apr;1(4):330–336. doi: 10.1038/nm0495-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau J. Y., Bird G. L., Naoumov N. V., Williams R. Hepatic HLA antigen display in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Relation to hepatic expression of HBV genome/gene products and liver histology. Dig Dis Sci. 1993 May;38(5):888–895. doi: 10.1007/BF01295916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. D., Lo K. J., Wu J. C., Tsai Y. T., Wang J. Y., Ting L. P., Tong M. J. Prevention of maternal-infant hepatitis B virus transmission by immunization: the role of serum hepatitis B virus DNA. Hepatology. 1986 May-Jun;6(3):369–373. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Missale G., Redeker A., Person J., Fowler P., Guilhot S., Schlicht H. J., Ferrari C., Chisari F. V. HLA-A31- and HLA-Aw68-restricted cytotoxic T cell responses to a single hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid epitope during acute viral hepatitis. J Exp Med. 1993 Mar 1;177(3):751–762. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mota A. H., Fainboim H., Terg R., Fainboim L. Association of chronic active hepatitis and HLA B35 in patients with hepatitis B virus. Tissue Antigens. 1987 Nov;30(5):238–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1987.tb01628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassal M. The arginine-rich domain of the hepatitis B virus core protein is required for pregenome encapsidation and productive viral positive-strand DNA synthesis but not for virus assembly. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4107–4116. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4107-4116.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayersina R., Fowler P., Guilhot S., Missale G., Cerny A., Schlicht H. J., Vitiello A., Chesnut R., Person J. L., Redeker A. G. HLA A2 restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses to multiple hepatitis B surface antigen epitopes during hepatitis B virus infection. J Immunol. 1993 May 15;150(10):4659–4671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Onda H., Sasada R., Igarashi K., Sugino Y., Nishioka K. The complete nucleotide sequences of the cloned hepatitis B virus DNA; subtype adr and adw. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1747–1757. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul R. G., Roodman S. T., Campbell C. R., Bodicky C. J., Perrillo R. P. HLA class I antigen expression as a measure of response to antiviral therapy of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 1991 May;13(5):820–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignatelli M., Waters J., Brown D., Lever A., Iwarson S., Schaff Z., Gerety R., Thomas H. C. HLA class I antigens on the hepatocyte membrane during recovery from acute hepatitis B virus infection and during interferon therapy in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 1986 May-Jun;6(3):349–353. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pircher H., Moskophidis D., Rohrer U., Bürki K., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M. Viral escape by selection of cytotoxic T cell-resistant virus variants in vivo. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):629–633. doi: 10.1038/346629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehermann B., Ferrari C., Pasquinelli C., Chisari F. V. The hepatitis B virus persists for decades after patients' recovery from acute viral hepatitis despite active maintenance of a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response. Nat Med. 1996 Oct;2(10):1104–1108. doi: 10.1038/nm1096-1104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehermann B., Fowler P., Sidney J., Person J., Redeker A., Brown M., Moss B., Sette A., Chisari F. V. The cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to multiple hepatitis B virus polymerase epitopes during and after acute viral hepatitis. J Exp Med. 1995 Mar 1;181(3):1047–1058. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.3.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehermann B., Lau D., Hoofnagle J. H., Chisari F. V. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte responsiveness after resolution of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Clin Invest. 1996 Apr 1;97(7):1655–1665. doi: 10.1172/JCI118592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehermann B., Pasquinelli C., Mosier S. M., Chisari F. V. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) sequence variation of cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitopes is not common in patients with chronic HBV infection. J Clin Invest. 1995 Sep;96(3):1527–1534. doi: 10.1172/JCI118191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampliner R. E., Bias W. B., Carney E., Hillis A., Hillis W. D. HLA antigens and HBV infection: evaluation in the chronic carrier state and in a large family. Tissue Antigens. 1981 Oct;18(4):247–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1981.tb01388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storkus W. J., Alexander J., Payne J. A., Dawson J. R., Cresswell P. Reversal of natural killing susceptibility in target cells expressing transfected class I HLA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2361–2364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thursz M. R., Kwiatkowski D., Allsopp C. E., Greenwood B. M., Thomas H. C., Hill A. V. Association between an MHC class II allele and clearance of hepatitis B virus in the Gambia. N Engl J Med. 1995 Apr 20;332(16):1065–1069. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199504203321604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. L., Chen M. H., Yeh C. T., Chu C. M., Lin A. N., Chiou F. H., Chang T. H., Liaw Y. F. Purification and characterization of a naturally processed hepatitis B virus peptide recognized by CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1996 Jan 15;97(2):577–584. doi: 10.1172/JCI118450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudin M., Wolstenholme A. J., Tsiquaye K. N., Zuckerman A. J., Harrison T. J. The complete nucleotide sequence of the genome of a hepatitis B virus isolated from a naturally infected chimpanzee. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jun;69(Pt 6):1383–1389. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-6-1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemmour J., Little A. M., Schendel D. J., Parham P. The HLA-A,B "negative" mutant cell line C1R expresses a novel HLA-B35 allele, which also has a point mutation in the translation initiation codon. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1941–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoulim F., Seeger C. Reverse transcription in hepatitis B viruses is primed by a tyrosine residue of the polymerase. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):6–13. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.6-13.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Campos-Lima P. O., Gavioli R., Zhang Q. J., Wallace L. E., Dolcetti R., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Masucci M. G. HLA-A11 epitope loss isolates of Epstein-Barr virus from a highly A11+ population. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):98–100. doi: 10.1126/science.7682013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hattum J., Schreuder G. M., Schalm S. W. HLA antigens in patients with various courses after hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 1987 Jan-Feb;7(1):11–14. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]